
Which muscle cell is spindle-shaped?
(a) Smooth muscle cell
(b) Striated muscle cell
(c) Cardiac muscle cell
(d) None of the above
Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint: These are nonstiff, non-striated, and involuntary muscles found in the walls of various organs and structures present in our body. These muscles help the organs in performing their functions very well. These muscles are used to apply pressure to vessels and organs by various systems in our body.
Complete answer:
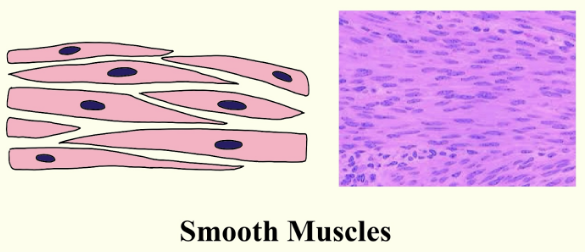
The smooth muscle cell is a spindle-shaped muscle cell. In the smooth muscle cell, the nucleus is centrally located and they are not straight in appearance due to the absence of bands of the proteins actin and myosin that are present along the length of muscle fiber. In our body, these muscles are found within the walls of organs and structures like the esophagus, stomach, intestines, bronchi, uterus, urethra, bladder, blood vessels, and thereafter the arrector pili in the skin.
-The smooth muscle remains present within the walls of blood vessels these are specifically termed as vascular smooth muscle such as in the tunica media layer of large (aorta) and small arteries, arterioles, and veins.
-Smooth muscle is additionally found in lymphatic vessels, the urinary bladder, uterus where it termed as uterine smooth muscle, reproductive tracts of both male and female, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, the arrector pili of skin, the ciliary muscle, and also in the iris of the eye.
-The structure and functions of smooth muscles are basically the same in different organs, but in order to perform individual effects, the inducing stimuli differ substantially in the body at individual times.
-The mesangial cells are the glomeruli of the kidneys that contain smooth muscle-like cells.
-Smooth muscle cells are found in almost all organ systems such as hollow organs e.g. stomach, bladder, tubular structures e.g. vessels, bile ducts, sphincters, in the uterus, in the eye, etc.
-It fulfills various tasks like sealing orifices for eg. pylorus, uterine, etc., and also the transport of the chyme through wavelike contractions of the intestinal tube.
-The smooth muscle cells contract slower than skeletal muscle cells, because they are stronger, more sustained, and require less energy.
So, the correct answer is,’ Smooth muscle cell’.
Note:
-The smooth muscle cells are not straight in appearance due to the absence of bands of the proteins actin and myosin that are present along the length of muscle fiber.
-The smooth muscle cells play an important role in the ducts of exocrine glands.
-Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is also involuntary, and it does not require any stimulus for functioning.
Complete answer:
The smooth muscle cell is a spindle-shaped muscle cell. In the smooth muscle cell, the nucleus is centrally located and they are not straight in appearance due to the absence of bands of the proteins actin and myosin that are present along the length of muscle fiber. In our body, these muscles are found within the walls of organs and structures like the esophagus, stomach, intestines, bronchi, uterus, urethra, bladder, blood vessels, and thereafter the arrector pili in the skin.
-The smooth muscle remains present within the walls of blood vessels these are specifically termed as vascular smooth muscle such as in the tunica media layer of large (aorta) and small arteries, arterioles, and veins.
-Smooth muscle is additionally found in lymphatic vessels, the urinary bladder, uterus where it termed as uterine smooth muscle, reproductive tracts of both male and female, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, the arrector pili of skin, the ciliary muscle, and also in the iris of the eye.
-The structure and functions of smooth muscles are basically the same in different organs, but in order to perform individual effects, the inducing stimuli differ substantially in the body at individual times.
-The mesangial cells are the glomeruli of the kidneys that contain smooth muscle-like cells.
-Smooth muscle cells are found in almost all organ systems such as hollow organs e.g. stomach, bladder, tubular structures e.g. vessels, bile ducts, sphincters, in the uterus, in the eye, etc.
-It fulfills various tasks like sealing orifices for eg. pylorus, uterine, etc., and also the transport of the chyme through wavelike contractions of the intestinal tube.
-The smooth muscle cells contract slower than skeletal muscle cells, because they are stronger, more sustained, and require less energy.
So, the correct answer is,’ Smooth muscle cell’.
Note:
-The smooth muscle cells are not straight in appearance due to the absence of bands of the proteins actin and myosin that are present along the length of muscle fiber.
-The smooth muscle cells play an important role in the ducts of exocrine glands.
-Unlike skeletal muscle, smooth muscle is also involuntary, and it does not require any stimulus for functioning.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




