
Which of the following compounds is optically active?
A. $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{COOH}$
B. $\text{HOOC - C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{- COOH}$
C. $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{CH(OH)COOH}$
D. $\text{C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{CHCOOH}$
Answer
597k+ views
Hint: A substance which has optical activity, is a substance which rotates the plane of plane polarized light. To know whether a compound is optical active we need to consider the property of chirality. By chirality we mean a carbon having 4 different groups attached to it. If we find any chiral centre, then that compound is optically active. With this approach, we can find out which of the compounds mentioned in the options are optically active.
Complete step by step answer:
Option A mentions the compound $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{COOH}$ which has an IUPAC name of propanoic acid has a molecular structure of,
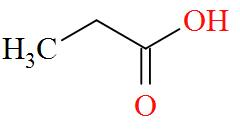
As per the definition, no carbon atom in propanoic acid is seen to be bonded to four different atoms or groups of atoms. Hence, propanoic acid is optically inactive in nature.
Option B mentions the compound $\text{HOOC - C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{- COOH}$ also known as Malonic acid has a molecular structure of,
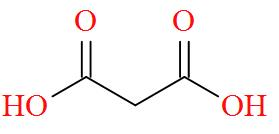
As per the definition, no carbon atom in Malonic acid is seen to be bonded to four different atoms or groups of atoms. Hence, Malonic acid is optically inactive in nature.
Option C mentions the compound $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{CH(OH)COOH}$ which has an IUPAC name of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid, also known as lactic acid has a molecular structure of,
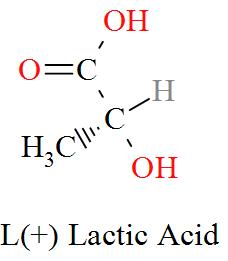
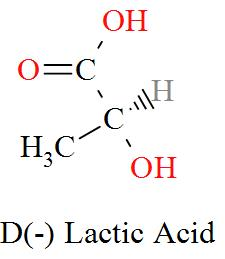
As per the definition, here we can see one carbon atom in Lactic acid is seen to be bonded to four different atoms or groups of atoms forming a Levo and a Dextro structure. Hence, Lactic acid is optically active in nature.
Option D mentions the compound $\text{C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{CHCOOH}$ which has an IUPAC name of dichloroacetic acid has a molecular structure of,
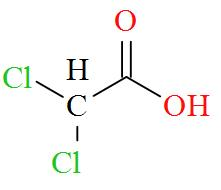
As per the definition, no carbon atom in dichloroacetic acid is seen to be bonded to four different atoms or groups of atoms. Hence, dichloroacetic acid is optically inactive in nature.
Therefore, the correct option is Option C.
Note: Therefore, we can say that chiral molecules are optically active, which implies that when a beam of plane polarized light passes through a chiral molecule. This will make sure that it interacts with the molecule in such a way that the angle of the plane of oscillation rotates.
Complete step by step answer:
Option A mentions the compound $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{COOH}$ which has an IUPAC name of propanoic acid has a molecular structure of,

As per the definition, no carbon atom in propanoic acid is seen to be bonded to four different atoms or groups of atoms. Hence, propanoic acid is optically inactive in nature.
Option B mentions the compound $\text{HOOC - C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{- COOH}$ also known as Malonic acid has a molecular structure of,

As per the definition, no carbon atom in Malonic acid is seen to be bonded to four different atoms or groups of atoms. Hence, Malonic acid is optically inactive in nature.
Option C mentions the compound $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{CH(OH)COOH}$ which has an IUPAC name of 2-hydroxypropanoic acid, also known as lactic acid has a molecular structure of,


As per the definition, here we can see one carbon atom in Lactic acid is seen to be bonded to four different atoms or groups of atoms forming a Levo and a Dextro structure. Hence, Lactic acid is optically active in nature.
Option D mentions the compound $\text{C}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{CHCOOH}$ which has an IUPAC name of dichloroacetic acid has a molecular structure of,

As per the definition, no carbon atom in dichloroacetic acid is seen to be bonded to four different atoms or groups of atoms. Hence, dichloroacetic acid is optically inactive in nature.
Therefore, the correct option is Option C.
Note: Therefore, we can say that chiral molecules are optically active, which implies that when a beam of plane polarized light passes through a chiral molecule. This will make sure that it interacts with the molecule in such a way that the angle of the plane of oscillation rotates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




