
Which of the following is modified to form an air cavity in aquatic plants?
(a) Aerenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Collenchyma
(d) None of the above
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: In certain plants, a special cavity is present that functions as a diffusion chamber and helps in gaseous exchange by interconnecting the intercellular spaces of the plant cells. These cavities are known as sub-stomatal cavities which are located proximal to the stoma.
Complete answer:
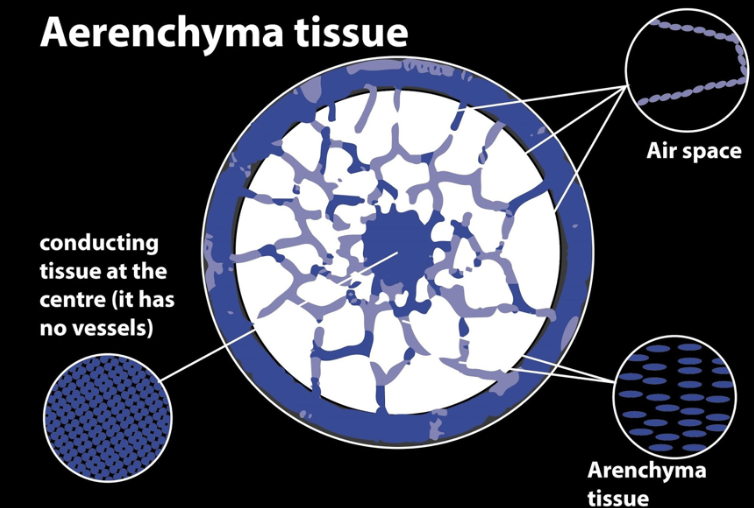
Aerenchyma is modified to form their cavities in aquatic plants. It is a spongy tissue that forms spaces or their channels. They allow the exchange of gases between the shoot and the root and provide a low resistance internal pathway for the exchange of gases. Hypoxia gets developed in Aerenchyma when the soil gets flooded as the microorganisms consume oxygen faster than the diffusion occurs. It allows the plant to grow without the metabolic cost of anaerobic respiration.
Additional information:
Sclerenchyma: Sclerenchyma consists of hardwood D cells which are usually dead cells and have heavily thickened secondary walls that contain lignin. The cells are non-stretchable and rigid. They usually grow in the non-growing regions of plant bodies like the bark or the mature stems. Fibers and sclereids add to the main types of sclerenchyma tissue. Fiber is elongated cells with tapering ends that provide maximum support to the plant. They are used in the textile industry as a raw material. Sclereids are present in the tissues of the plant such as xylem, phloem, periderm, cortex, and pith. They constitute the hard shells of nuts and sometimes known as stone cells which are responsible for the gritty texture of pears and guavas.
Collenchyma: Collenchyma is living elongated cells that have irregular cell walls. They have thick deposits of cellulose on their cell walls and appear in cross-section. The thickened cell walls provide the strength to the tissue and the longitudinal interlocking of the cell. It can extend and adjust to the increased growth of the organ. It is found in the cortex of the stem and leaves and provides primary support to the tissues for many herbaceous plants.
So, the correct answer is 'Aerenchyma'.
Note: Parenchyma cells are the most diverse and versatile cell type which are composed of a majority of cells in plants. Sclerenchyma cells have a lignified cell wall and a strong cell wall which are usually dead at maturity. The least common type of plant cell type is collenchyma cells. collenchymatous cells have temporary organs such as petioles and leaves.
Complete answer:
Aerenchyma is modified to form their cavities in aquatic plants. It is a spongy tissue that forms spaces or their channels. They allow the exchange of gases between the shoot and the root and provide a low resistance internal pathway for the exchange of gases. Hypoxia gets developed in Aerenchyma when the soil gets flooded as the microorganisms consume oxygen faster than the diffusion occurs. It allows the plant to grow without the metabolic cost of anaerobic respiration.
Additional information:
Sclerenchyma: Sclerenchyma consists of hardwood D cells which are usually dead cells and have heavily thickened secondary walls that contain lignin. The cells are non-stretchable and rigid. They usually grow in the non-growing regions of plant bodies like the bark or the mature stems. Fibers and sclereids add to the main types of sclerenchyma tissue. Fiber is elongated cells with tapering ends that provide maximum support to the plant. They are used in the textile industry as a raw material. Sclereids are present in the tissues of the plant such as xylem, phloem, periderm, cortex, and pith. They constitute the hard shells of nuts and sometimes known as stone cells which are responsible for the gritty texture of pears and guavas.

Collenchyma: Collenchyma is living elongated cells that have irregular cell walls. They have thick deposits of cellulose on their cell walls and appear in cross-section. The thickened cell walls provide the strength to the tissue and the longitudinal interlocking of the cell. It can extend and adjust to the increased growth of the organ. It is found in the cortex of the stem and leaves and provides primary support to the tissues for many herbaceous plants.
So, the correct answer is 'Aerenchyma'.
Note: Parenchyma cells are the most diverse and versatile cell type which are composed of a majority of cells in plants. Sclerenchyma cells have a lignified cell wall and a strong cell wall which are usually dead at maturity. The least common type of plant cell type is collenchyma cells. collenchymatous cells have temporary organs such as petioles and leaves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




