
Which of the following is the correct representation of electron dot structure of nitrogen?
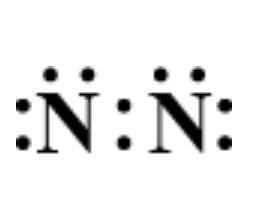
A.
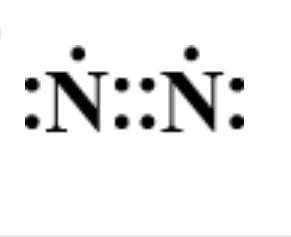
B.
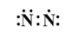
C.
D.
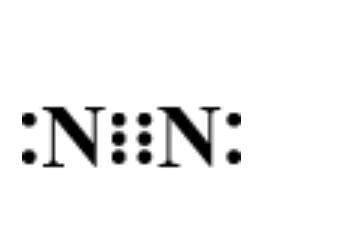
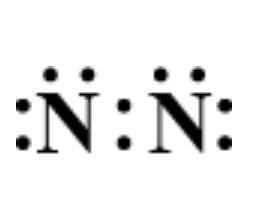
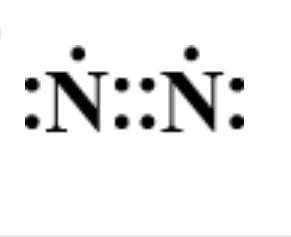
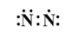
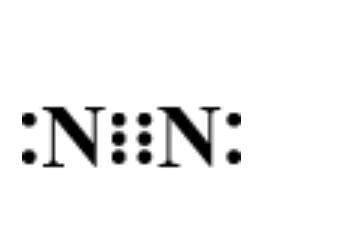
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Chemical bonding refers to the formation of a chemical bond between two or more atoms, molecules, or ions to give rise to a chemical compound. Moreover, these chemical bonds are what keeps the atoms together in the resulting compound.
Complete step by step answer:
-Albert Kossel and Gilbert Lewis were the first to explain the formation of chemical bonds successfully in the year 1916. Further, a Lewis theory of chemical bonding was given. Some of the points of this theory are given below:
1.An atom can be viewed as a positively charged Kernel and as the outer shell.
2.The outer shell can accommodate a maximum of eight electrons only.
3.Atoms can achieve the stable configuration by forming chemical bonds with other atoms. 4.Moreover, this chemical bond can be formed either by gaining or losing an electron or in some cases due to the sharing of an electron.
Generally, the valency of an element is either equal to the number of dots in the corresponding Lewis symbol or eight minus the number of dots.
Now, let’s determine the electron dot structure of nitrogen. The atomic weight of nitrogen is and its electronic configuration is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3}$ . Thus, three electrons remain in the ‘p’ orbital which forms the extremely strong triple bond in elemental nitrogen. Hence, its structure is represented as:
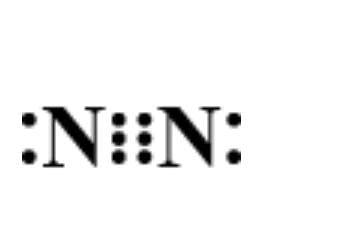
Hence, option D is correct.
Note:
Atoms having eight electrons in their last orbit are stable and have no tendency to react whereas the atoms having less than eight electrons react with other atoms to get eight electrons in their outermost orbit and become stable. Moreover, the atoms that cannot either lose or gain electrons may share to get the octet configuration.
Complete step by step answer:
-Albert Kossel and Gilbert Lewis were the first to explain the formation of chemical bonds successfully in the year 1916. Further, a Lewis theory of chemical bonding was given. Some of the points of this theory are given below:
1.An atom can be viewed as a positively charged Kernel and as the outer shell.
2.The outer shell can accommodate a maximum of eight electrons only.
3.Atoms can achieve the stable configuration by forming chemical bonds with other atoms. 4.Moreover, this chemical bond can be formed either by gaining or losing an electron or in some cases due to the sharing of an electron.
Generally, the valency of an element is either equal to the number of dots in the corresponding Lewis symbol or eight minus the number of dots.
Now, let’s determine the electron dot structure of nitrogen. The atomic weight of nitrogen is and its electronic configuration is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3}$ . Thus, three electrons remain in the ‘p’ orbital which forms the extremely strong triple bond in elemental nitrogen. Hence, its structure is represented as:
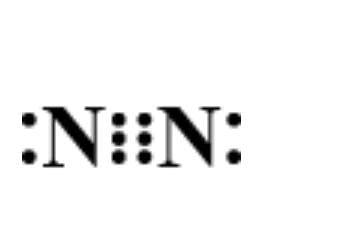
Hence, option D is correct.
Note:
Atoms having eight electrons in their last orbit are stable and have no tendency to react whereas the atoms having less than eight electrons react with other atoms to get eight electrons in their outermost orbit and become stable. Moreover, the atoms that cannot either lose or gain electrons may share to get the octet configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




