
Which of the following is/are contact forces
A. Normal force
B. Tension force
C. Friction force
D. All
Answer
605.7k+ views
Hint: In this question we need to start by understanding the meaning of contact. A contact force is a force that happens when there is contact. Then we see what are the examples of different contact forces that are present, these are externally applied force, frictional force, spring force, air resistance, and tension force. So all the three options are correct.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
There are two types of forces: contact forces and non-contact forces. A contact force is a force that happens when there is contact. Contact forces are present everywhere and are the cause of most of the visible interactions between different objects and surfaces. Some of the day to day examples where contact force comes into picture is hitting a ball with a cricket bat or pulling a trolley up a hill. In the first scenario, force is delivered in a short impulse, whereas in the second scenario the force is continuously applied by the person on the trolley for pulling it.
Contact forces are usually divided into orthogonal components, one that is parallel to the surface in contact, which is known as friction, and one that is perpendicular to the surface in contact, known as a normal force. These things can be clearly seen in figure 1.
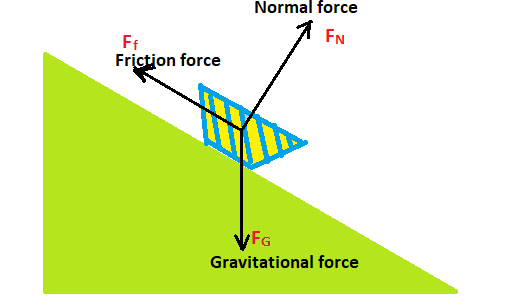
Figure 1
The following are the examples of contact forces that are externally applied force, friction, spring force, air resistance, and tension force. So option D is correct.
A non-contact force is a force that acts on a body without getting in contact with it. Examples of non contact forces are Gravitational force, Electromagnetic force, and nuclear forces both strong and weak.
Note: For these types of questions we need to remember different types of forces that are contact and noncontact forces. A contact force is a force that happens when there is contact. Whereas a non-contact force is a force that acts on a body without getting in contact with it. Then we need to know in which category different forces are gravitational force, electromagnetic force, nuclear force, externally applied force, frictional force, spring force, air resistance, and tension force lies.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
There are two types of forces: contact forces and non-contact forces. A contact force is a force that happens when there is contact. Contact forces are present everywhere and are the cause of most of the visible interactions between different objects and surfaces. Some of the day to day examples where contact force comes into picture is hitting a ball with a cricket bat or pulling a trolley up a hill. In the first scenario, force is delivered in a short impulse, whereas in the second scenario the force is continuously applied by the person on the trolley for pulling it.
Contact forces are usually divided into orthogonal components, one that is parallel to the surface in contact, which is known as friction, and one that is perpendicular to the surface in contact, known as a normal force. These things can be clearly seen in figure 1.

Figure 1
The following are the examples of contact forces that are externally applied force, friction, spring force, air resistance, and tension force. So option D is correct.
A non-contact force is a force that acts on a body without getting in contact with it. Examples of non contact forces are Gravitational force, Electromagnetic force, and nuclear forces both strong and weak.
Note: For these types of questions we need to remember different types of forces that are contact and noncontact forces. A contact force is a force that happens when there is contact. Whereas a non-contact force is a force that acts on a body without getting in contact with it. Then we need to know in which category different forces are gravitational force, electromagnetic force, nuclear force, externally applied force, frictional force, spring force, air resistance, and tension force lies.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




