
Which of the following photosynthetic bacteria have both PS-I and PS-II?
(a) Purple sulphur bacteria
(b) Cyanobacteria
(c) Purple non-sulphur bacteria
(d) Green sulphur bacteria
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: Photosystem-II is related to the photolysis of water and non-cyclic photophosphorylation. This leads to the evolution of O2 gas inside the thylakoid. So, any organism which has photosystem-II will evolve oxygen.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Cyanobacteria are known as the first organism to release oxygen into the air i.e. they were the first organisms to perform oxygenic photosynthesis. This was possible because of the presence of photosystem-II in them along with photosystem-I. Water is oxidized on the inner side of the thylakoid membrane to supply electrons to PS-II to perform non-cyclic photophosphorylation. This also produces a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane which is necessary for the production of ATP. Oxygen is released in this reaction as a byproduct.
So, the correct answer is 'Cyanobacteria'.
Additional information: Let us learn more about photosystems: There are many pigments present in the chloroplasts of leaves such as chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-b, carotenoids, xanthophylls, etc. These pigments are responsible for trapping the energy from sunlight. These pigments are organized into a reaction centre and antennae within photosystem-I and photosystem-II.
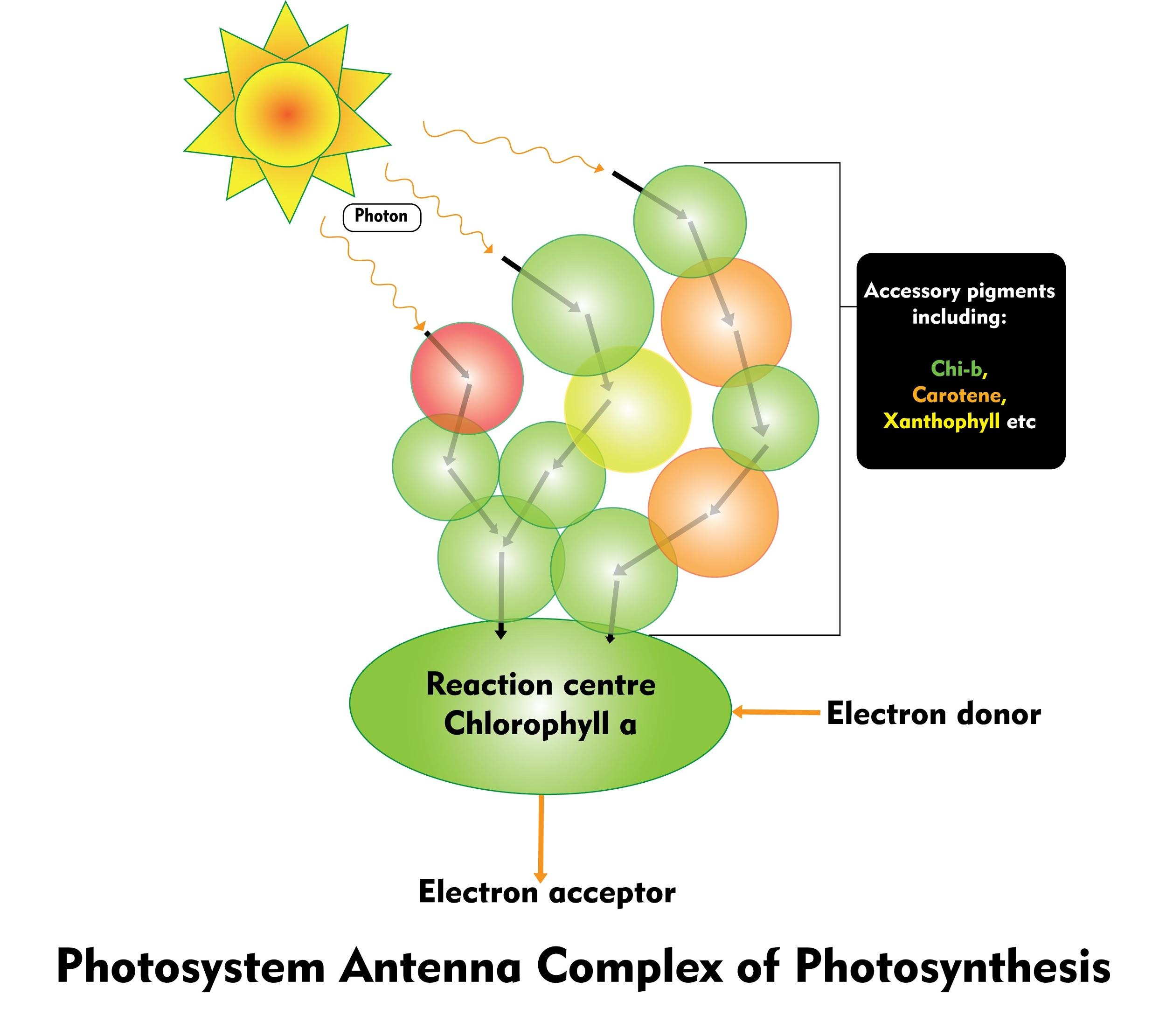
Antennae have all pigments in it except for chlorophyll-a and its function is to trap all energy from different wavelengths. The reaction centre has one molecule of chlorophyll a and receives energy trapped by antennae.
Note: In the reaction centre of photosystem-I, there is an absorption peak at 700nm of wavelength, hence it is known as P700. Whereas in photosystem-II there is a peak at 680nm hence known as P680.
Chlorophyll-b, carotenoids and xanthophylls are known as accessory pigments and their function is to trap energy from a wider wavelength and prevent photo-oxidation of chlorophyll-a.
Chlorophyll-a is blue-green, chlorophyll-b is yellow-green, xanthophylls are yellow and carotenoids are yellow-orange.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Cyanobacteria are known as the first organism to release oxygen into the air i.e. they were the first organisms to perform oxygenic photosynthesis. This was possible because of the presence of photosystem-II in them along with photosystem-I. Water is oxidized on the inner side of the thylakoid membrane to supply electrons to PS-II to perform non-cyclic photophosphorylation. This also produces a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane which is necessary for the production of ATP. Oxygen is released in this reaction as a byproduct.
So, the correct answer is 'Cyanobacteria'.
Additional information: Let us learn more about photosystems: There are many pigments present in the chloroplasts of leaves such as chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-b, carotenoids, xanthophylls, etc. These pigments are responsible for trapping the energy from sunlight. These pigments are organized into a reaction centre and antennae within photosystem-I and photosystem-II.

Antennae have all pigments in it except for chlorophyll-a and its function is to trap all energy from different wavelengths. The reaction centre has one molecule of chlorophyll a and receives energy trapped by antennae.
Note: In the reaction centre of photosystem-I, there is an absorption peak at 700nm of wavelength, hence it is known as P700. Whereas in photosystem-II there is a peak at 680nm hence known as P680.
Chlorophyll-b, carotenoids and xanthophylls are known as accessory pigments and their function is to trap energy from a wider wavelength and prevent photo-oxidation of chlorophyll-a.
Chlorophyll-a is blue-green, chlorophyll-b is yellow-green, xanthophylls are yellow and carotenoids are yellow-orange.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




