
What is Torsional stress?
Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: The twisting of an object due to an applied torque is called torsion. In solid mechanics, stress is a given material’s resistance to an external applied force, and strain is the deformation that results from that stress.
Complete answer:
Shear stress (which is caused by torsional load) occurs when a force is applied parallel or tangent to an area. Shear stress is of two types - Direct shear stress and Torsional shear stress.
Torsional stress can be defined as the shear stress that acts on a transverse cross section which is caused by the action of a twist.
Let us consider a cylinder of cross sectional area $A$ with radius $r$ . Let an equal and opposite twisting moment $T$ be applied on both of its sides. This is represented in the following diagram:
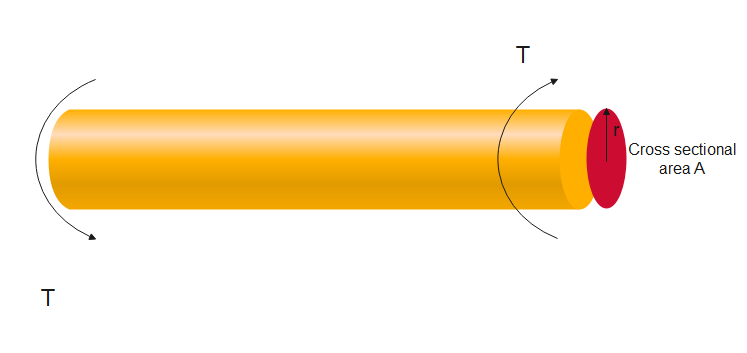
The resulting stress can be given by the formula
\[\tau = r \times \dfrac{T}{J}\] where $\tau $ is the Torsional stress induced at the outer surface of the cylinder which experiences the maximum stress, $r$ is the radius of the cylinder, $T$ is the twisting moment or the torque and $J$ is the polar moment of inertia.
Note:
The ability to resist the torsion is known as the torsional stiffness of the body. The measure of the torsional stiffness is known as the polar moment of inertia.
From this, the torsional rigidity can be defined as the product of the polar moment of inertia and the Rigidity of shaft material.
$Torsional\,Rigidity = C \times J$ where $C$ is the modulus of rigidity for the shaft material and $J$ is the polar moment of inertia.
Complete answer:
Shear stress (which is caused by torsional load) occurs when a force is applied parallel or tangent to an area. Shear stress is of two types - Direct shear stress and Torsional shear stress.
Torsional stress can be defined as the shear stress that acts on a transverse cross section which is caused by the action of a twist.
Let us consider a cylinder of cross sectional area $A$ with radius $r$ . Let an equal and opposite twisting moment $T$ be applied on both of its sides. This is represented in the following diagram:

The resulting stress can be given by the formula
\[\tau = r \times \dfrac{T}{J}\] where $\tau $ is the Torsional stress induced at the outer surface of the cylinder which experiences the maximum stress, $r$ is the radius of the cylinder, $T$ is the twisting moment or the torque and $J$ is the polar moment of inertia.
Note:
The ability to resist the torsion is known as the torsional stiffness of the body. The measure of the torsional stiffness is known as the polar moment of inertia.
From this, the torsional rigidity can be defined as the product of the polar moment of inertia and the Rigidity of shaft material.
$Torsional\,Rigidity = C \times J$ where $C$ is the modulus of rigidity for the shaft material and $J$ is the polar moment of inertia.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




