
Which of the following is the most acidic in nature \[?\]
A.
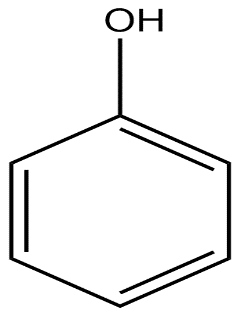
B. \[C{H_3}COOH\]
C.
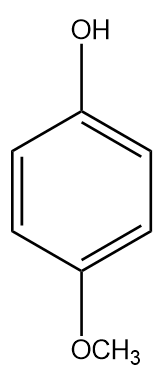
D.



Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: Acids are chemical species that can donate a proton $[{H^ + }]$ . On releasing a proton, the resulting species becomes negatively charged and is the conjugate base of the acid. The stability of the resulting conjugate base determines the acidity of the acid. pKa values of an acid determines the acidity, higher the pKa value weaker the acid.
Complete answer:
According to Bronsted – Lowry theory, an acid releases $[{H^ + }]$ i.e., it is a proton donor. On donating a proton the acid becomes a conjugate base which is a potent proton acceptor.
The conjugate bases of above chemical species are :
(a)
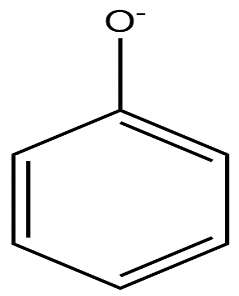
(b)
(c) $C{H_3}CO{O^ - }$
(d)
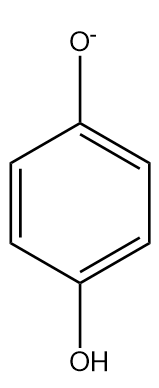
In phenoxide ion, the negative charge on oxygen atoms is stabilised by the benzene ring by resonance. It is resonated between the less electronegative carbon atoms. We know, negative charge on a less electronegative atom is less stable. The charge is delocalised less present on the oxygen atom.
In acetate, it is resonated between two electronegative oxygen atoms of the carboxylate. This is a far stable conjugate base.
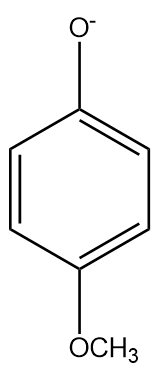
The $ - OC{H_3}$ at the para position has a negligible $ - I$ (inductive) effect since it is highly dependent on distance and the para position is far. The methoxy group destabilises the phenyl ring as it is electron donating and increases the electrons in the benzene ring ($ + R$) in addition to the electrons from oxygen. Therefore, it is a weaker acid than phenol.
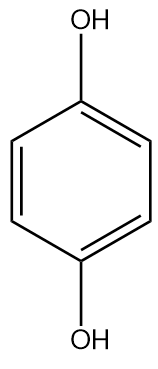
Hydroquinone or benzene-1,4-diol is a weaker acid than phenol since two oxygen atoms para to each other destabilised the benzene ring. It has electron donating nature but the $ - I$ fades away due to distance.
On the basis of stability of the conjugate base, acetate ion is more stable and acetic acid is the most acidic.
The answer is (B) \[C{H_3}COOH\] .
Note:
The stability of conjugate bases are determined by the $ \pm R$ effect, $ \pm I$ effect , hyper conjugation, resonance stabilisation ,hydrogen bonding etc.
The pKa values of the above species are $10,\,\,4.75,\,\,10.05,\,\,9.9$ respectively. Therefore, acetic acid with lower pKa is the strongest acid.
Presence of electron withdrawing groups on a benzene ring can add to its stability while an electron donating group lowers it.
Complete answer:
According to Bronsted – Lowry theory, an acid releases $[{H^ + }]$ i.e., it is a proton donor. On donating a proton the acid becomes a conjugate base which is a potent proton acceptor.
The conjugate bases of above chemical species are :
(a)

(b)

(c) $C{H_3}CO{O^ - }$
(d)

In phenoxide ion, the negative charge on oxygen atoms is stabilised by the benzene ring by resonance. It is resonated between the less electronegative carbon atoms. We know, negative charge on a less electronegative atom is less stable. The charge is delocalised less present on the oxygen atom.
In acetate, it is resonated between two electronegative oxygen atoms of the carboxylate. This is a far stable conjugate base.
The $ - OC{H_3}$ at the para position has a negligible $ - I$ (inductive) effect since it is highly dependent on distance and the para position is far. The methoxy group destabilises the phenyl ring as it is electron donating and increases the electrons in the benzene ring ($ + R$) in addition to the electrons from oxygen. Therefore, it is a weaker acid than phenol.
Hydroquinone or benzene-1,4-diol is a weaker acid than phenol since two oxygen atoms para to each other destabilised the benzene ring. It has electron donating nature but the $ - I$ fades away due to distance.
On the basis of stability of the conjugate base, acetate ion is more stable and acetic acid is the most acidic.
The answer is (B) \[C{H_3}COOH\] .
Note:
The stability of conjugate bases are determined by the $ \pm R$ effect, $ \pm I$ effect , hyper conjugation, resonance stabilisation ,hydrogen bonding etc.
The pKa values of the above species are $10,\,\,4.75,\,\,10.05,\,\,9.9$ respectively. Therefore, acetic acid with lower pKa is the strongest acid.
Presence of electron withdrawing groups on a benzene ring can add to its stability while an electron donating group lowers it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




