
What is the structure of gymnosperms?
Answer
508.5k+ views
Hint: The word “gymnosperm” is derived from two Greek words – “gymnos” meaning naked and “Sperma” meaning seed; therefore, gymnosperm means naked seeds. Gymnosperms produce seeds without fruits.
Complete answer:
In gymnosperms, the ovules are not enclosed within the ovary wall. It is exposed before fertilization and remains exposed after fertilization and before seed development. The stems can either be branched or unbranched. The leaves are needle-like, with sunken stomata and thick cuticles to reduce water loss.
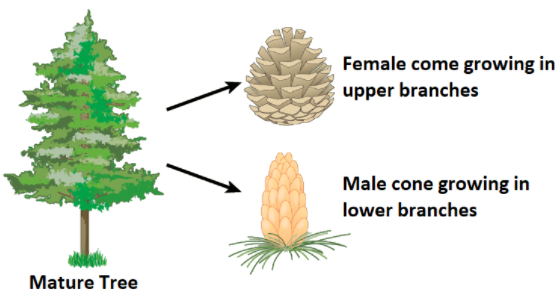
Gymnosperms have two types of haploid spores. These are called microspores and megaspores. They are produced in sporangia. These sporangia are present on the micro and megasporophylls respectively. The sporophylls are arranged spirally along an axis. This arrangement is known as cones or stability.
Gymnosperms have very few species. The main reason for this is that the seeds do not have any protection from animals, weather conditions, or other factors. The seeds have to reach the ground immediately after being released or they risk being damaged.
Additional information Both angiosperms and gymnosperms are seed-bearing plants. Angiosperms are more diverse than gymnosperms. The higher diversity indicates that angiosperms are adapted to many different types of terrestrial ecosystems. Another major characteristic of angiosperms is its flowers and the production of fruits. The primary reason for gymnosperms being less diverse is the absence of protection of seeds.
Note: Both angiosperms and gymnosperms are seed-bearing plants. They have a few similarities. The presence of these similarities is due to the fact that they may have shared common ancestors. Angiosperms evolved at least 200 million years after the first gymnosperms were present.
Complete answer:
In gymnosperms, the ovules are not enclosed within the ovary wall. It is exposed before fertilization and remains exposed after fertilization and before seed development. The stems can either be branched or unbranched. The leaves are needle-like, with sunken stomata and thick cuticles to reduce water loss.
Gymnosperms have two types of haploid spores. These are called microspores and megaspores. They are produced in sporangia. These sporangia are present on the micro and megasporophylls respectively. The sporophylls are arranged spirally along an axis. This arrangement is known as cones or stability.
Gymnosperms have very few species. The main reason for this is that the seeds do not have any protection from animals, weather conditions, or other factors. The seeds have to reach the ground immediately after being released or they risk being damaged.

Additional information Both angiosperms and gymnosperms are seed-bearing plants. Angiosperms are more diverse than gymnosperms. The higher diversity indicates that angiosperms are adapted to many different types of terrestrial ecosystems. Another major characteristic of angiosperms is its flowers and the production of fruits. The primary reason for gymnosperms being less diverse is the absence of protection of seeds.
Note: Both angiosperms and gymnosperms are seed-bearing plants. They have a few similarities. The presence of these similarities is due to the fact that they may have shared common ancestors. Angiosperms evolved at least 200 million years after the first gymnosperms were present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




