
Which of the following is a benzenoid compound?
A.Benzene
B.Toluene
C.Xylene
D.All of the above
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: The compounds which have a benzene ring are called benzenoid compounds. They are stable due to the resonance effect of the pi – electrons of the benzene ring.
Complete step by step answer:
Benzenoids are a class of chemical compounds with at least one benzene ring. These compounds have increased stability from resonance in the benzene rings. Most of the aromatic hydrocarbons are benzenoid compounds. Aromatic compounds are chemical compounds that consist of conjugated planar ring systems accompanied by delocalized pi-electron clouds in place of individual alternating double and single bonds. They are also called aromatics or arenes.
In the given question, we’ll need to investigate each option individually
A.Benzene
Benzene is an aromatic compound with the molecular formula \[{C_6}{H_6}\]. The carbon atoms in a benzene molecule are joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. The structure of benzene is:
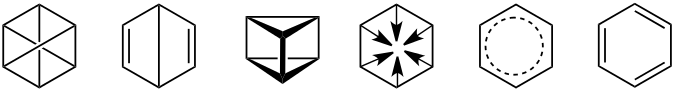
B.Toluene
Toluene is an aromatic hydrocarbon which has one methyl group attached to the phenyl group. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative. It is a colourless, water-insoluble liquid. The structure of toluene is:
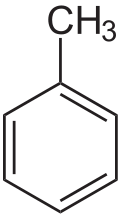
C.Xylene
Xylene is an aromatic compound which has two methyl groups attached to the phenyl group. It is a colourless, flammable liquid. There are three isomers of xylene: o – xylene, m – xylene and p – xylene. The structure of o – xylene is:
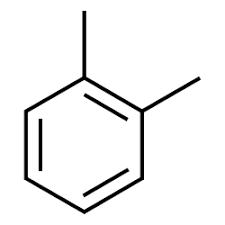
Hence, the correct answer is (D).
Note: Remember that all aromatic compounds are not benzenoid compounds. Some examples are: cyclooctadecanonaene, azulene and trans-bicalicene.
Complete step by step answer:
Benzenoids are a class of chemical compounds with at least one benzene ring. These compounds have increased stability from resonance in the benzene rings. Most of the aromatic hydrocarbons are benzenoid compounds. Aromatic compounds are chemical compounds that consist of conjugated planar ring systems accompanied by delocalized pi-electron clouds in place of individual alternating double and single bonds. They are also called aromatics or arenes.
In the given question, we’ll need to investigate each option individually
A.Benzene
Benzene is an aromatic compound with the molecular formula \[{C_6}{H_6}\]. The carbon atoms in a benzene molecule are joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. The structure of benzene is:

B.Toluene
Toluene is an aromatic hydrocarbon which has one methyl group attached to the phenyl group. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative. It is a colourless, water-insoluble liquid. The structure of toluene is:

C.Xylene
Xylene is an aromatic compound which has two methyl groups attached to the phenyl group. It is a colourless, flammable liquid. There are three isomers of xylene: o – xylene, m – xylene and p – xylene. The structure of o – xylene is:

Hence, the correct answer is (D).
Note: Remember that all aromatic compounds are not benzenoid compounds. Some examples are: cyclooctadecanonaene, azulene and trans-bicalicene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




