
Which of the following is a chain-growth polymer?
(A) Nucleic acid
(B) Starch
(C) Polystyrene
(D) Proteins
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Draw the structure of the polymers given above. By doing this you can identify the monomeric unit of the long polymeric chain. Chain growth polymers will form the polymer at once and a long chain of molecules is formed at the end, unlike step-growth polymers. Understand the mechanism of chain growth to find the polymers which obey the reaction mechanism.
Complete step by step solution:
-Polymerization is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form long polymer chains.
-In chemical compounds, polymerization can occur by various types of reaction mechanisms that vary in complexity due to the functional groups present in the reactants and the steric effects that are present.
-In simple polymerizations, alkenes form polymers through relatively simple free radical reactions; in contrast, reactions involving substitution at a carbonyl group require more complex synthesis due to the way in which reactants polymerize and the steric hindrance offered by neighbouring groups.
-Alkanes are polymerized, with the help of strong mineral acids.
-The two main classes of polymerisation reaction mechanisms are step-growth and chain-growth polymerisation.
-In step-growth polymerisation, the pairs of reactants combine at each step to form a longer polymer chain. The average molar mass increases slowly, long chains are formed only at the end of the reaction.
-However, in the case of chain growth polymerisation, the addition of monomers to the growing chain with active centre (like free radical, cation, anion) is the chain extension step. Long chains are formed from the starting of the reaction only.
-In the options mentioned above, polystyrene is a chain-growth polymer. The polymerisation reaction is given below:
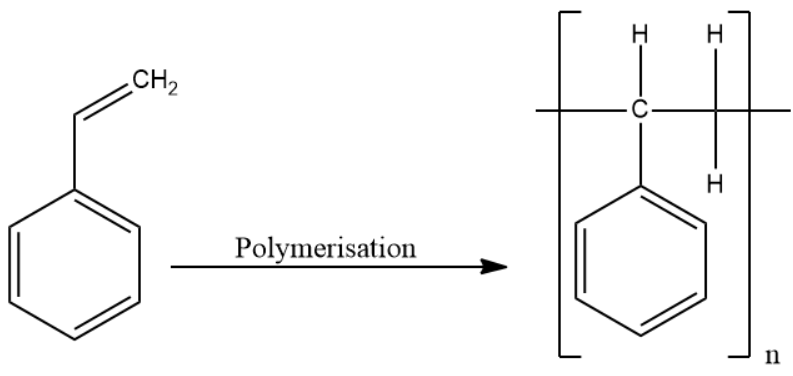
Therefore, the answer is option (C).
Note: Polymerization is divided into 2 types based on the number of monomers used, namely homo polymerisation and copolymerisation. The polymerisation reaction involving a single monomer is known as homo polymerisation. Copolymerisation is the type of polymerisation reaction involving more than one type of monomer. The number of monomers involved in the reaction is usually 2.
Complete step by step solution:
-Polymerization is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form long polymer chains.
-In chemical compounds, polymerization can occur by various types of reaction mechanisms that vary in complexity due to the functional groups present in the reactants and the steric effects that are present.
-In simple polymerizations, alkenes form polymers through relatively simple free radical reactions; in contrast, reactions involving substitution at a carbonyl group require more complex synthesis due to the way in which reactants polymerize and the steric hindrance offered by neighbouring groups.
-Alkanes are polymerized, with the help of strong mineral acids.
-The two main classes of polymerisation reaction mechanisms are step-growth and chain-growth polymerisation.
-In step-growth polymerisation, the pairs of reactants combine at each step to form a longer polymer chain. The average molar mass increases slowly, long chains are formed only at the end of the reaction.
-However, in the case of chain growth polymerisation, the addition of monomers to the growing chain with active centre (like free radical, cation, anion) is the chain extension step. Long chains are formed from the starting of the reaction only.
-In the options mentioned above, polystyrene is a chain-growth polymer. The polymerisation reaction is given below:

Therefore, the answer is option (C).
Note: Polymerization is divided into 2 types based on the number of monomers used, namely homo polymerisation and copolymerisation. The polymerisation reaction involving a single monomer is known as homo polymerisation. Copolymerisation is the type of polymerisation reaction involving more than one type of monomer. The number of monomers involved in the reaction is usually 2.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




