
Which has the least heat of hydrogenation?
A. cis-2-butene
B. trans-2-butene
C. 1,3-dimethyl-2-butene
D. 2-methyl propene
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Heat of hydrogenation represented as$\vartriangle {{\text{H}}_{\text{hydro}}}\text{ or }\vartriangle {{\text{H}}^{\text{o}}}$is the standard enthalpy of catalytic hydrogenation of an alkene. Its value is always exothermic. Smaller the value of heat of hydrogenation of an alkene, more stable will be that alkene or double bond.
Complete answer:
Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is the measure of the stability of carbon-carbon double bonds. Let us see the factors on which heat of hydrogenation depends:
(1) Stability of an alkene: Higher the numerical value of heat of hydrogenation, more energy will be released which means that the double bond was broken down more easily or that the double bond was less stable. Thus, stability of an alkene is inversely proportional to heat of hydrogenation. $\text{heat of hydrogenation}\propto \dfrac{1}{\text{stability}}$.
(2) Number of double bonds: The heat of hydrogenation is proportional to the number of double bonds. More the number of double bonds, more heat will be released when the alkene will undergo hydrogenation. $\text{HOH}\propto \text{ number of double bonds}$.
Let us now compare the options on the basis of stability and number of double bonds present:
Hence, the order of stability will be\[\text{1,3-dimethyl-2-butene}>\text{2-methyl propene}>\text{trans-2-butene}>\text{cis-2-butene}\]; most stable compound among all is ‘1,3-dimethyl-2-butene’. So, it will have the least heat of hydrogenation because $\text{heat of hydrogenation}\propto \dfrac{1}{\text{stability}}$.
The correct answer is option ‘c’.
Note:
Priority in factors while checking HOH:
First, while checking the heat of hydrogenation, the number of double bonds should be checked first (prior) then, if the number of double bonds is the same then stability is seen. The compound is more stable and has less heat of hydrogenation.
Complete answer:
Heat of hydrogenation of alkenes is the measure of the stability of carbon-carbon double bonds. Let us see the factors on which heat of hydrogenation depends:
(1) Stability of an alkene: Higher the numerical value of heat of hydrogenation, more energy will be released which means that the double bond was broken down more easily or that the double bond was less stable. Thus, stability of an alkene is inversely proportional to heat of hydrogenation. $\text{heat of hydrogenation}\propto \dfrac{1}{\text{stability}}$.
(2) Number of double bonds: The heat of hydrogenation is proportional to the number of double bonds. More the number of double bonds, more heat will be released when the alkene will undergo hydrogenation. $\text{HOH}\propto \text{ number of double bonds}$.
Let us now compare the options on the basis of stability and number of double bonds present:
| Name of compound | Explanation of structure | Structure | Number of double bonds | Reason of stability |
| cis-2-butene | 4-membered chain (but) with a double at the centre and two methyl groups present on same side so ‘cis’ alkene. | 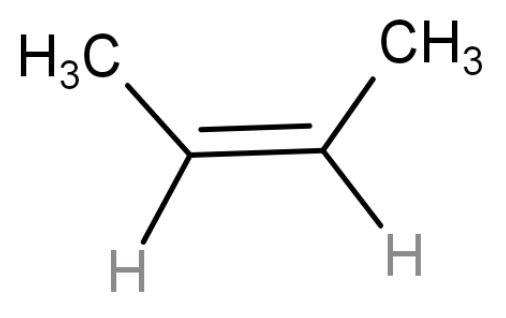
| 1 | Have 6 hyper conjugating structures (number of$\alpha $- hydrogens). Less stable due to non-symmetrical packing because of the bulky methyl groups. |
| trans-2-butene | 4-membered chain (but) with a double at the centre and two methyl groups present on opposite sides so ‘trans’ alkene. | 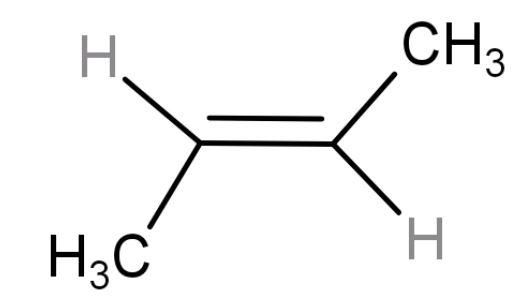
| 1 | Have 6 hyper conjugating structures. But stable than ‘cis-form’ because of its symmetrical structure. Packing can be done easily. |
| 1,3-dimethyl-2-butene | Have 1 double bond and the two methyl groups are attached at first and third carbon atoms. | 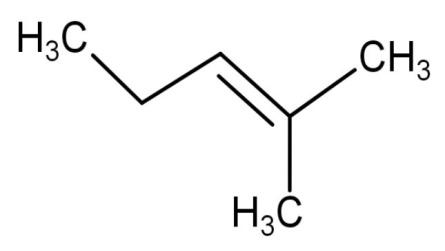
| 1 | It has 8 hyper conjugating structures. |
| 2-methylpropene | ‘Prop’ means three, so three carbon atoms are present. Methyl group is attached to the second carbon atom. | 
| 1 | Have 6 hyper conjugating structures. More stable than trans-but-2-ene as it has lower heat of combustion. |
Hence, the order of stability will be\[\text{1,3-dimethyl-2-butene}>\text{2-methyl propene}>\text{trans-2-butene}>\text{cis-2-butene}\]; most stable compound among all is ‘1,3-dimethyl-2-butene’. So, it will have the least heat of hydrogenation because $\text{heat of hydrogenation}\propto \dfrac{1}{\text{stability}}$.
The correct answer is option ‘c’.
Note:
Priority in factors while checking HOH:
First, while checking the heat of hydrogenation, the number of double bonds should be checked first (prior) then, if the number of double bonds is the same then stability is seen. The compound is more stable and has less heat of hydrogenation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




