
Which of the following substances, if introduced into the bloodstream, would cause coagulation of blood at the site of its introduction-
(a) Thromboplastin
(b) Fibrinogen
(c) Heparin
(d) Prothrombin
Answer
540.9k+ views
Hint: The substance is made up of phospholipids and certain tissue factors, they also help in the clotting and coagulation of blood. It is an enzyme that converts inactive prothrombin to its active form called thrombin.
Complete answer:
Thromboplastin would cause coagulation of blood at the site of its introduction if introduced into the bloodstream because the whole reaction is dependent on thromboplastin, so it can cause coagulation of blood at the site of its introduction.
Clotting refers to the formation of a blood clump. Blood changes into a gel state from the liquid state. In response to an injury or trauma, blood exhibits clotting to prevent excessive loss of blood from the body. A clot (reddish-brown scum) is formed at the site of injury by a network of threads called fibrins. The fibrins are a result of the conversion of inactive fibrinogens in the plasma by the enzyme thrombin. Prothrombin (an inactive substance) present in plasma results in the formation of thrombin by an enzyme complex involving thromboplastin. The following mechanism is illustrated below:
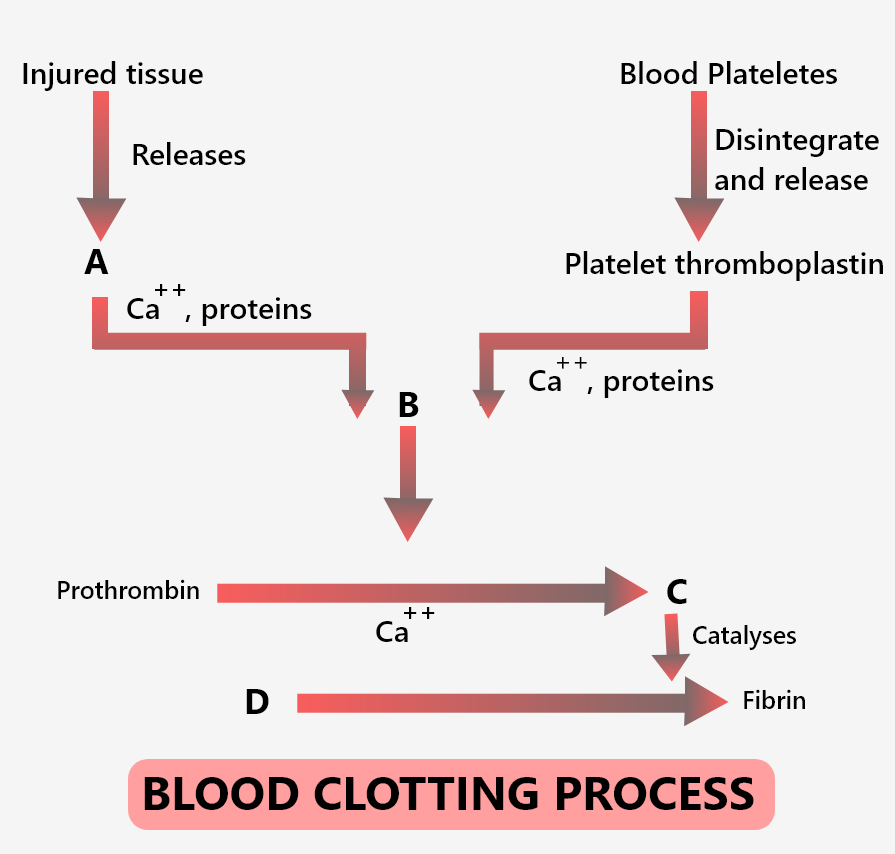
Heparin is a glycosaminoglycan that prevents the blood clot formation, hence known as an anticoagulant and used extensively during blood isolation experiments. Heparin works by blocking the action of thrombin and fibrin co-factors.
Thrombokinase is also known as thromboplastin. Blood vessels produce thrombokinase only when they face any injury.
So, the correct answer is 'Thromboplastin’.
Note:
- An injury stimulates platelets to release factors that activate the mechanism of clotting.
- Thromboplastin is also known as thrombokinase.
- Calcium ions are known to play a very important role in clotting.
Complete answer:
Thromboplastin would cause coagulation of blood at the site of its introduction if introduced into the bloodstream because the whole reaction is dependent on thromboplastin, so it can cause coagulation of blood at the site of its introduction.
Clotting refers to the formation of a blood clump. Blood changes into a gel state from the liquid state. In response to an injury or trauma, blood exhibits clotting to prevent excessive loss of blood from the body. A clot (reddish-brown scum) is formed at the site of injury by a network of threads called fibrins. The fibrins are a result of the conversion of inactive fibrinogens in the plasma by the enzyme thrombin. Prothrombin (an inactive substance) present in plasma results in the formation of thrombin by an enzyme complex involving thromboplastin. The following mechanism is illustrated below:

Heparin is a glycosaminoglycan that prevents the blood clot formation, hence known as an anticoagulant and used extensively during blood isolation experiments. Heparin works by blocking the action of thrombin and fibrin co-factors.
Thrombokinase is also known as thromboplastin. Blood vessels produce thrombokinase only when they face any injury.
So, the correct answer is 'Thromboplastin’.
Note:
- An injury stimulates platelets to release factors that activate the mechanism of clotting.
- Thromboplastin is also known as thrombokinase.
- Calcium ions are known to play a very important role in clotting.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




