
What is uniform acceleration?
Answer
530.4k+ views
Hint: To understand what uniform acceleration is, we will first understand how acceleration is produced in the body. What type of quantity is acceleration and what are the criterias that are essential for a body to be called uniformly accelerating. We shall proceed ahead in our problem in this manner.
Complete step-by-step solution:
When a force or a collection of several forces is applied on a body, the body experiences changes in its physical properties. When this force tends to move the body from one point in space to another, we say the body has moved under the effect of the applied force.
This force is written as the product of the mass of the body and its acceleration. Mathematically, this could be written as:
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow{F}=m\overrightarrow{a}$
Where,
‘$\overrightarrow{F}$ ’ is the summation of all the force vectors.
‘m’ is the mass of the object. And,
‘$\overrightarrow{a}$’ is the acceleration vector.
Now, a body is said to be uniformly accelerating when its acceleration vector does not change with time, that is, the direction and magnitude of acceleration is constant with respect to time. This implies that the net force on the body should also be a constant vector, that is, even the net force vector should not change with time.
This acceleration-time graph of a uniformly accelerating body should be parallel to the time axis and can be shown as follows:
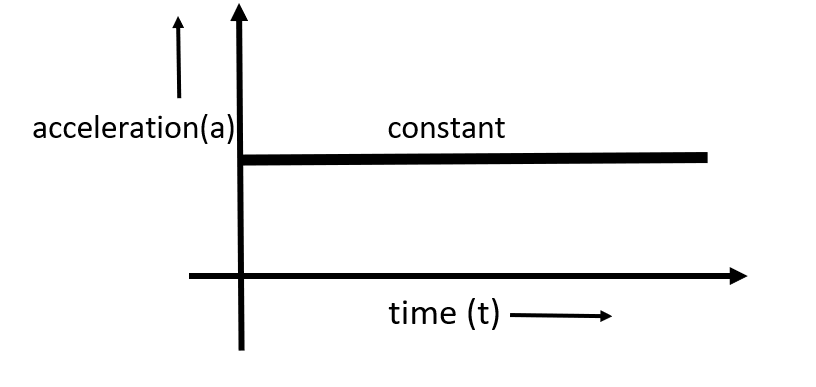
Hence, uniform acceleration is acceleration that is constant with respect to time.
Note: A free falling object is an example of uniformly accelerating object. Also, the other type of acceleration is called non-uniform acceleration. In this type of acceleration, either the magnitude or the direction or even both the parameters of the acceleration might be changing with respect to time.
Complete step-by-step solution:
When a force or a collection of several forces is applied on a body, the body experiences changes in its physical properties. When this force tends to move the body from one point in space to another, we say the body has moved under the effect of the applied force.
This force is written as the product of the mass of the body and its acceleration. Mathematically, this could be written as:
$\Rightarrow \overrightarrow{F}=m\overrightarrow{a}$
Where,
‘$\overrightarrow{F}$ ’ is the summation of all the force vectors.
‘m’ is the mass of the object. And,
‘$\overrightarrow{a}$’ is the acceleration vector.
Now, a body is said to be uniformly accelerating when its acceleration vector does not change with time, that is, the direction and magnitude of acceleration is constant with respect to time. This implies that the net force on the body should also be a constant vector, that is, even the net force vector should not change with time.
This acceleration-time graph of a uniformly accelerating body should be parallel to the time axis and can be shown as follows:

Hence, uniform acceleration is acceleration that is constant with respect to time.
Note: A free falling object is an example of uniformly accelerating object. Also, the other type of acceleration is called non-uniform acceleration. In this type of acceleration, either the magnitude or the direction or even both the parameters of the acceleration might be changing with respect to time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




