
Which molecule has V-shape? This question has multiple correct options
(A) \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]
(B) \[{\text{SnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\]
(C) \[{\text{PbC}}{{\text{1}}_{\text{2}}}\]
(D) None of these
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: In each molecule, determine the hybridization of the central atom. From the hybridization, determine the electron pair geometry and the molecular geometry.
Complete step-by-step answer:
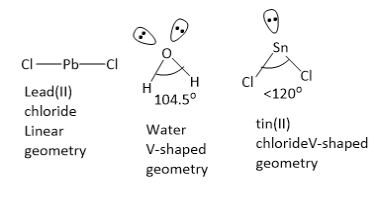
\[{\text{PbC}}{{\text{1}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule has linear geometry. In water molecules, the central oxygen atom has 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs of electrons. Oxygen atom is \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\] hybridized with tetrahedral electron pair geometry and V shaped molecular geometry. The ideal tetrahedral bond angle is \[{\text{10}}{{\text{9}}^o}{\text{28'}}\] , but in water molecule, the \[{\text{H}} - {\text{O}} - {\text{H}}\] bond angle is \[{\text{104}}{\text{.}}{{\text{5}}^o}\] . This is due to greater lone pair lone pair repulsion and lone pair bond pair repulsion as compared to bond pair bond pair repulsion.
In \[{\text{SnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule, the central tin atom has 2 bond pairs and 1 lone pair of electrons. Tin atom is \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\] hybridized with Trigonal planar electron pair geometry and V shaped molecular geometry. The ideal bond angle is \[{\text{12}}{{\text{0}}^o}\] , but in \[{\text{SnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule, the \[{\text{Cl}} - {\text{Sn}} - {\text{Cl}}\] bond angle is less \[{\text{12}}{{\text{0}}^o}\] . This is due to greater lone pair bond pair repulsion as compared to bond pair bond pair repulsion. The molecules \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]and \[{\text{SnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] have V-shaped geometries.
Hence, the options (A) and (B) are the correct answers.
Note: For several molecules, the electron pair geometry is different from the molecular geometry. This is due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons on the central atom.
Complete step-by-step answer:
\[{\text{PbC}}{{\text{1}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule has linear geometry. In water molecules, the central oxygen atom has 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs of electrons. Oxygen atom is \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\] hybridized with tetrahedral electron pair geometry and V shaped molecular geometry. The ideal tetrahedral bond angle is \[{\text{10}}{{\text{9}}^o}{\text{28'}}\] , but in water molecule, the \[{\text{H}} - {\text{O}} - {\text{H}}\] bond angle is \[{\text{104}}{\text{.}}{{\text{5}}^o}\] . This is due to greater lone pair lone pair repulsion and lone pair bond pair repulsion as compared to bond pair bond pair repulsion.
In \[{\text{SnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule, the central tin atom has 2 bond pairs and 1 lone pair of electrons. Tin atom is \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\] hybridized with Trigonal planar electron pair geometry and V shaped molecular geometry. The ideal bond angle is \[{\text{12}}{{\text{0}}^o}\] , but in \[{\text{SnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule, the \[{\text{Cl}} - {\text{Sn}} - {\text{Cl}}\] bond angle is less \[{\text{12}}{{\text{0}}^o}\] . This is due to greater lone pair bond pair repulsion as compared to bond pair bond pair repulsion. The molecules \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]and \[{\text{SnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\] have V-shaped geometries.
Hence, the options (A) and (B) are the correct answers.

Note: For several molecules, the electron pair geometry is different from the molecular geometry. This is due to the presence of lone pairs of electrons on the central atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




