
Which of the following is true for nucleolus? A. It takes part in spindle formation B. Larger nucleoli are present in dividing cells C. It is a site for active ribosomal RNA synthesis D. It is a membrane bound structure
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: Nucleolus is a small, dense structure which helps in the site of transcription and processing of ribosome assembly.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The nucleolus is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is a tiny, dense and spherical structure present inside the nucleus of the cell. It is a dense portion because there is proteins, DNA and RNA which are present from particular regions called nucleolar organizing regions.
It is the best known as the site of transcription and processing of ribosomal RNA and ribosome assembly or ribosome biogenesis. Nuclei also participate in the formation of signal recognition particles and function in the response of cells to stress. Nucleoli are proteins, DNA and RNA and form around a specific part of chromosome known as nucleolar structural area.
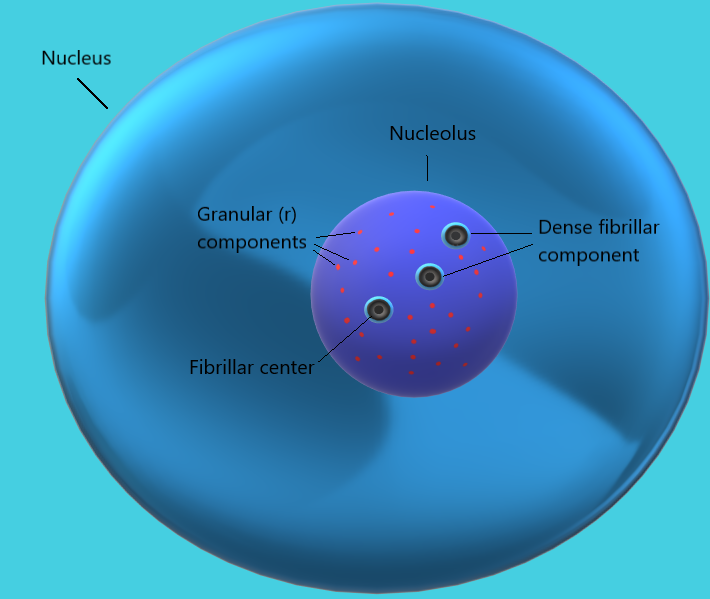
Nucleolus
Ribosome biogenesis is a very tightly regulated process and is closely linked to other cellular activities such as growth and division. As soon as the mature r-proteins are imported into the nucleus and finally into the nucleolus. The association and maturation of Rrna and r-proteins result in the formation of the 40S and 60S subunits of the complete ribosome.
These are transferred by the help of nuclear pore complexes to the cytoplasm where they are free or become associated with the endoplasmic reticulum and form rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Therefore the correct answer is C.
Note:
Several human ribosomopathy genetic diseases include inherited bone marrow failure syndromes which are characterized by a predisposition to cancer and a reduced number of blood cells linked with a mutation in ribosome biogenesis.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The nucleolus is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is a tiny, dense and spherical structure present inside the nucleus of the cell. It is a dense portion because there is proteins, DNA and RNA which are present from particular regions called nucleolar organizing regions.
It is the best known as the site of transcription and processing of ribosomal RNA and ribosome assembly or ribosome biogenesis. Nuclei also participate in the formation of signal recognition particles and function in the response of cells to stress. Nucleoli are proteins, DNA and RNA and form around a specific part of chromosome known as nucleolar structural area.

Nucleolus
Ribosome biogenesis is a very tightly regulated process and is closely linked to other cellular activities such as growth and division. As soon as the mature r-proteins are imported into the nucleus and finally into the nucleolus. The association and maturation of Rrna and r-proteins result in the formation of the 40S and 60S subunits of the complete ribosome.
These are transferred by the help of nuclear pore complexes to the cytoplasm where they are free or become associated with the endoplasmic reticulum and form rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Therefore the correct answer is C.
Note:
Several human ribosomopathy genetic diseases include inherited bone marrow failure syndromes which are characterized by a predisposition to cancer and a reduced number of blood cells linked with a mutation in ribosome biogenesis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




