
Which of the following pairs of d-orbitals will have electron density along the axis.
A. ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$
B. ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xy}}}},{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$
C. ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}{\text{,}}\,{{\text{d}}_{xz}}$
D. ${{\text{d}}_{xz}},{{\text{d}}_{yz}}$
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: The ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ and ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ orbitals which lies on the axis and the ${{\text{d}}_{xz}}$,${{\text{d}}_{yz}}$, and ${{\text{d}}_{xy}}$ lies in between the axis. Total five orbitals are present in the d - orbitals.
Complete step by step answer:
The position of electron density depends upon the position of the orbitals.
The d-orbital is a set of five denigrate orbitals named as ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{xz}}$,${{\text{d}}_{yz}}$, and ${{\text{d}}_{xy}}$.
The positions of these five d-orbitals on the axis is represented as follows:
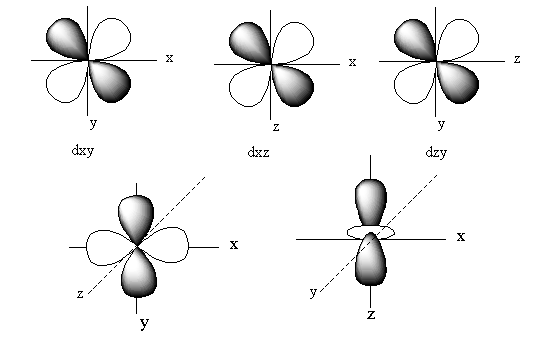
The orbitals of ${{\text{d}}_{xy}}$ lie in between the x and y-axis. So, the electron density of the ${{\text{d}}_{xy}}$ lies in between the x and y-axis.
The orbitals of ${{\text{d}}_{yz}}$ lie in between the z and y-axis. So, the electron density of the ${{\text{d}}_{yz}}$ lies in between the z and y-axis.
The orbitals of ${{\text{d}}_{xz}}$ lie in between the x and z-axis. So, the electron density of the ${{\text{d}}_{xz}}$ lies in between the x and z-axis.
The orbital of ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$lies on the z-axis. So, the electron density of the ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$lies on the z-axis.
The orbitals of ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ lie on the x and y-axis. So, the electron density of the ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ lies on the x and y-axis.
So, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ pairs of d-orbitals will have electron density along the axis.
Therefore, option (A) ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ is correct.
Note: Out of five d-orbitals, two lie on the axis and three lie in between the axis. So, when ligands form a complex with the metal it affects the three orbitals differently and two orbitals differently, so the five d-orbitals break into two parts of three and two.
Complete step by step answer:
The position of electron density depends upon the position of the orbitals.
The d-orbital is a set of five denigrate orbitals named as ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{xz}}$,${{\text{d}}_{yz}}$, and ${{\text{d}}_{xy}}$.
The positions of these five d-orbitals on the axis is represented as follows:

The orbitals of ${{\text{d}}_{xy}}$ lie in between the x and y-axis. So, the electron density of the ${{\text{d}}_{xy}}$ lies in between the x and y-axis.
The orbitals of ${{\text{d}}_{yz}}$ lie in between the z and y-axis. So, the electron density of the ${{\text{d}}_{yz}}$ lies in between the z and y-axis.
The orbitals of ${{\text{d}}_{xz}}$ lie in between the x and z-axis. So, the electron density of the ${{\text{d}}_{xz}}$ lies in between the x and z-axis.
The orbital of ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$lies on the z-axis. So, the electron density of the ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$lies on the z-axis.
The orbitals of ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ lie on the x and y-axis. So, the electron density of the ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ lies on the x and y-axis.
So, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ pairs of d-orbitals will have electron density along the axis.
Therefore, option (A) ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}{\text{,}}{{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^2} - {{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ is correct.
Note: Out of five d-orbitals, two lie on the axis and three lie in between the axis. So, when ligands form a complex with the metal it affects the three orbitals differently and two orbitals differently, so the five d-orbitals break into two parts of three and two.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




