
Which of the following carbocation is expected to be most stable?
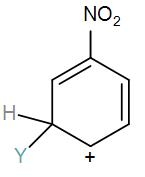
[A]
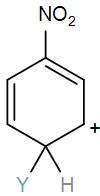
[B]
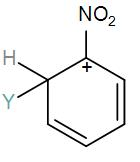
[C]
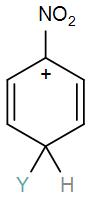
[D]




Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: The stability of a carbocation depends upon several factors but here we have an electron-withdrawing group so consider its effect while answering the question. Nitro group is a meta directing group.
Complete step by step answer:
Before answering this question, we have to know what a carbonium ion is and what affects its stability.
Carbonium ion is a pentavalent cation of carbon. We also know it as carbocation. Here, we don’t have any carbocation with alkyl groups attached to them so we will discuss the effect of the nitro group present.
- A carbocation is stabilized through the +R effect i.e. resonance of the positive charge around the ring. But there are some cases where an alkyl carbocation with a +I effect is more stable than a carbocation with +R group although resonance effect has higher priority.
- Now, let us discuss the carbocations given to us.
Here, we have a nitro group attached to the benzene ring. We know that a nitro group is an electron-withdrawing group thus it will immediately destabilize the positive charge directly attached to it.
- And We know that the nitro group is a meta directing group in electrophilic substitution reaction because of the high amount of electrons at the meta position.
The mechanism is as follows.
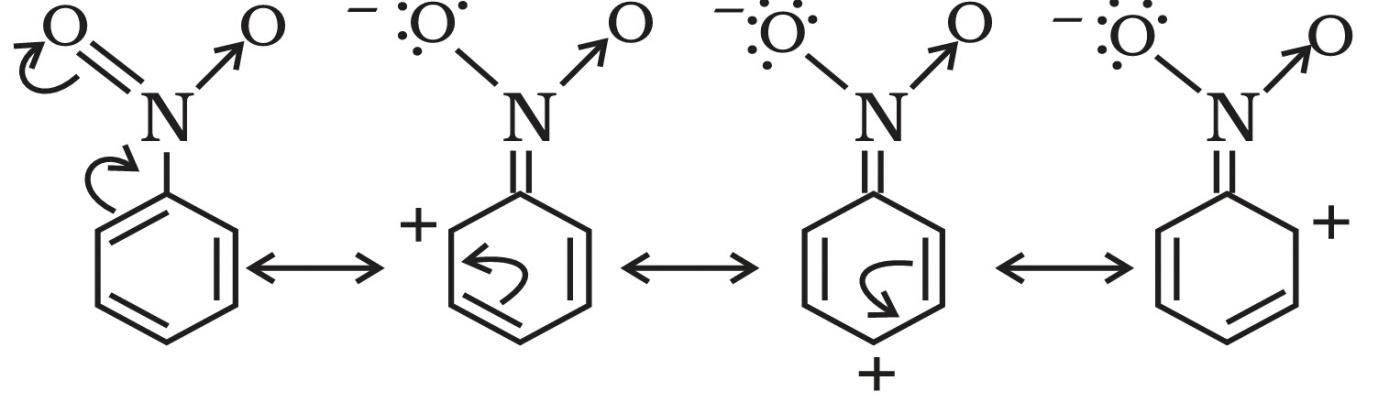
Therefore if there is a positive charge at meta position then the molecule is more stable because the positive charge won’t involve resonance then it is more stable.
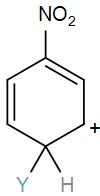
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The stability of a carbocation depends upon several factors-
-Alkyl group stabilizes carbocation by both the +I effect and the hyper-conjugative effect.
- +R groups also stabilize a carbocation.
- Bulky groups attached to the carbocation stabilized it by preventing the carbon atom to return to the $s{{p}^{3}}$ state.
- Some carbocations are also stabilized due to aromatization.
Complete step by step answer:
Before answering this question, we have to know what a carbonium ion is and what affects its stability.
Carbonium ion is a pentavalent cation of carbon. We also know it as carbocation. Here, we don’t have any carbocation with alkyl groups attached to them so we will discuss the effect of the nitro group present.
- A carbocation is stabilized through the +R effect i.e. resonance of the positive charge around the ring. But there are some cases where an alkyl carbocation with a +I effect is more stable than a carbocation with +R group although resonance effect has higher priority.
- Now, let us discuss the carbocations given to us.
Here, we have a nitro group attached to the benzene ring. We know that a nitro group is an electron-withdrawing group thus it will immediately destabilize the positive charge directly attached to it.
- And We know that the nitro group is a meta directing group in electrophilic substitution reaction because of the high amount of electrons at the meta position.
The mechanism is as follows.

Therefore if there is a positive charge at meta position then the molecule is more stable because the positive charge won’t involve resonance then it is more stable.

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The stability of a carbocation depends upon several factors-
-Alkyl group stabilizes carbocation by both the +I effect and the hyper-conjugative effect.
- +R groups also stabilize a carbocation.
- Bulky groups attached to the carbocation stabilized it by preventing the carbon atom to return to the $s{{p}^{3}}$ state.
- Some carbocations are also stabilized due to aromatization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




