
Which of the following is the correct order of C-O bond length?
$\begin{align}
& a)CO < C{{O}_{3}}^{2-} < C{{O}_{2}} \\
& b)CO < C{{O}_{3}}^{-} < C{{O}_{2}} \\
& c)CO < C{{O}_{2}} < C{{O}_{3}}^{2-} \\
& d)C{{O}_{2}} < C{{O}_{3}}^{2-} < CO \\
\end{align}$
Answer
604.2k+ views
Hint: The length of the bond is determined by the number of bonded electrons (the bond order). The higher the bond order, the stronger the pull between the two atoms and the shorter the bond length.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us first define the term bond length so that there are no confusions about its true meaning later.
In molecular geometry, bond length or bond distance is defined as the average distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. It is a transferable property of a bond between atoms of fixed types, relatively independent of the rest of the molecule. Bond length is inversely proportional to bond order: when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond is shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy: all other factors being equal, a stronger bond will be shorter. In a bond between two identical atoms, half the bond distance is equal to the covalent radius.
As we have established, since Bond length is inversely proportional to bond order, and bond order depends on the number of bonds. Here CO will have triple bonds, $C{{O}_{2}}$ will have two double bonds (linear structure with carbon as central atom O=C=O). However, in case of $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$ , the bond character lies between single and double bonds due to resonance.
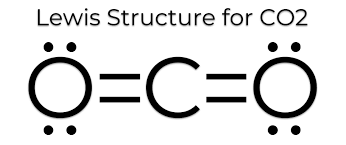
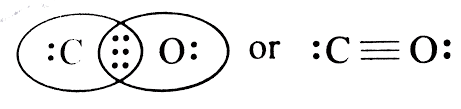
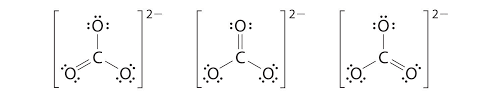
Hence, bond length order will be $CO < C{{O}_{2}} < C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$. Thus, the answer to this question is c)
Note: While knowing the exact values of these bond lengths is also certainly an acceptable way to solve this question, the real reason behind this order lies in the relationship between bond order and bond length and going through the later approach would be much more conducive to your understanding. This relationship is very important in further concepts of Chemistry as well, therefore it is advisable that you solve this question through this method.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us first define the term bond length so that there are no confusions about its true meaning later.
In molecular geometry, bond length or bond distance is defined as the average distance between nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. It is a transferable property of a bond between atoms of fixed types, relatively independent of the rest of the molecule. Bond length is inversely proportional to bond order: when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond is shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy: all other factors being equal, a stronger bond will be shorter. In a bond between two identical atoms, half the bond distance is equal to the covalent radius.
As we have established, since Bond length is inversely proportional to bond order, and bond order depends on the number of bonds. Here CO will have triple bonds, $C{{O}_{2}}$ will have two double bonds (linear structure with carbon as central atom O=C=O). However, in case of $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$ , the bond character lies between single and double bonds due to resonance.

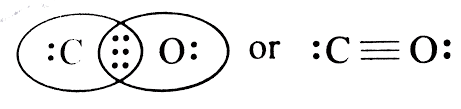

Hence, bond length order will be $CO < C{{O}_{2}} < C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$. Thus, the answer to this question is c)
Note: While knowing the exact values of these bond lengths is also certainly an acceptable way to solve this question, the real reason behind this order lies in the relationship between bond order and bond length and going through the later approach would be much more conducive to your understanding. This relationship is very important in further concepts of Chemistry as well, therefore it is advisable that you solve this question through this method.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




