
Which of the following compounds gives only one monochlorination product on its chlorination in the presence of sunlight?
A. n-butane
B. Isopentane
C. Neopentane
D. Isobutane
Answer
513.3k+ views
Hint: Free radical is an intermediate which is formed by a homolytic cleavage of a bond and electrons are arranged in such a manner that each atom has an unshared electron known as free radical. When a chemical reaction involves substitution of free radicals then the reaction is known as free radical substitution reactions.
Complete answer: The chlorination of compounds in the presence of sunlight follows a free radical substitution reaction. The number of monochlorination products depends on the number of distinct carbon atoms available for the substitution reaction. Let us discuss the structure of each given compound and number of distinct carbon atoms available for monochlorination.
Compound (A): n-butane
Structurally the given compound can be represented as follows:

As from the structure it is clear that n-butane consists of two distinct carbon atoms i.e., carbon (1) and carbon (2) which can participate in the chlorination reaction to form a monochlorination product. Carbon (3) and carbon (4) will undergo a substitution reaction equivalent to that of carbon (1) and carbon (2) due to symmetry. Therefore, the number of monochlorinated products formed in the reaction $ = 2$.
Compound (B): Isopentane
Structurally the given compound can be represented as follows:

As from the structure it is clear that due to the presence of the methyl group at carbon (2), all four carbon atoms become distinct and due to this number of monochlorination products possible for the given compound $ = 4$.
Compound (C): Neopentane
Structurally the given compound can be represented as follows:
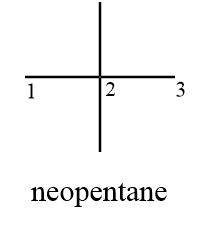
As from the structure it is clear that the compound consists of only two distinct carbon atoms i.e., carbon (1) and carbon (2) while carbon (3) is equivalent to carbon (1) due to symmetry. But carbon (2) does not have a hydrogen atom to substitute so will not take part in the reaction. Hence only carbon (1) will participate in chlorination reaction and the number of monochlorinated products formed $ = 1$
Compound (D): Isobutane
Structurally the given compound can be represented as follows:
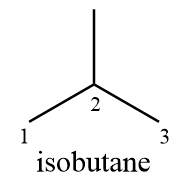
As from the structure it is clear that the compound consists of only two distinct carbon atoms i.e., carbon (1) and carbon (2) while carbon (3) is equivalent to carbon (1) due to symmetry. Hence only carbon (1) and carbon (2) will participate in chlorination reaction and the number of monochlorinated products formed $ = 2$
Therefore, the compound which gives only one monochlorination product on its chlorination in the presence of sunlight is neopentane.
So, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that stereoisomers of the products are not included here. After considering the stereoisomers of the formed product, the number of products will be increased on the basis of the number of chiral centres present in the molecule.
Complete answer: The chlorination of compounds in the presence of sunlight follows a free radical substitution reaction. The number of monochlorination products depends on the number of distinct carbon atoms available for the substitution reaction. Let us discuss the structure of each given compound and number of distinct carbon atoms available for monochlorination.
Compound (A): n-butane
Structurally the given compound can be represented as follows:

As from the structure it is clear that n-butane consists of two distinct carbon atoms i.e., carbon (1) and carbon (2) which can participate in the chlorination reaction to form a monochlorination product. Carbon (3) and carbon (4) will undergo a substitution reaction equivalent to that of carbon (1) and carbon (2) due to symmetry. Therefore, the number of monochlorinated products formed in the reaction $ = 2$.
Compound (B): Isopentane
Structurally the given compound can be represented as follows:

As from the structure it is clear that due to the presence of the methyl group at carbon (2), all four carbon atoms become distinct and due to this number of monochlorination products possible for the given compound $ = 4$.
Compound (C): Neopentane
Structurally the given compound can be represented as follows:

As from the structure it is clear that the compound consists of only two distinct carbon atoms i.e., carbon (1) and carbon (2) while carbon (3) is equivalent to carbon (1) due to symmetry. But carbon (2) does not have a hydrogen atom to substitute so will not take part in the reaction. Hence only carbon (1) will participate in chlorination reaction and the number of monochlorinated products formed $ = 1$
Compound (D): Isobutane
Structurally the given compound can be represented as follows:

As from the structure it is clear that the compound consists of only two distinct carbon atoms i.e., carbon (1) and carbon (2) while carbon (3) is equivalent to carbon (1) due to symmetry. Hence only carbon (1) and carbon (2) will participate in chlorination reaction and the number of monochlorinated products formed $ = 2$
Therefore, the compound which gives only one monochlorination product on its chlorination in the presence of sunlight is neopentane.
So, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that stereoisomers of the products are not included here. After considering the stereoisomers of the formed product, the number of products will be increased on the basis of the number of chiral centres present in the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




