
Which of the following is/are an amphiprotic ion?
a.) Chlorate ion
b.) Acetate ion
c.) Sulphate ion
d.) Bicarbonate ion
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: The word ‘amphi’ means both and protic refers to proton. All the ions in the option are oxyanions; we can relate the ions with the acid base concept.
Complete step by step answer:
Amphiprotic ions can donate as well as accept a proton. Let us understand with options given.
Chlorate ion: \[Cl{O_4}^ - \] the structure of this ion is as follows:
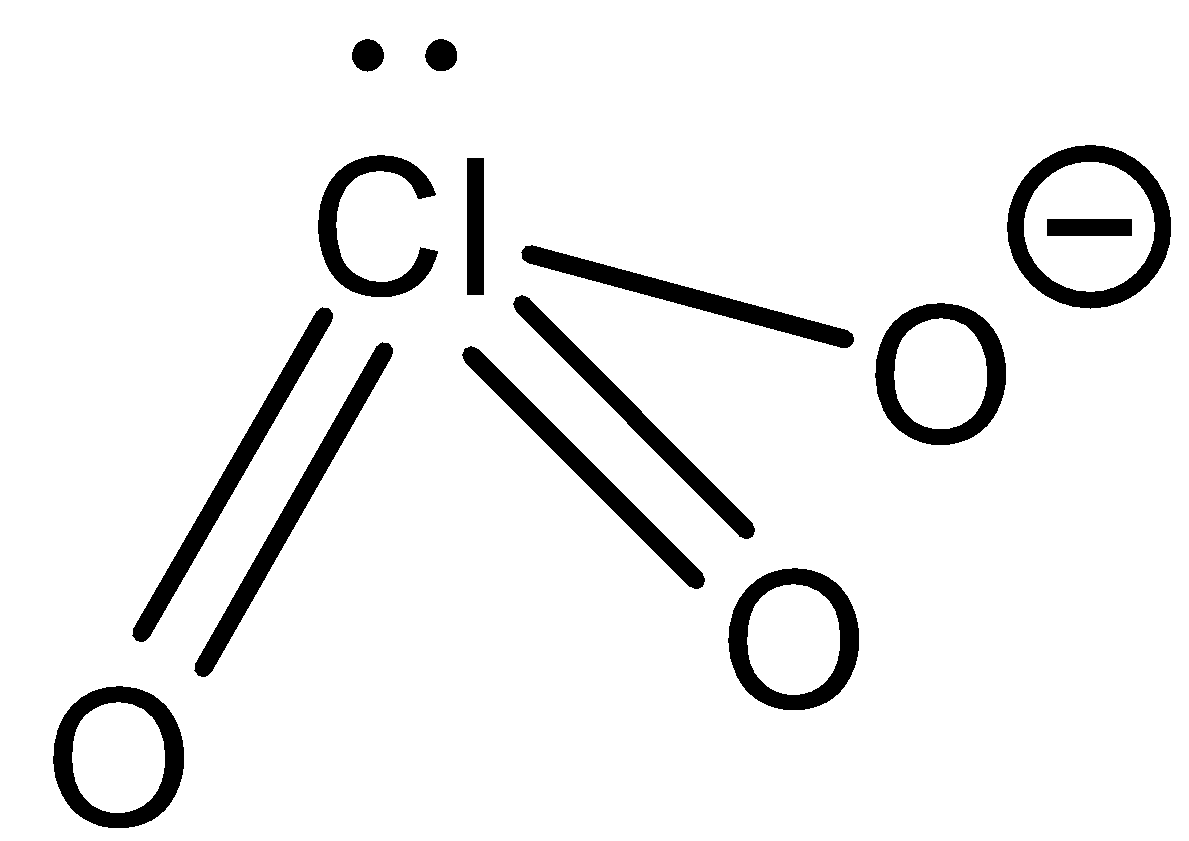
From this structure we can observe that there are no protons which can be donated. So chlorate ions cannot donate protons. Now let us see how the chlorate ions react with strong acid.
$Cl{O_4}^ - + {H_3}{O^ + } \to HCl{O_4} + {H_2}O$
From the reaction we can observe that the chlorate ion can accept a proton to form perchloric acid. So a chlorate ion is not an amphiprotic ion.
Acetate ion: \[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ - }}}\] The structure of the ion is as follows:

From this structure we can observe that though there are hydrogen atoms in the structure they are not bonded to highly electronegative atoms. Due to this, the hydrogen atoms are not acidic. Thus the ion cannot donate the protons. Now when acetate ion is reacted with strong acid then there will be formation of acetic acid and water.
$C{H_3}CO{O^ - } + {H_3}{O^ + } \to C{H_3}COOH + {H_2}O$
From this reaction we can observe that the acetate ion can accept a proton. So acetate ion is not an amphiprotic ion since it can only accept a proton.
Sulphate ion: \[{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}^{{\text{2 - }}}\] The structure of the ion is as follows:
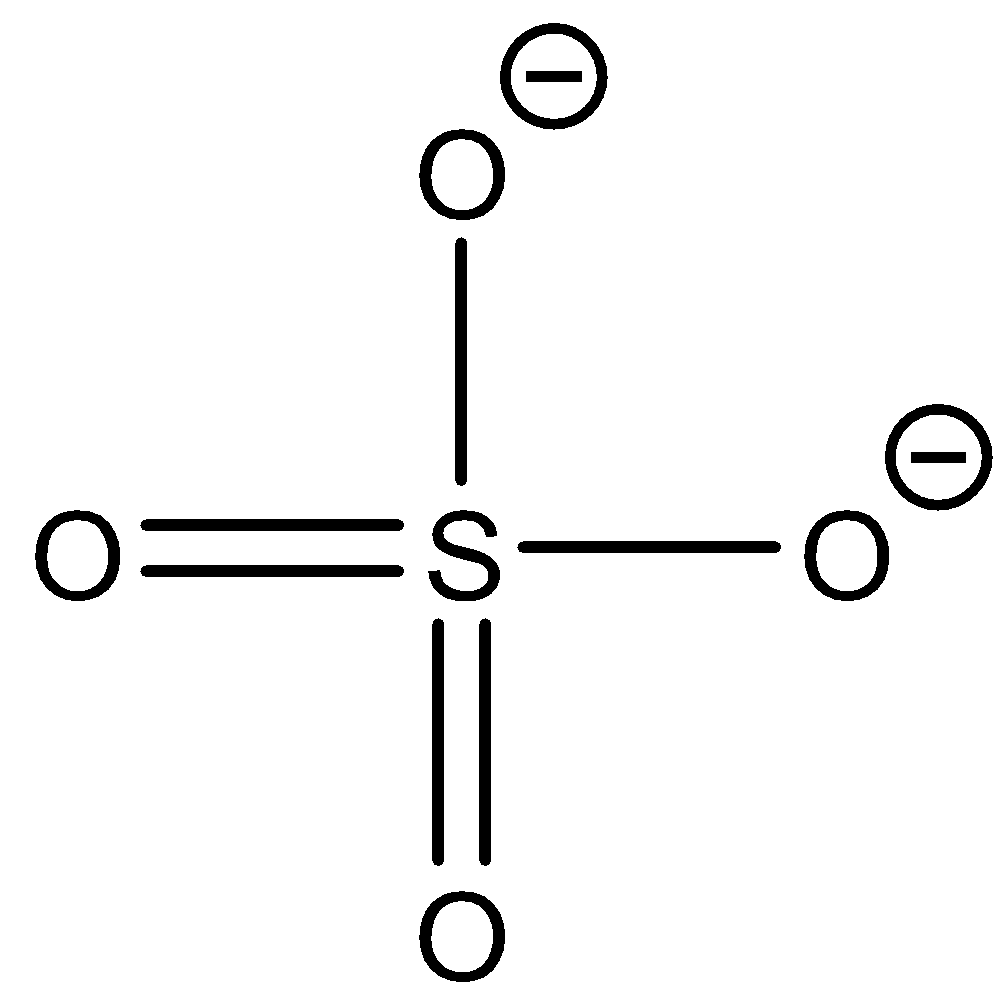
This ion does not contain hydrogen atoms to be donated as protons. So sulphate ions cannot donate protons.
Now, when the ion is reacted with strong acid, it will give sulphuric acid and water.
$S{O_4}^ - + 2{H_3}{O^ + } \to {H_2}S{O_4} + 2{H_2}O$
From this reaction we can observe that the acetate ion can accept a proton. So acetate ion is not an amphiprotic ion since it can only accept a proton.
Bicarbonate ion: \[{\text{HC}}{{\text{O}}_3}^{\text{ - }}\] The structure of the ion is as follows:

From the structure it is observed that the hydrogen is attached to the oxygen atom which makes the hydrogen atom acidic. This means that it can lose a proton. The reaction will be as follows:
$HC{O_3}^ - \to C{O_3}^{2 - } + {H^ + }$
The bicarbonate ion can lose the proton and form carbonate ions. Now when the bicarbonate ion is reacted with strong acid it will produce carbonic acid and water.
$HC{O_3}^ - + {H_3}{O^ + } \to {H_2}C{O_3} + {H_2}O$
From this reaction we can see that bicarbonate ions can accept a proton as well. So bicarbonate ions are amphiprotic ions.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: When an ion accepts a proton then it behaves as a base and when it donates a proton then it behaves as an acid. Conjugate base of strong acid is weak while the conjugate base of weak acid is strong in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
Amphiprotic ions can donate as well as accept a proton. Let us understand with options given.
Chlorate ion: \[Cl{O_4}^ - \] the structure of this ion is as follows:

From this structure we can observe that there are no protons which can be donated. So chlorate ions cannot donate protons. Now let us see how the chlorate ions react with strong acid.
$Cl{O_4}^ - + {H_3}{O^ + } \to HCl{O_4} + {H_2}O$
From the reaction we can observe that the chlorate ion can accept a proton to form perchloric acid. So a chlorate ion is not an amphiprotic ion.
Acetate ion: \[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ - }}}\] The structure of the ion is as follows:

From this structure we can observe that though there are hydrogen atoms in the structure they are not bonded to highly electronegative atoms. Due to this, the hydrogen atoms are not acidic. Thus the ion cannot donate the protons. Now when acetate ion is reacted with strong acid then there will be formation of acetic acid and water.
$C{H_3}CO{O^ - } + {H_3}{O^ + } \to C{H_3}COOH + {H_2}O$
From this reaction we can observe that the acetate ion can accept a proton. So acetate ion is not an amphiprotic ion since it can only accept a proton.
Sulphate ion: \[{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}^{{\text{2 - }}}\] The structure of the ion is as follows:

This ion does not contain hydrogen atoms to be donated as protons. So sulphate ions cannot donate protons.
Now, when the ion is reacted with strong acid, it will give sulphuric acid and water.
$S{O_4}^ - + 2{H_3}{O^ + } \to {H_2}S{O_4} + 2{H_2}O$
From this reaction we can observe that the acetate ion can accept a proton. So acetate ion is not an amphiprotic ion since it can only accept a proton.
Bicarbonate ion: \[{\text{HC}}{{\text{O}}_3}^{\text{ - }}\] The structure of the ion is as follows:

From the structure it is observed that the hydrogen is attached to the oxygen atom which makes the hydrogen atom acidic. This means that it can lose a proton. The reaction will be as follows:
$HC{O_3}^ - \to C{O_3}^{2 - } + {H^ + }$
The bicarbonate ion can lose the proton and form carbonate ions. Now when the bicarbonate ion is reacted with strong acid it will produce carbonic acid and water.
$HC{O_3}^ - + {H_3}{O^ + } \to {H_2}C{O_3} + {H_2}O$
From this reaction we can see that bicarbonate ions can accept a proton as well. So bicarbonate ions are amphiprotic ions.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: When an ion accepts a proton then it behaves as a base and when it donates a proton then it behaves as an acid. Conjugate base of strong acid is weak while the conjugate base of weak acid is strong in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




