
Which of the following is an aromatic compound?
A. Phenol
B. Naphthalene
C. Pyridine
D. All of the above
Answer
559.5k+ views
Hint: Aromatic compounds are also known by another name aromatic or arenes. These are categorized into the hydrocarbons having sigma bonds and pi electrons delocalised between carbon atoms in a ring. The most important condition for aromatic compounds is to satisfy the Huckel rule. Benzene is an example of an aromatic compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us discuss the most important condition mentioned for aromatic compounds, i.e. Huckel rule.
According to the Huckel rule, a compound will be aromatic if it satisfies the below- mentioned characteristics:
1.The compound should be planar
2.There should be complete delocalization of pi (\[\pi \]) electrons in the ring
3.There must be the presence of $(4n + 2)\pi $ electrons in the ring, where n is an integer.
Now, we will look at the given options one by one.
Phenol
The structure of phenol is as follows:
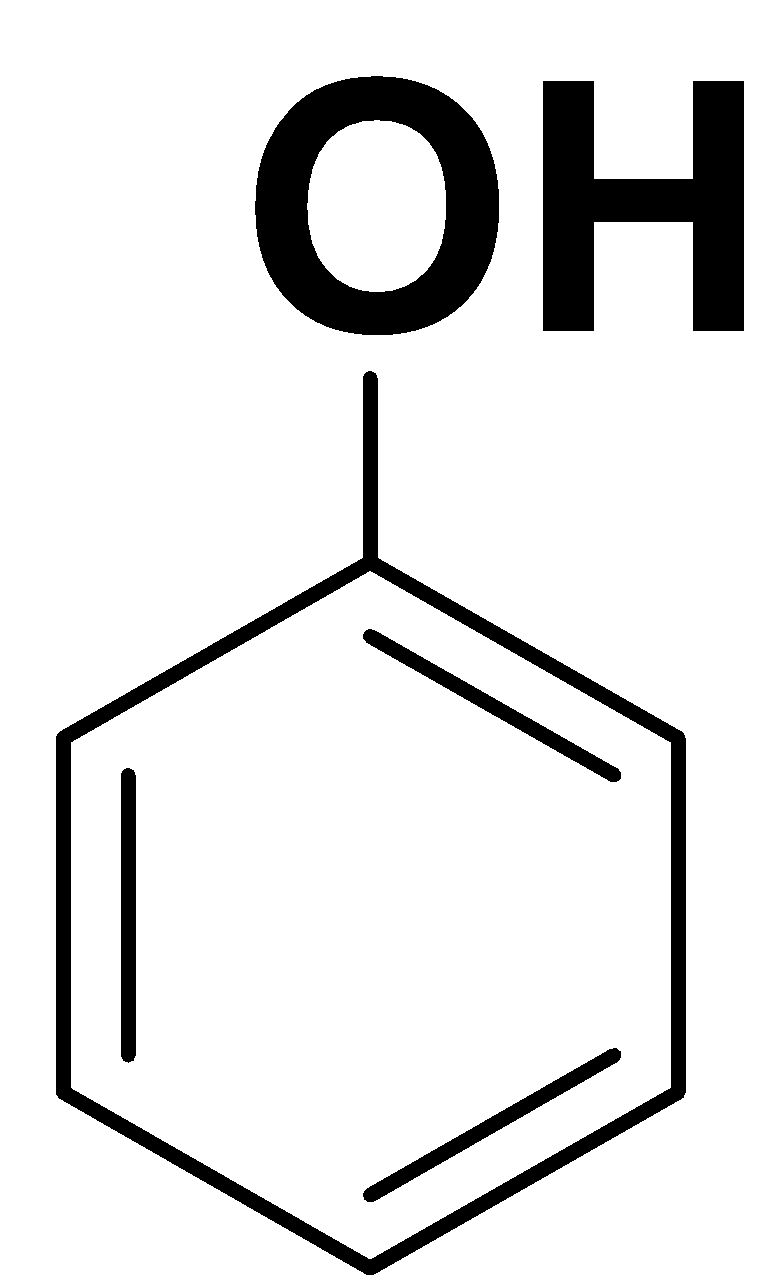
Here, we can see that the compound is planar and there is complete delocalization of pi electrons in the ring. Here, n is 1. So,
$n = 1$
$ \Rightarrow (4 \times 1 + 2)\pi $
$ \Rightarrow 6\pi $ electrons
In the phenol, alkoxide ion (${O^ - }$) is delocalized over the benzene ring. Thus, phenol is an aromatic compound.
Naphthalene
The structure of naphthalene is as follows:
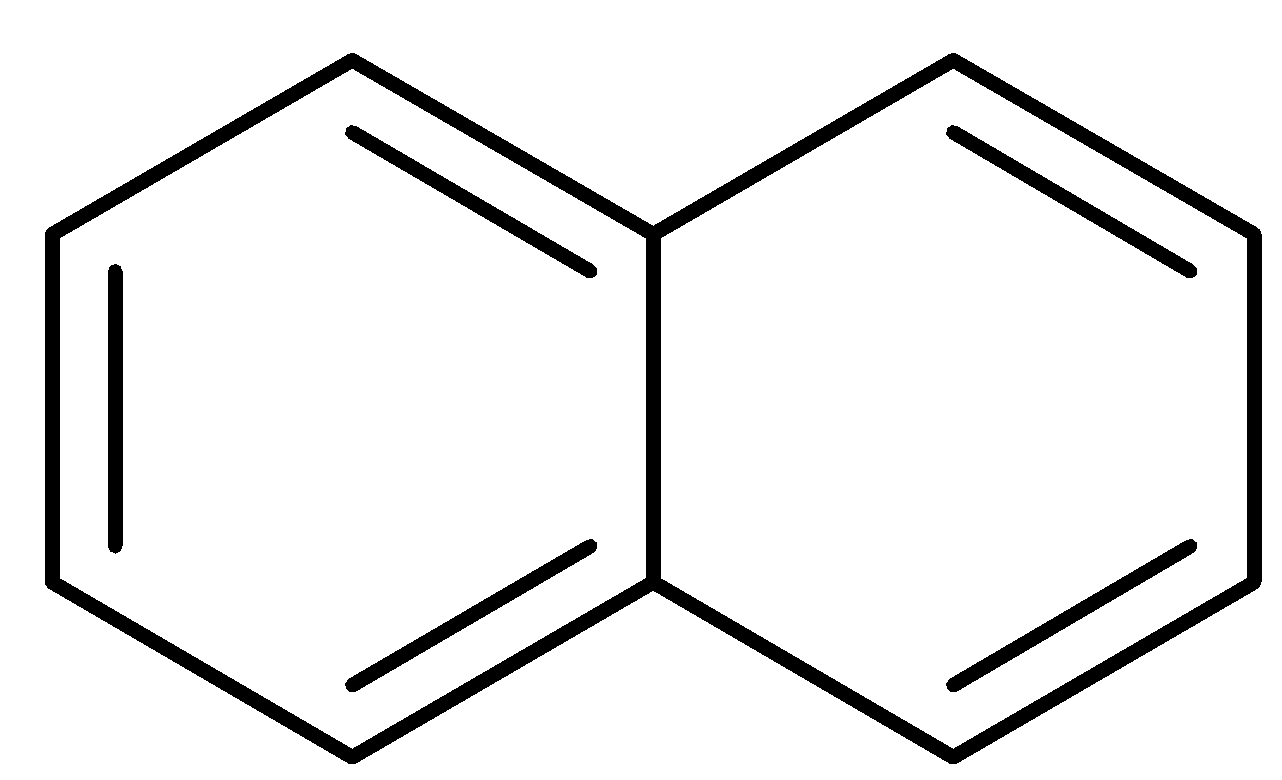
Similarly, like phenol, naphthalene is also planar and exhibits complete delocalization of pi electrons. Here, n is 2. So,
$n = 2$
$ \Rightarrow (4 \times 2 + 2)\pi $
$ \Rightarrow 10\pi $ electrons
Thus, naphthalene is an aromatic compound.
Pyridine
The structure of pyridine is as follows:
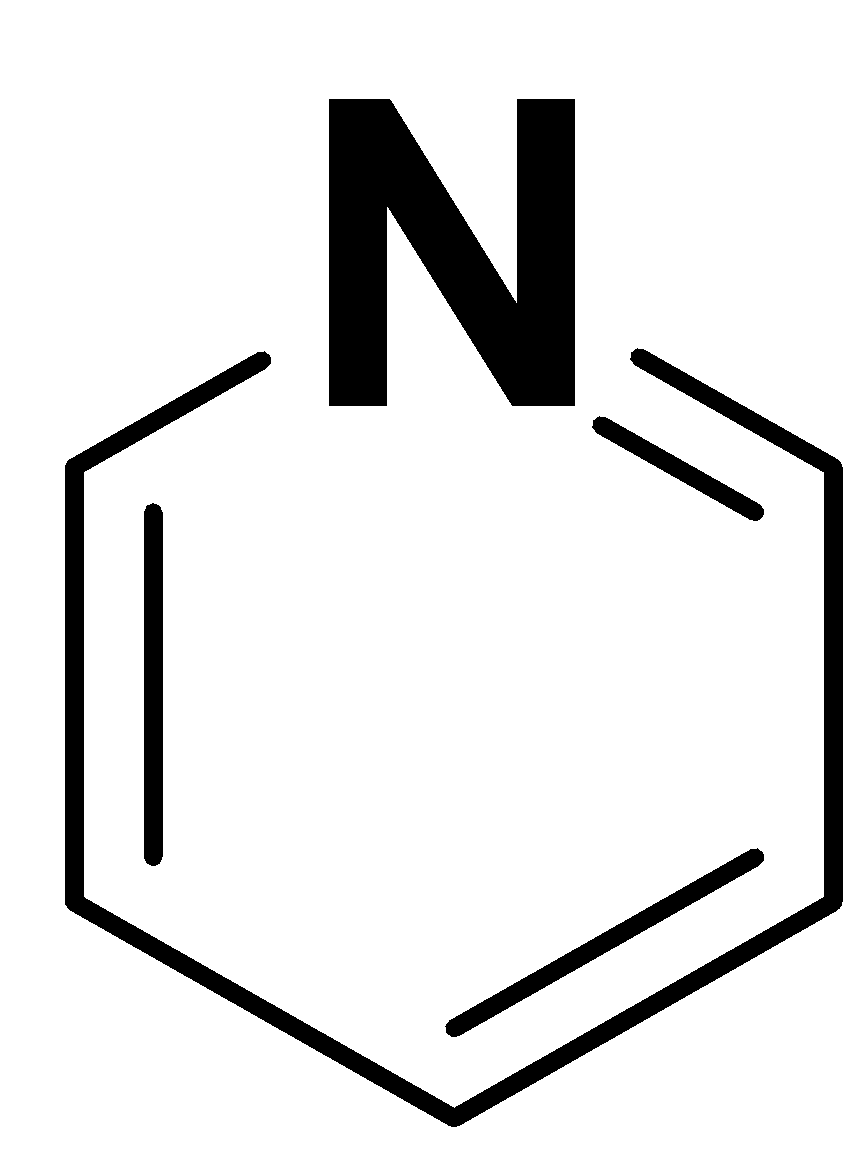
Pyridine is a six-membered ring with heteroatom i.e. nitrogen. It is not based on a benzene ring. So, we can say that it is an example of heteroarenes.
Pyridine follows the $(4n + 2)\pi $ condition.
So, it is an aromatic compound.
In the last, we can conclude that phenol, naphthalene and pyridine are aromatic compounds.
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: Aromatic compounds are categorized further into two categories i.e. Benzenoids and non-Benzenoids. Benzenoids are the compounds having at least one benzene ring. For example, Phenol etc. Non- Benzenoids are the compounds which don’t have benzene rings. In that one carbon is replaced with heteroatoms like sulphur, nitrogen etc. For example, pyridine. Non-Benzenoids are also known as heteroarenes.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us discuss the most important condition mentioned for aromatic compounds, i.e. Huckel rule.
According to the Huckel rule, a compound will be aromatic if it satisfies the below- mentioned characteristics:
1.The compound should be planar
2.There should be complete delocalization of pi (\[\pi \]) electrons in the ring
3.There must be the presence of $(4n + 2)\pi $ electrons in the ring, where n is an integer.
Now, we will look at the given options one by one.
Phenol
The structure of phenol is as follows:

Here, we can see that the compound is planar and there is complete delocalization of pi electrons in the ring. Here, n is 1. So,
$n = 1$
$ \Rightarrow (4 \times 1 + 2)\pi $
$ \Rightarrow 6\pi $ electrons
In the phenol, alkoxide ion (${O^ - }$) is delocalized over the benzene ring. Thus, phenol is an aromatic compound.
Naphthalene
The structure of naphthalene is as follows:

Similarly, like phenol, naphthalene is also planar and exhibits complete delocalization of pi electrons. Here, n is 2. So,
$n = 2$
$ \Rightarrow (4 \times 2 + 2)\pi $
$ \Rightarrow 10\pi $ electrons
Thus, naphthalene is an aromatic compound.
Pyridine
The structure of pyridine is as follows:

Pyridine is a six-membered ring with heteroatom i.e. nitrogen. It is not based on a benzene ring. So, we can say that it is an example of heteroarenes.
Pyridine follows the $(4n + 2)\pi $ condition.
So, it is an aromatic compound.
In the last, we can conclude that phenol, naphthalene and pyridine are aromatic compounds.
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: Aromatic compounds are categorized further into two categories i.e. Benzenoids and non-Benzenoids. Benzenoids are the compounds having at least one benzene ring. For example, Phenol etc. Non- Benzenoids are the compounds which don’t have benzene rings. In that one carbon is replaced with heteroatoms like sulphur, nitrogen etc. For example, pyridine. Non-Benzenoids are also known as heteroarenes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




