
Which of the following steps should be performed by a person in order to visualize the bands of DNA fragments obtained from gel electrophoresis?
(a). Exposure of DNA fragments to UV radiations
(b). Staining with bromophenol blue followed by exposure to UV radiations
(c). Staining with ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiations
(d). The person can see the bands without staining
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: It is a technique used to separate DNA fragments according to their size. DNA samples are loaded into wells (indentations) at one end of a gel, and an electrical current is applied to tug them through the gel. When a gel is stained with a DNA-binding dye, the DNA fragments are often seen as bands, each representing a gaggle of same-sized DNA fragments.
Complete answer:
Gel electrophoresis may be a technique to separate DNA fragments (or other macromolecules, like RNA and proteins) that support their size and charge. Electrophoresis includes running a current through a gel containing the atoms of interest. Based on their size and charge, the molecules will travel through the gel in several directions or at different speeds, allowing them to be separated from each other.
Ethidium bromide stains the DNA orange and helps in visualization upon exposure to UV radiation. EtBr gets intercalated between the base pairs helping in visualization.
Additional information:
All DNA molecules have an equivalent amount of charge per mass. Along these lines, gel electrophoresis of DNA sections isolates them upheld size as it were. Using electrophoresis, we will see what percentage of different DNA fragments are present during a sample and the way large they're relative to at least one another. We can also determine absolutely the size of a bit of DNA by examining it next to a typical "yardstick" made from DNA fragments of known sizes.
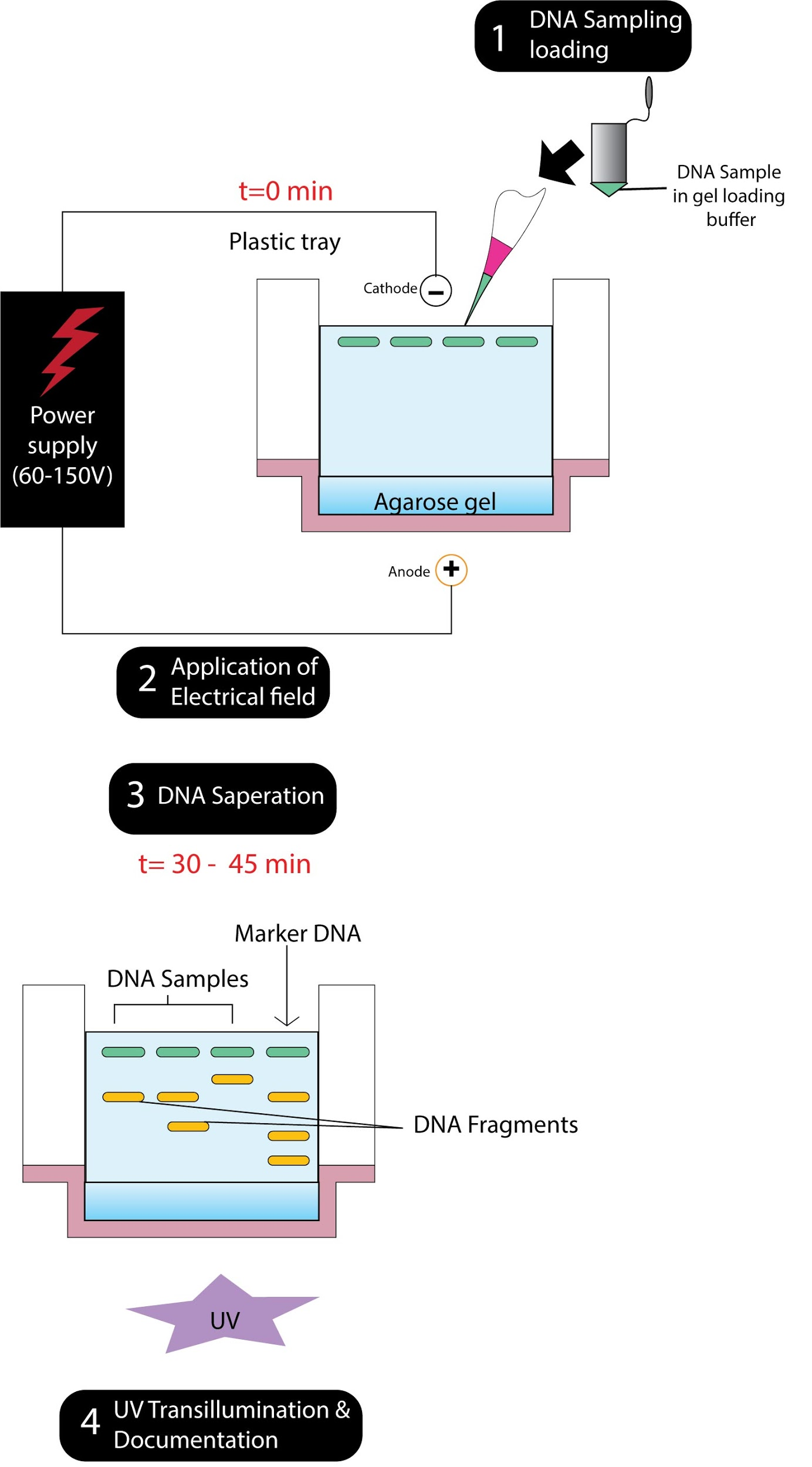
So the correct answer is ‘Staining with ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiations’.
Note: Gels for DNA separation are often made out of a polysaccharide called agarose, which comes as dry, powdered flakes. When the agarose is heated during a buffer (water with some salts in it) and allowed to chill, it'll form a solid, slightly squishy gel. At the molecular level, the gel is a matrix of agarose molecules that are held together by hydrogen bonds and from tiny pores.
Complete answer:
Gel electrophoresis may be a technique to separate DNA fragments (or other macromolecules, like RNA and proteins) that support their size and charge. Electrophoresis includes running a current through a gel containing the atoms of interest. Based on their size and charge, the molecules will travel through the gel in several directions or at different speeds, allowing them to be separated from each other.
Ethidium bromide stains the DNA orange and helps in visualization upon exposure to UV radiation. EtBr gets intercalated between the base pairs helping in visualization.
Additional information:
All DNA molecules have an equivalent amount of charge per mass. Along these lines, gel electrophoresis of DNA sections isolates them upheld size as it were. Using electrophoresis, we will see what percentage of different DNA fragments are present during a sample and the way large they're relative to at least one another. We can also determine absolutely the size of a bit of DNA by examining it next to a typical "yardstick" made from DNA fragments of known sizes.

So the correct answer is ‘Staining with ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiations’.
Note: Gels for DNA separation are often made out of a polysaccharide called agarose, which comes as dry, powdered flakes. When the agarose is heated during a buffer (water with some salts in it) and allowed to chill, it'll form a solid, slightly squishy gel. At the molecular level, the gel is a matrix of agarose molecules that are held together by hydrogen bonds and from tiny pores.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




