
Which of the following is most acidic?
(A) Benzyl alcohol
(B) 2-Butanol
(C) tert-Butyl alcohol
(D) Hydroxybenzene
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: For a compound to be acidic, its conjugate base (formed after losing a proton) should be stable. A conjugate base having higher delocalization of pi-electrons in the ring is more stable. Also more is the inductive effect on the carbon having acidic group, lesser will be the acidic character.
Complete step by step answer:
-Here we can see that all the options are alcohol only.
We also know that the stability of the alcohols is based on the stability of the respective conjugate bases. More is the stability of the conjugate base, more is the compound’s acidic character. We see the stability of the conjugate base by checking its resonating structures. More resonating structures means more stability of conjugate base. More acidic compounds will easily lose ${H^ + }$ ion to gain stability.
-So, now we will see the structures given in the options and their conjugate bases.
For (A) Benzyl alcohol: It has a molecular formula of: ${C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2}OH$ and after losing an ${H^ + }$ ion it forms its conjugate base of formula: ${C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2}{O^ - }$. This conjugate base does not show any resonating structures and so is unstable. Thus, Benzyl alcohol is less acidic.
For (B) 2-Butanol: It has a molecular formula of: ${C_4}{H_{10}}O$ or $C{H_3} - CH(OH) - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$. Its conjugate base would be: $C{H_3} - CH({O^ - }) - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$ and here we see that it posses large (+I) inductive effect making the base unstable. So, 2-Butanol is less acidic.
For (C) tert-Butyl alcohol: It has a formula of ${(C{H_3})_3}C - OH$. Here also we can see that there is (+I) inductive effect from 3 methyl groups thus making it less acidic.
For (D) Hydroxybenzene: It has a molecular formula of ${C_6}{H_5}OH$. Its conjugate base is a phenoxide ion (${C_6}{H_5}{O^ - }$). This ion is highly stable due to resonance or charge delocalization in the ring. Therefore hydroxybenzene is most acidic. The charge delocalization in phenoxide ion is shown below:
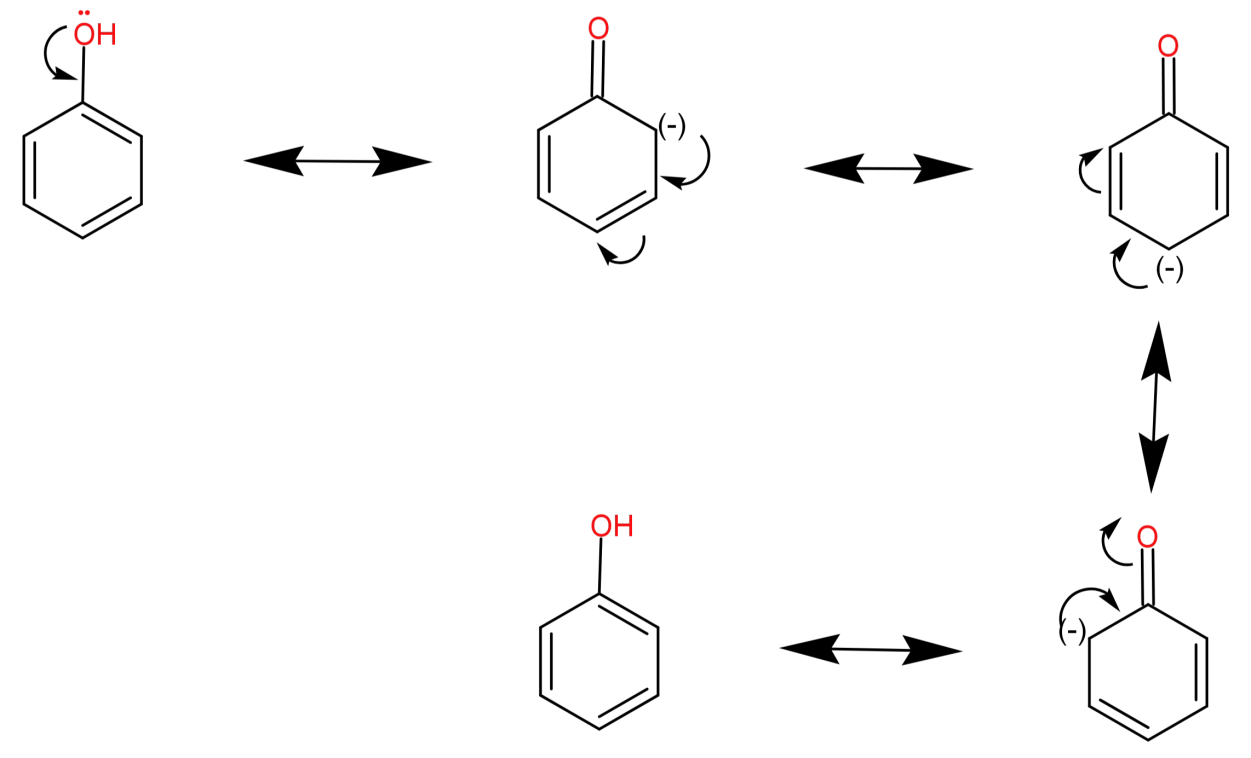
Thus, among all the hydroxybenzene is most acidic.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Remember that a more stable compound will not lose hydrogen ion easily, so it won’t be acidic. But a compound that gains stability after losing a hydrogen ion is acidic because its conjugate base would be stable. Both of these are different things, don’t get confused.
Complete step by step answer:
-Here we can see that all the options are alcohol only.
We also know that the stability of the alcohols is based on the stability of the respective conjugate bases. More is the stability of the conjugate base, more is the compound’s acidic character. We see the stability of the conjugate base by checking its resonating structures. More resonating structures means more stability of conjugate base. More acidic compounds will easily lose ${H^ + }$ ion to gain stability.
-So, now we will see the structures given in the options and their conjugate bases.
For (A) Benzyl alcohol: It has a molecular formula of: ${C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2}OH$ and after losing an ${H^ + }$ ion it forms its conjugate base of formula: ${C_6}{H_5} - C{H_2}{O^ - }$. This conjugate base does not show any resonating structures and so is unstable. Thus, Benzyl alcohol is less acidic.
For (B) 2-Butanol: It has a molecular formula of: ${C_4}{H_{10}}O$ or $C{H_3} - CH(OH) - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$. Its conjugate base would be: $C{H_3} - CH({O^ - }) - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$ and here we see that it posses large (+I) inductive effect making the base unstable. So, 2-Butanol is less acidic.
For (C) tert-Butyl alcohol: It has a formula of ${(C{H_3})_3}C - OH$. Here also we can see that there is (+I) inductive effect from 3 methyl groups thus making it less acidic.
For (D) Hydroxybenzene: It has a molecular formula of ${C_6}{H_5}OH$. Its conjugate base is a phenoxide ion (${C_6}{H_5}{O^ - }$). This ion is highly stable due to resonance or charge delocalization in the ring. Therefore hydroxybenzene is most acidic. The charge delocalization in phenoxide ion is shown below:

Thus, among all the hydroxybenzene is most acidic.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Remember that a more stable compound will not lose hydrogen ion easily, so it won’t be acidic. But a compound that gains stability after losing a hydrogen ion is acidic because its conjugate base would be stable. Both of these are different things, don’t get confused.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




