
Which molecule has a \[120\] degree bond angle?
Answer
506.1k+ views
Hint: We need to know that the bond angle is the angle present between two bonds which is occupied in a covalent species. Hence, there should be at least two bonds in that covalent species. The lone pair repulsion mainly affects the bond angle. Therefore, if the central atom contains the lone pair of electrons, the angle of the compound will decrease.
Complete answer:
As we know, the bond angle of boron trichloride is equal to \[120^\circ \]. Here, the boron is the central atom and three hydrogen atoms are linked with three chlorine atoms. But it does not contain any lone pair of electrons. Let’s see the structure of \[BC{l_3}\]
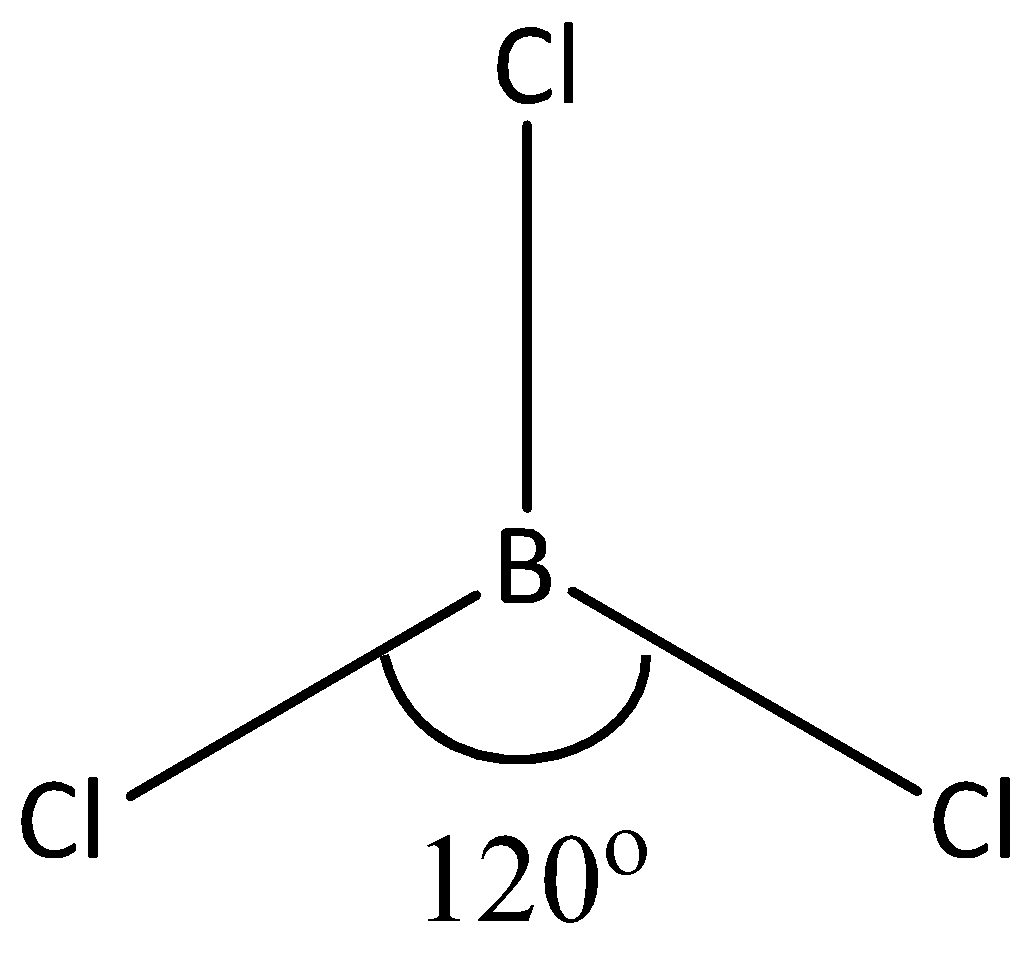
The structure of boron trichloride is equal to trigonal planar with \[s{p^2}\] hybridization. The boron trichloride is a non – polar compound due to its symmetrical structure. The boron – chlorine bond is polar. Because, there is a difference between the electronegativity of boron and chlorine. Hence, all the B – Cl bonds lie at the bond angle \[120^\circ \]. According to VSEPR theory, the molecular geometry of \[BC{l_3}\] is equal to trigonal planar. And the bond angle of boron trifluoride is also \[120^\circ \]. Here, the bromine is connected with three fluorine atoms.
Note:
We need to remember that the bond angle mainly depends on the shape and hybridization of a compound. If the compounds have the same hybridization, then the sum of lone pair and bond pair is equal to the same. Hence, the bond angle becomes equal. And the electronegativity and shape of molecules also affect the bond angle. The bond angle decreases with decreasing electronegativity.
Complete answer:
As we know, the bond angle of boron trichloride is equal to \[120^\circ \]. Here, the boron is the central atom and three hydrogen atoms are linked with three chlorine atoms. But it does not contain any lone pair of electrons. Let’s see the structure of \[BC{l_3}\]

The structure of boron trichloride is equal to trigonal planar with \[s{p^2}\] hybridization. The boron trichloride is a non – polar compound due to its symmetrical structure. The boron – chlorine bond is polar. Because, there is a difference between the electronegativity of boron and chlorine. Hence, all the B – Cl bonds lie at the bond angle \[120^\circ \]. According to VSEPR theory, the molecular geometry of \[BC{l_3}\] is equal to trigonal planar. And the bond angle of boron trifluoride is also \[120^\circ \]. Here, the bromine is connected with three fluorine atoms.
Note:
We need to remember that the bond angle mainly depends on the shape and hybridization of a compound. If the compounds have the same hybridization, then the sum of lone pair and bond pair is equal to the same. Hence, the bond angle becomes equal. And the electronegativity and shape of molecules also affect the bond angle. The bond angle decreases with decreasing electronegativity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




