
Which of the following species can form hydrogen bonds with water?
A) $C{H_4}$
B) $HCOOH$
C) $N{a^ + }$
D) ${C_6}{H_6}$
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: We know that, Molecules in liquids are held together by intermolecular interactions, which are weaker than the intramolecular interactions that hold the atoms together within molecules and polyatomic ions. Higher the intermolecular forces are higher the melting and boiling point.
The three major types of intermolecular interactions are,
-Dipole-dipole interactions
-London dispersion forces
-Hydrogen bonds
Complete step by step solution:
Let us discuss the hydrogen bond in detail.
In a molecule, when an atom is linked to a highly electronegative atom, it attracts the shared pair of electrons more so it becomes a slightly negative end while the opposite end becomes slightly positive. The negative end of the molecule attracts the positive end of the opposite and as a result, a weak bond is made between them. This bond is named a hydrogen bond.
There are two types of the hydrogen bond. They are,
-Intermolecular hydrogen bond.
-Intramolecular Hydrogen bond.
At the point when formic corrosive is blended in with water, it structures hydrogen holding. H-molecule of \[{H_2}O\] bonds with \[COO - \] of \[HCOOH\] while Hydrogen-atom of \[HCOOH\] bonds with \[OH\] -of\[{H_2}O\]. Thus option B is correct. The given below image clearly shows how hydrogen bonding takes place in formic acid as,
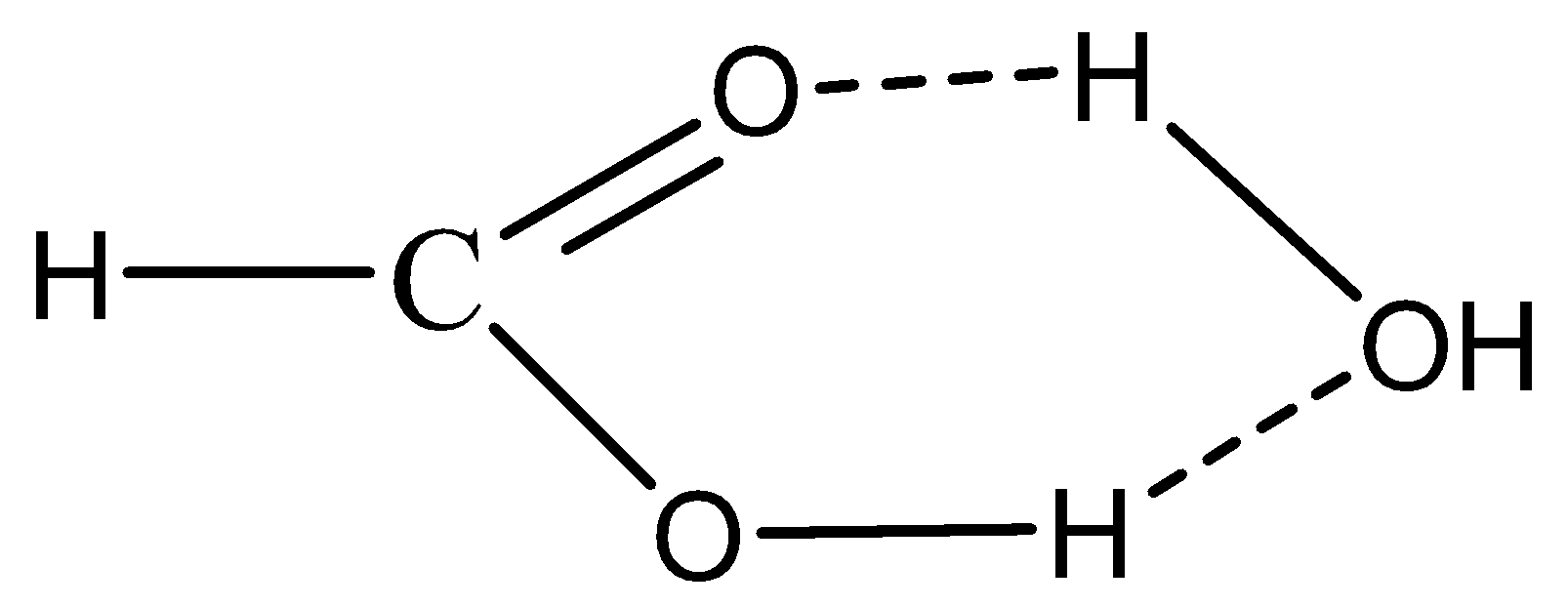
In case of option A methane, due to the absence of electronegative atoms there is no hydrogen bonding. Therefore, the option A is incorrect.
In case of option C, there is no electronegative species so the hydrogen bonding is absent. Therefore, the option C is incorrect.
In case of option D, due to the absence of electronegative atoms in benzene the hydrogen bonding nature is absent. Therefore, the option D is incorrect.
Therefore, the option B is correct.
Note:
Now we can discuss about how intermolecular hydrogen bonding and intramolecular hydrogen bonding differ from each other as,
-Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding:
If the hydrogen bond takes place between different molecules of the same or different compounds, it is called intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Example – hydrogen bonding in water.
-Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding:
If the hydrogen bonding takes place within a molecule itself is called intramolecular hydrogen bonding. It takes place in compounds containing two groups such that one group contains a hydrogen atom linked to an electronegative atom and the other group contains a highly electronegative atom linked to a lesser electronegative atom of the other group.
The three major types of intermolecular interactions are,
-Dipole-dipole interactions
-London dispersion forces
-Hydrogen bonds
Complete step by step solution:
Let us discuss the hydrogen bond in detail.
In a molecule, when an atom is linked to a highly electronegative atom, it attracts the shared pair of electrons more so it becomes a slightly negative end while the opposite end becomes slightly positive. The negative end of the molecule attracts the positive end of the opposite and as a result, a weak bond is made between them. This bond is named a hydrogen bond.
There are two types of the hydrogen bond. They are,
-Intermolecular hydrogen bond.
-Intramolecular Hydrogen bond.
At the point when formic corrosive is blended in with water, it structures hydrogen holding. H-molecule of \[{H_2}O\] bonds with \[COO - \] of \[HCOOH\] while Hydrogen-atom of \[HCOOH\] bonds with \[OH\] -of\[{H_2}O\]. Thus option B is correct. The given below image clearly shows how hydrogen bonding takes place in formic acid as,

In case of option A methane, due to the absence of electronegative atoms there is no hydrogen bonding. Therefore, the option A is incorrect.
In case of option C, there is no electronegative species so the hydrogen bonding is absent. Therefore, the option C is incorrect.
In case of option D, due to the absence of electronegative atoms in benzene the hydrogen bonding nature is absent. Therefore, the option D is incorrect.
Therefore, the option B is correct.
Note:
Now we can discuss about how intermolecular hydrogen bonding and intramolecular hydrogen bonding differ from each other as,
-Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding:
If the hydrogen bond takes place between different molecules of the same or different compounds, it is called intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Example – hydrogen bonding in water.
-Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding:
If the hydrogen bonding takes place within a molecule itself is called intramolecular hydrogen bonding. It takes place in compounds containing two groups such that one group contains a hydrogen atom linked to an electronegative atom and the other group contains a highly electronegative atom linked to a lesser electronegative atom of the other group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




