
Which is the non- benzenoid aromatic compound?
A.Benzene
B.Pyridine
C.Toluene
D.Phenol
Answer
523.3k+ views
Hint: Aromatic compounds are unsaturated hydrocarbons having ring structure exhibiting special properties such as unusual stability. Most aromatic compounds contain benzene rings or related structure. Aromatic compounds also show fragrant properties. These compounds are often represented as resonance structures containing single and double bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
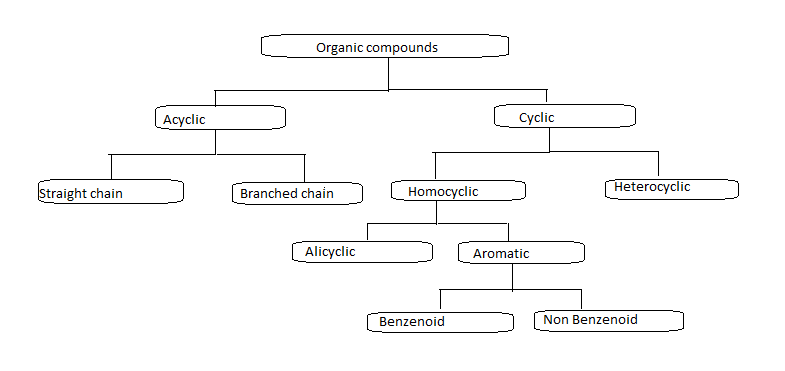
General criteria must be met if a molecule is said to show aromaticity.
An aromatic molecule must possess planar cyclic structure
Aromatic rings must contain only $s{p^2}$ hybridise atoms that can form a delocalised system of ${\text{\Pi }}$ molecular orbitals.
Aromatic compounds must follow Huckel rule which states that the number of ${\text{\Pi }}$ electrons in the delocalised system must be equal to ${\text{4n + 2}}$ , where ${\text{n}}$ is an integer.
If a compound follows the above rules then it is said to be an aromatic compound. When we look at flow charts Aromatic compounds are mainly divided into benzenoid and non-benzenoid compounds.
We already learn that aromatic compounds are mainly divided into two types: benzenoid and non benzenoid.
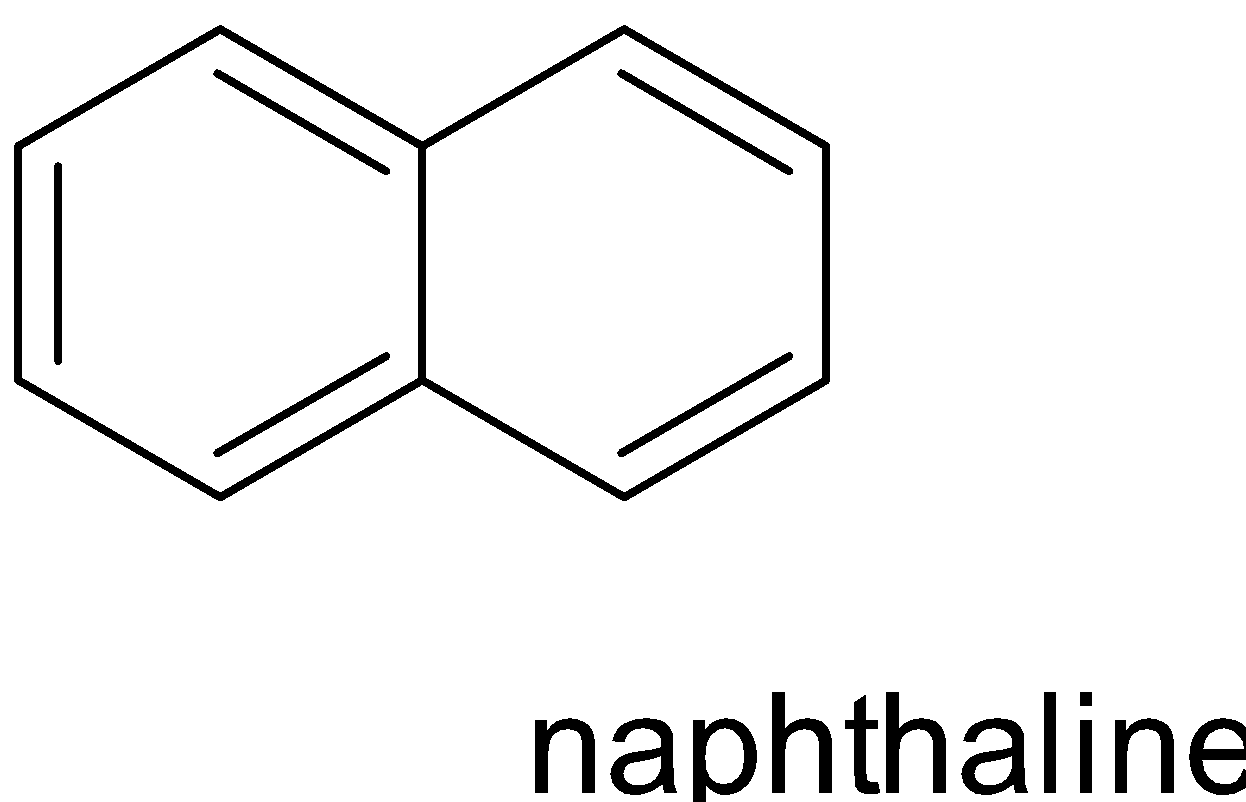
Benzenoid compounds are aromatic compounds that have at least one benzene ring at its chemical structure.it can be characterised by the presence of one or more fused or isolated benzene ring in their structure.
Depending on the number of benzene rings that are fused together in their structure , benzenoid compounds further classified into monocyclic , bicyclic, tricyclic
Example:
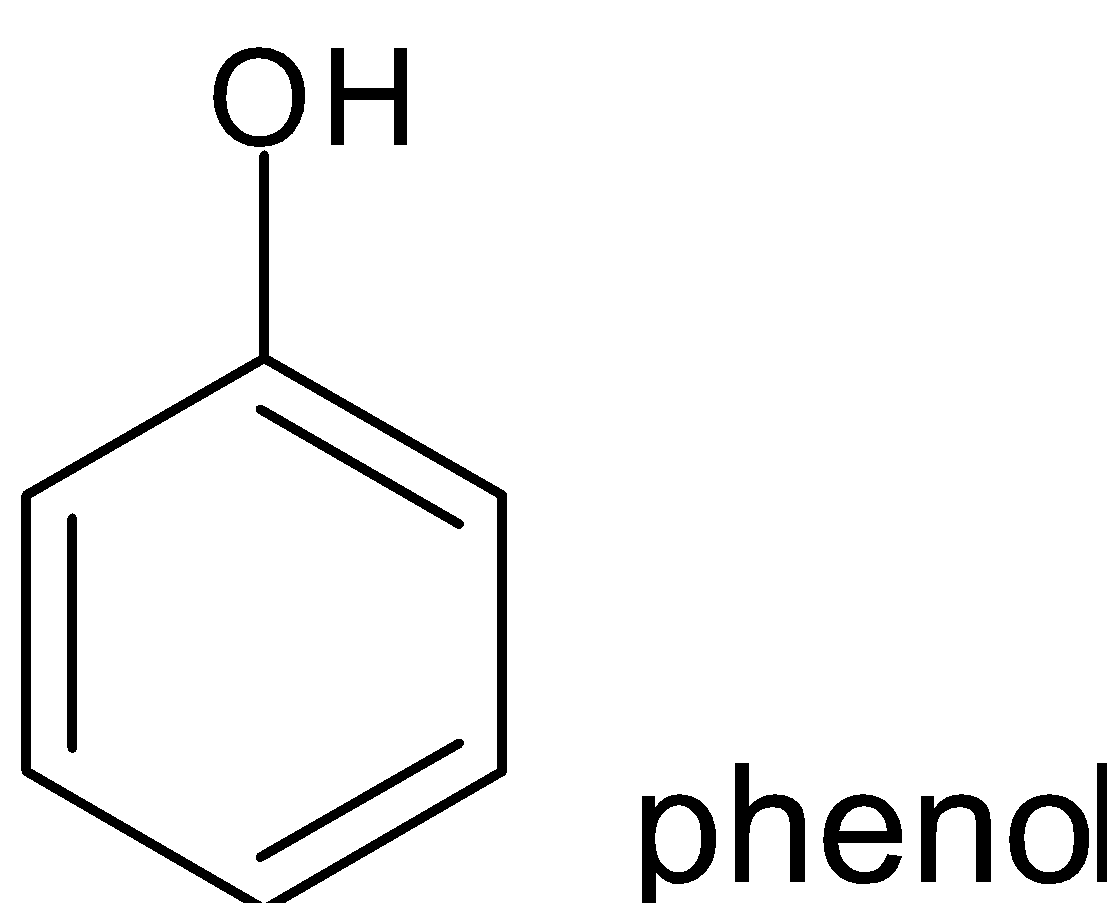
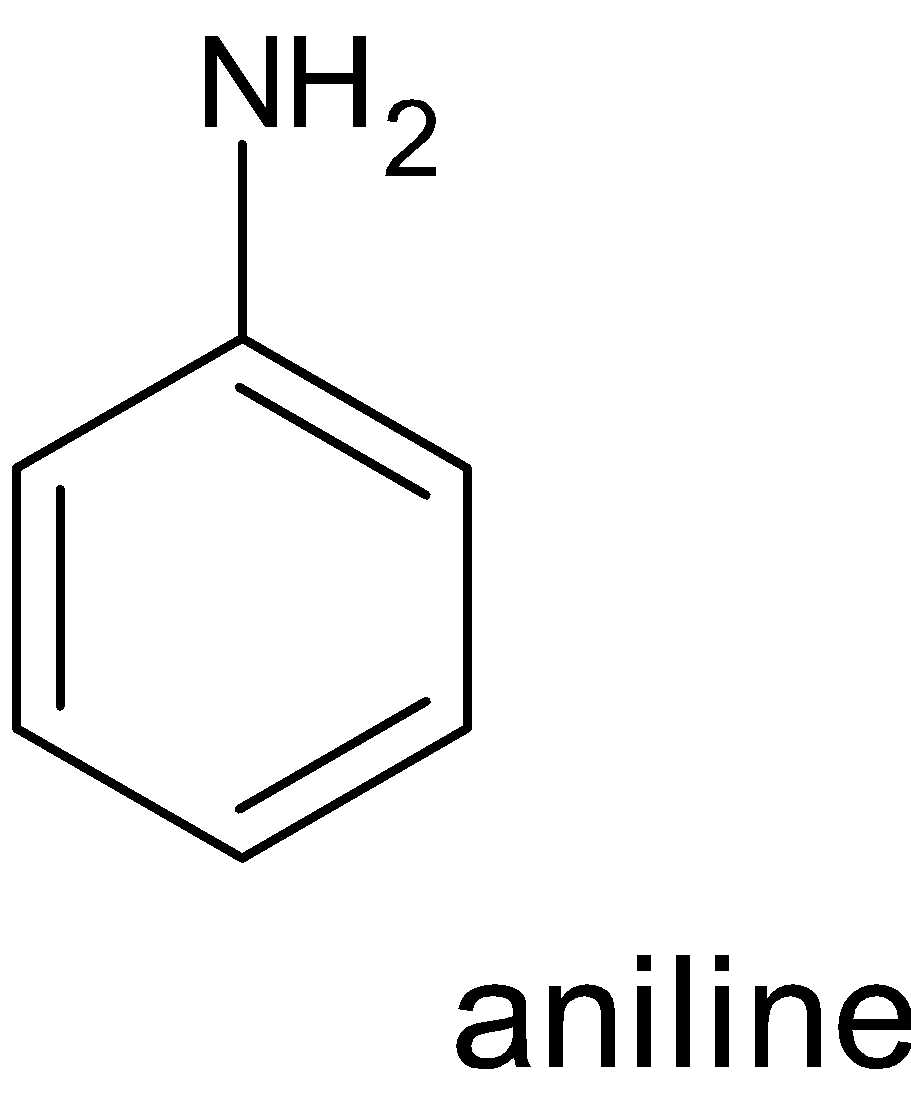
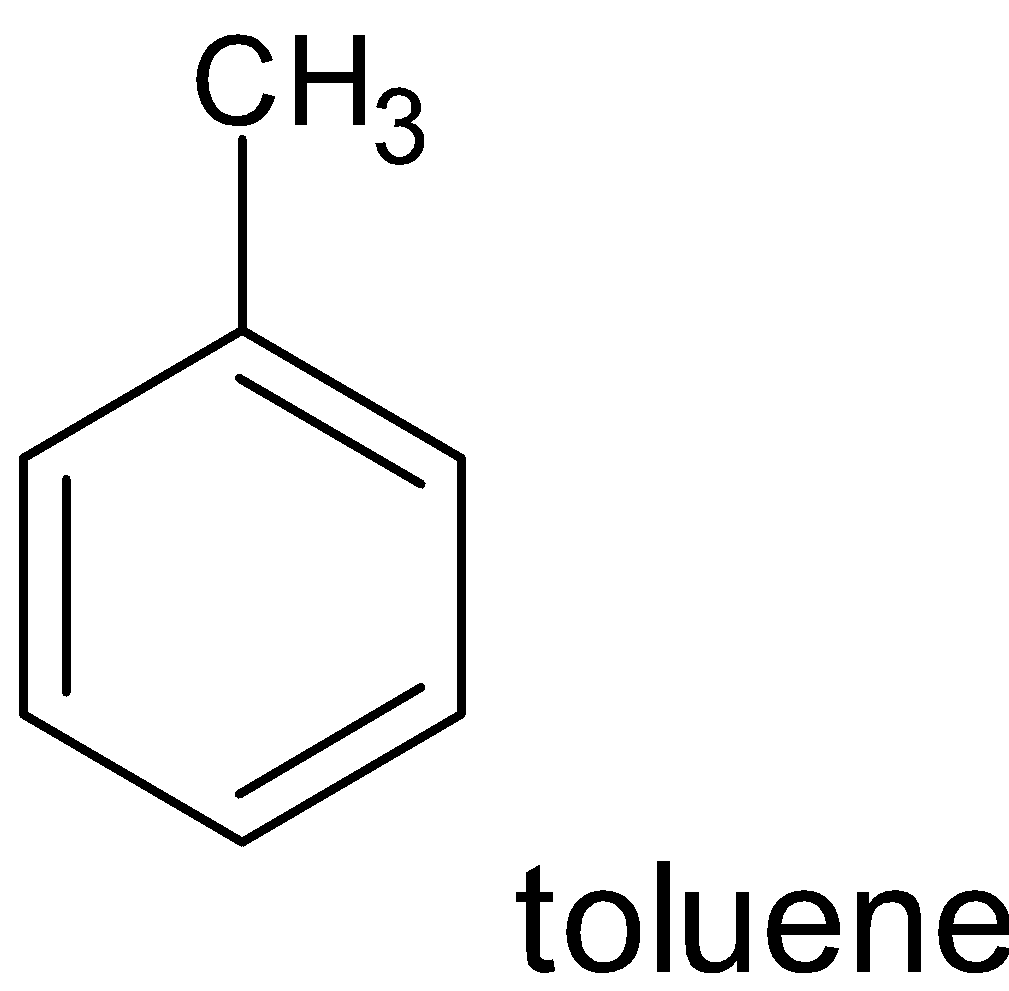
Non benzenoid compounds are aromatic compounds that having conjugated systems with planar cyclic structure do not have benzene rings in their structure . Heterocycles that contain nitrogen , oxygen etc can also be aromatic and come under non benzenoid structure.
Examples:
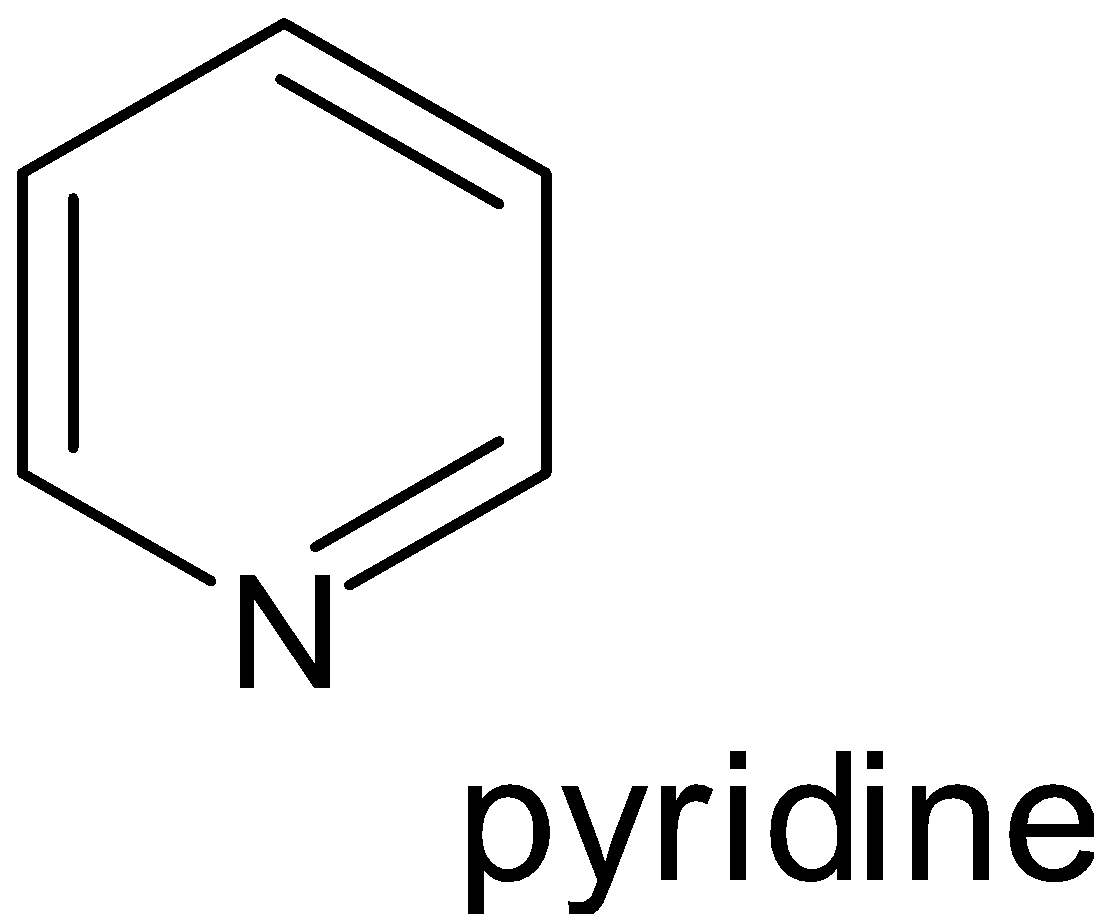
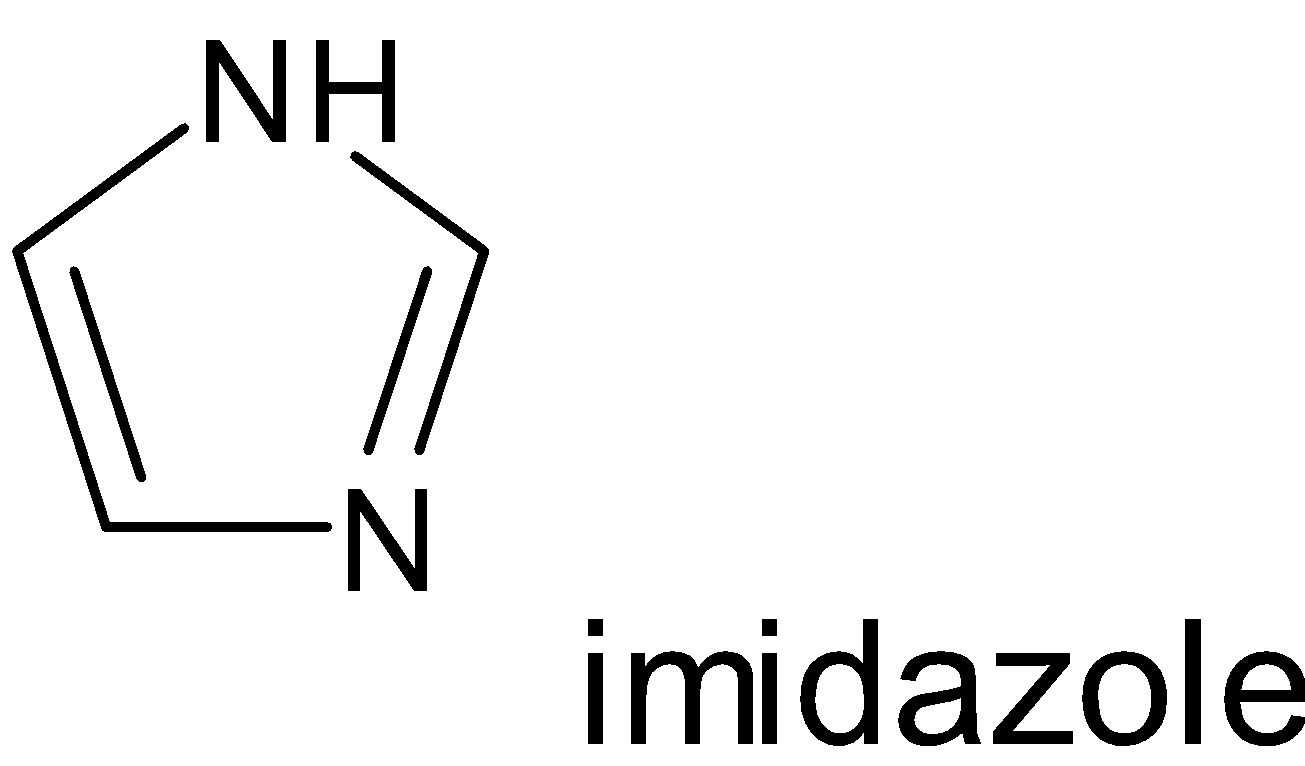
Hence when looking at the compounds phenol, pyridine, benzene and toluene the one which possesses non benzenoid structure is pyridine.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: Aromatic compounds are generally nonpolar and are immiscible in water. Most of the aromatic compounds undergo electrophilic substitution reactions. Aromatic compounds are often represented as resonance structures containing single and double bonds.
Complete step by step solution:

General criteria must be met if a molecule is said to show aromaticity.
An aromatic molecule must possess planar cyclic structure
Aromatic rings must contain only $s{p^2}$ hybridise atoms that can form a delocalised system of ${\text{\Pi }}$ molecular orbitals.
Aromatic compounds must follow Huckel rule which states that the number of ${\text{\Pi }}$ electrons in the delocalised system must be equal to ${\text{4n + 2}}$ , where ${\text{n}}$ is an integer.
If a compound follows the above rules then it is said to be an aromatic compound. When we look at flow charts Aromatic compounds are mainly divided into benzenoid and non-benzenoid compounds.
We already learn that aromatic compounds are mainly divided into two types: benzenoid and non benzenoid.
Benzenoid compounds are aromatic compounds that have at least one benzene ring at its chemical structure.it can be characterised by the presence of one or more fused or isolated benzene ring in their structure.
Depending on the number of benzene rings that are fused together in their structure , benzenoid compounds further classified into monocyclic , bicyclic, tricyclic
Example:




Non benzenoid compounds are aromatic compounds that having conjugated systems with planar cyclic structure do not have benzene rings in their structure . Heterocycles that contain nitrogen , oxygen etc can also be aromatic and come under non benzenoid structure.
Examples:


Hence when looking at the compounds phenol, pyridine, benzene and toluene the one which possesses non benzenoid structure is pyridine.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: Aromatic compounds are generally nonpolar and are immiscible in water. Most of the aromatic compounds undergo electrophilic substitution reactions. Aromatic compounds are often represented as resonance structures containing single and double bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




