
Which is the end product of oxidative phosphorylation?
(a) ATP
(b) ATP+H2O
(c) NADH
(d) Oxygen
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: Oxidative phosphorylation is the metabolic pathway in the cell with the use of enzymes to oxidize metabolites. One of the products consists of high energy phosphate bonds produced by the powerhouse of the cell mitochondria. The other ensures a continuous supply of electrons in non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Complete answer:
The oxidative phosphorylation pathway includes the delivery of electrons by NADH and FADH2, electron transfer and protein pumping, splitting of oxygen to form water lastly gradient driven synthesis of ATP.
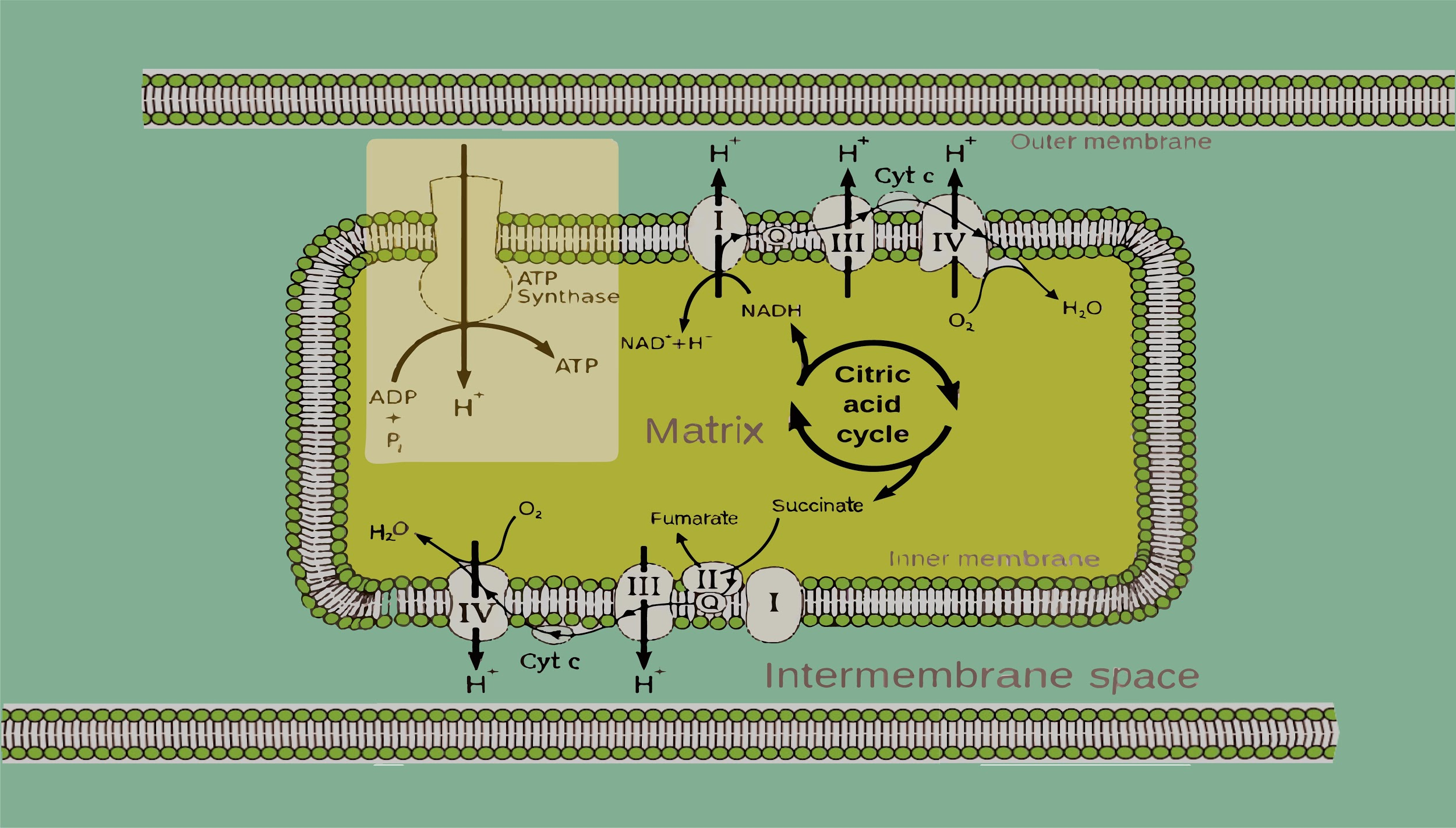
Additional Information
-Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
-It is a combination of an electron transport chain pathway and chemiosmosis.
-Chemiosmosis is a process in which energy is formed from a proton gradient.
-The delivery of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecules is marked as the beginning of the oxidative phosphorylation.
-The electron is released to move from a higher energy level to a lower energy level, the energy is used to pump H+ ion from out of the matrix to the intermembrane space which establishes an electrochemical gradient.
-The transfer of an electron to molecular oxygen combines with H+ to form water is marked as an end product in the oxidative phosphorylation pathway.
So, the correct answer is, ‘ATP+H2O.’
Note:
-Cyanide acts as a poison because of its ability to inhibit complex IV, which makes it unable to transport electrons which ultimately causes the electron transport chain to stop and the gradient would decrease.
-Dinitrophenol (DNP) is a chemical substance that acts as an uncoupling agent that causes the inner mitochondrial membrane leaky to protons. It was used as a weight-loss drug. It reduces the ATO production which leads to high body temperature.
Complete answer:
The oxidative phosphorylation pathway includes the delivery of electrons by NADH and FADH2, electron transfer and protein pumping, splitting of oxygen to form water lastly gradient driven synthesis of ATP.

Additional Information
-Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria.
-It is a combination of an electron transport chain pathway and chemiosmosis.
-Chemiosmosis is a process in which energy is formed from a proton gradient.
-The delivery of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecules is marked as the beginning of the oxidative phosphorylation.
-The electron is released to move from a higher energy level to a lower energy level, the energy is used to pump H+ ion from out of the matrix to the intermembrane space which establishes an electrochemical gradient.
-The transfer of an electron to molecular oxygen combines with H+ to form water is marked as an end product in the oxidative phosphorylation pathway.
So, the correct answer is, ‘ATP+H2O.’
Note:
-Cyanide acts as a poison because of its ability to inhibit complex IV, which makes it unable to transport electrons which ultimately causes the electron transport chain to stop and the gradient would decrease.
-Dinitrophenol (DNP) is a chemical substance that acts as an uncoupling agent that causes the inner mitochondrial membrane leaky to protons. It was used as a weight-loss drug. It reduces the ATO production which leads to high body temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




