
What is the Visceral Pericardium?
Answer
487.5k+ views
Hint: The visceral pericardium is the fibrous connective tissue. Let us know, pericardium microscopic structure in detail. The pericardium is a flask-shaped sac which fills the heart and proximal portions of the vessels. The pericardium is the mediastinal part of the parietal pleura except areas where ligaments anchor the pericardium to the sternum.
Complete answer:
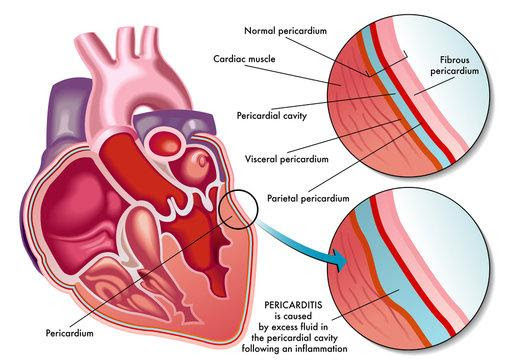
The pericardium is prominently divided into two parts- parietal and visceral pericardium. The parietal pericardium consists of outer fibrous tissue lined by serosa. The serosal component has a single mesothelium-investing fibrosa layer and extends over the root of great arteries to cover the external surface of the heart.
The pericardial sac is deposited by adipose tissues in the mediastinal surface and in cardio-phrenic angles. Hence, the visceral pericardium is developed by a sheet layer of fibrous tissue wrapped inside the myocardium invested by mesothelial cells. The single serosal layer which covers the entire heart is the visceral pericardium.
Present in all mammals, the pericardium separates the heart from body and its main function is to protect the heart from infection and heart related diseases and the trauma and all lubrications of the heart.
Note:
The visceral pericardium joins the serosa pericardium at the base of the heart. It is a thin red line overlying the myocardium. Mostly made of loose connective tissues, including elastic fibers and adipose tissue. It functions to protect the inner layers. It lubricates and maintains the fluid between the layers allowing the heart to expand and contract.
Complete answer:
The pericardium is prominently divided into two parts- parietal and visceral pericardium. The parietal pericardium consists of outer fibrous tissue lined by serosa. The serosal component has a single mesothelium-investing fibrosa layer and extends over the root of great arteries to cover the external surface of the heart.
The pericardial sac is deposited by adipose tissues in the mediastinal surface and in cardio-phrenic angles. Hence, the visceral pericardium is developed by a sheet layer of fibrous tissue wrapped inside the myocardium invested by mesothelial cells. The single serosal layer which covers the entire heart is the visceral pericardium.
Present in all mammals, the pericardium separates the heart from body and its main function is to protect the heart from infection and heart related diseases and the trauma and all lubrications of the heart.

Note:
The visceral pericardium joins the serosa pericardium at the base of the heart. It is a thin red line overlying the myocardium. Mostly made of loose connective tissues, including elastic fibers and adipose tissue. It functions to protect the inner layers. It lubricates and maintains the fluid between the layers allowing the heart to expand and contract.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




