
Which of the following carboxylic acids undergoes decarboxylation easily?
a) \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-CO-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH\]
b) \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-CO-COOH\]
c) \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-CO(OH)-COOH\]
d) \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-CO(N{{H}_{2}})-COOH\]
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: Carboxylic acid is the group which contains a (-COOH) group attached to the compound. Decarboxylation is the process of removal of this group in the form of carbon dioxide. Keep in mind that beta keto acids are quite unstable.
Complete step by step answer:
As the name suggests, decarboxylation is the process of removal of carboxy group from an organic compound by releasing it in the form of carbon dioxide. The general formula for this process can be written as –
\[RCOOH\xrightarrow{Decarboxylation}R-H+C{{O}_{2}}\]
To solve this question, keep in mind that beta-keto carboxylic acids are most unstable. Therefore, it undergoes decarboxylation quite easily. Looking at the options, we can say that the first compound is a beta-keto acid.
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-CO-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH\]
The mechanism for decarboxylation of this compound is given as –
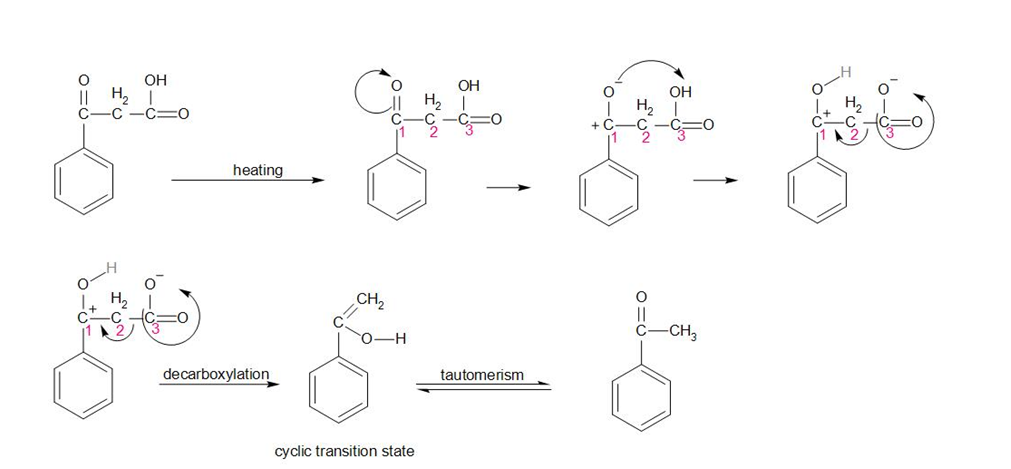
In the above reaction, on heating the compound, the oxygen attached to carbon 1 starts to break its bond and therefore develops a negative charge. Therefore, it attracts the hydrogen of the -OH group attached to carbon 3. This anionic compound is unstable in nature. Therefore, the carboxylic acid (carbon 3) group shifts its bond towards the carbon and leaves the compound.
The compound hence made is unstable, it undergoes tautomerism to make the final product.
Therefore, the answer is – option (a) – \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-CO-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH\].
Additional Information: Some of the named reactions for decarboxylation in organic chemistry includes - Barton decarboxylation, Kolbe electrolysis, Kochi reaction and Hunsdiecker reaction.
Note: We can also solve this question by checking the stability of carbanion formed in the process of decarboxylation. As we can see, carbanion formed in the compound is stable. Therefore, it undergoes decarboxylation easily.
Complete step by step answer:
As the name suggests, decarboxylation is the process of removal of carboxy group from an organic compound by releasing it in the form of carbon dioxide. The general formula for this process can be written as –
\[RCOOH\xrightarrow{Decarboxylation}R-H+C{{O}_{2}}\]
To solve this question, keep in mind that beta-keto carboxylic acids are most unstable. Therefore, it undergoes decarboxylation quite easily. Looking at the options, we can say that the first compound is a beta-keto acid.
\[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-CO-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH\]
The mechanism for decarboxylation of this compound is given as –

In the above reaction, on heating the compound, the oxygen attached to carbon 1 starts to break its bond and therefore develops a negative charge. Therefore, it attracts the hydrogen of the -OH group attached to carbon 3. This anionic compound is unstable in nature. Therefore, the carboxylic acid (carbon 3) group shifts its bond towards the carbon and leaves the compound.
The compound hence made is unstable, it undergoes tautomerism to make the final product.
Therefore, the answer is – option (a) – \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-CO-C{{H}_{2}}-COOH\].
Additional Information: Some of the named reactions for decarboxylation in organic chemistry includes - Barton decarboxylation, Kolbe electrolysis, Kochi reaction and Hunsdiecker reaction.
Note: We can also solve this question by checking the stability of carbanion formed in the process of decarboxylation. As we can see, carbanion formed in the compound is stable. Therefore, it undergoes decarboxylation easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




