
Which of the following will have meso-isomer also?
A) 2- chlorobutane
B) 2- hydroxypropanoic acid
C) 2, 3- dichloropentane
D) 2-3- dichlorobutane
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The meso compound or meso isomers have two or more stereocenters. These stereocenters have the opposite stereochemistry which cancels out. The 2,3-dichlorobutane has two stereocenters and the plane of symmetry divides the molecules in equal halves such that both halves are mirror images of each other.
Complete step by step answer:
In stereochemistry, the meso compounds are the isomers which have multiple chiral centres. The mirror image of the compound is superimposed on its mirror image. The meso compounds are optically inactive even the compound have the stereocenters.
In general, the meso compound contains the two or more identically substituted stereocenters. The mesocompound has the internal plane of symmetry. It divides the compound in equal halve such that the one half is a mirror image of the other.
Here, the stereochemistry cancels out at the stereocenters. The meso compounds are optically inactive compounds.
The meso compound is identified as follows,
1) Let A be the meso compound. It must have two or more stereocenters, an internal plane. First look at the internal plane within the compound.
2) Find out the stereochemistry (R and S configuration) of the compound concerning the stereocenters.
3) If the compound has R and S configuration at the neighbouring stereocenters, which cancels out are the meso compounds.
Let us have a look at the given compound in the question.
A) 2-Chlorobutane:
The compound is as follows:
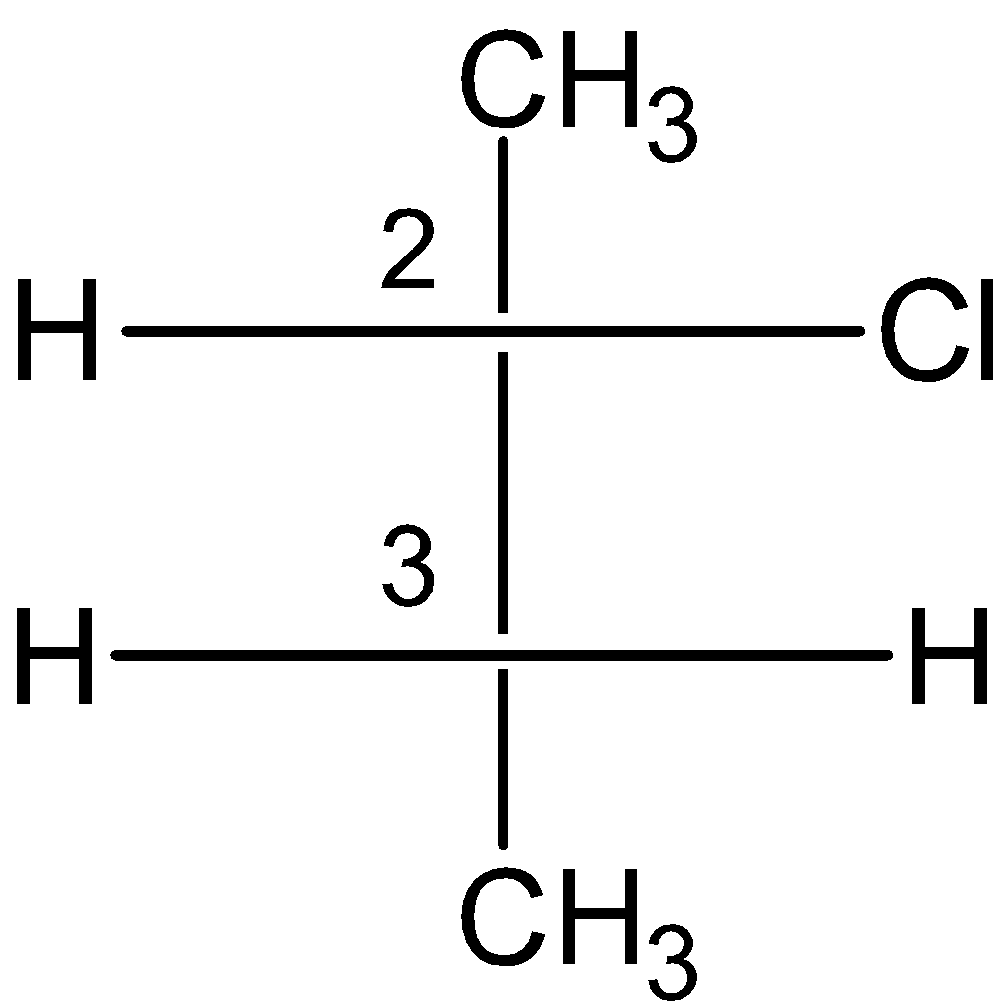
The compound does not possess the internal plane of symmetry. Since the chlorine at the 2 number carbon restricts the formation of the meso compound.
B) 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid:
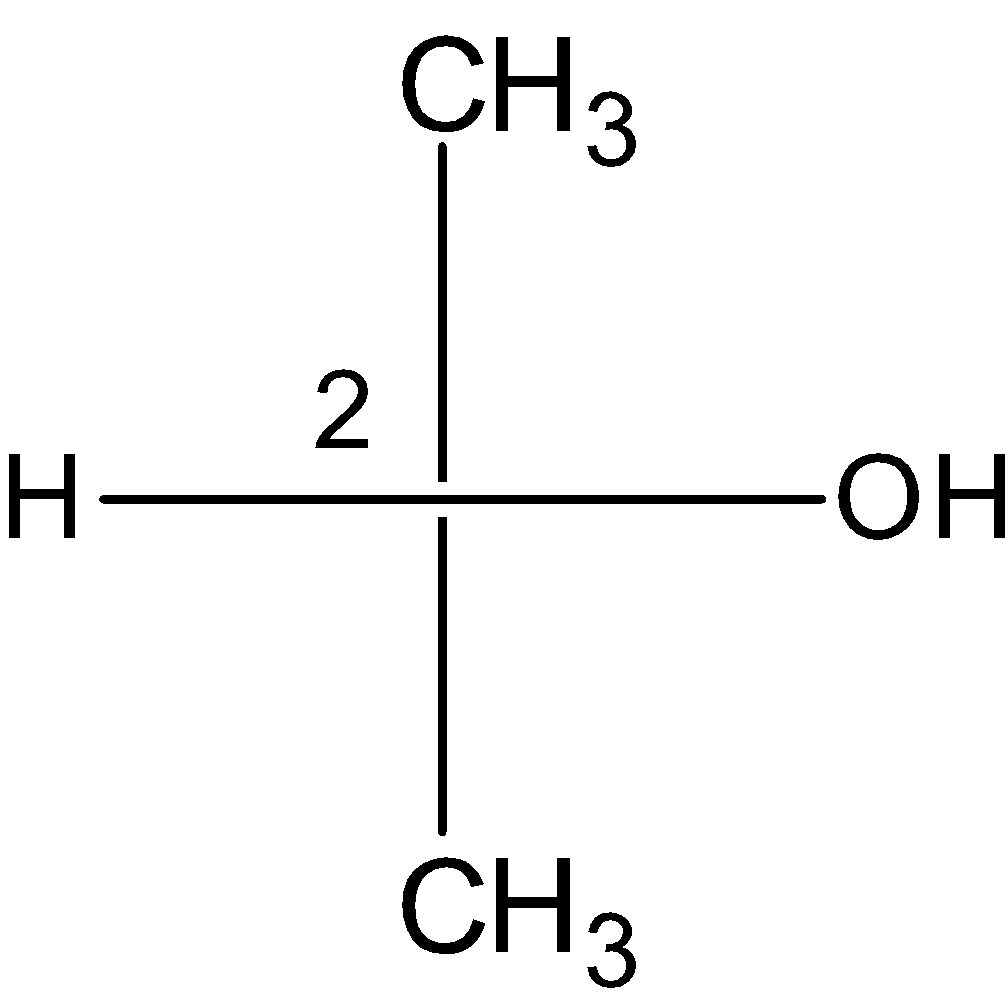
The compound contains an achiral centre at the ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}$ carbon. The compound does not contain the two or more stereocenters and therefore, the 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid is not a meso compound.
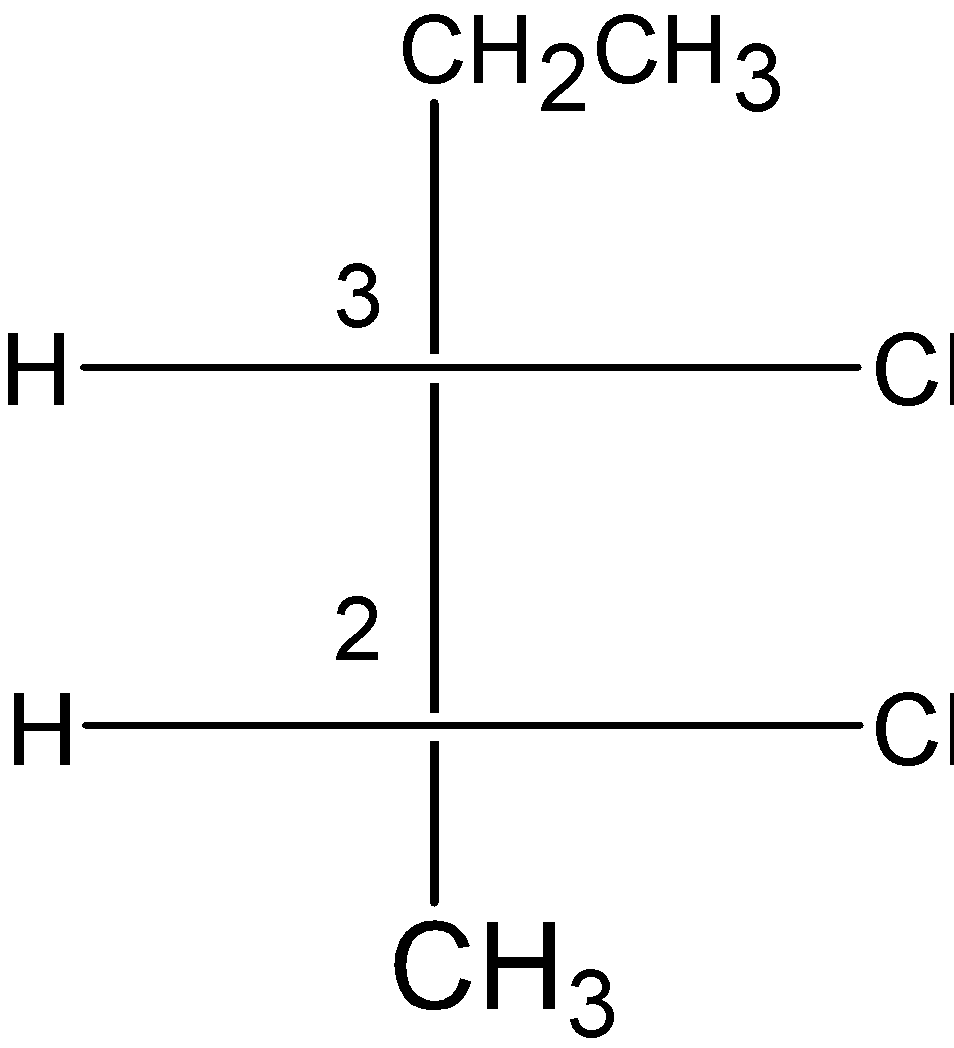
C) 2,3-dichloropentane :
2, 3-dichlorobenzene contains the two stereocenters at \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] and \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\]a carbon atom. The compound has an S configuration at the \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] carbon and R configuration at the \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\] carbon atom. But, the compound does not possess the internal plane of symmetry. As the compound have the methyl and ethyl group at the \[{{\text{C}}_{1}}\] and \[{{\text{C}}_{4}}\] carbon atoms. Therefore, 2, 3-dichloropentane is not a meso compound.
D) 2, 2-dichlorobutane:
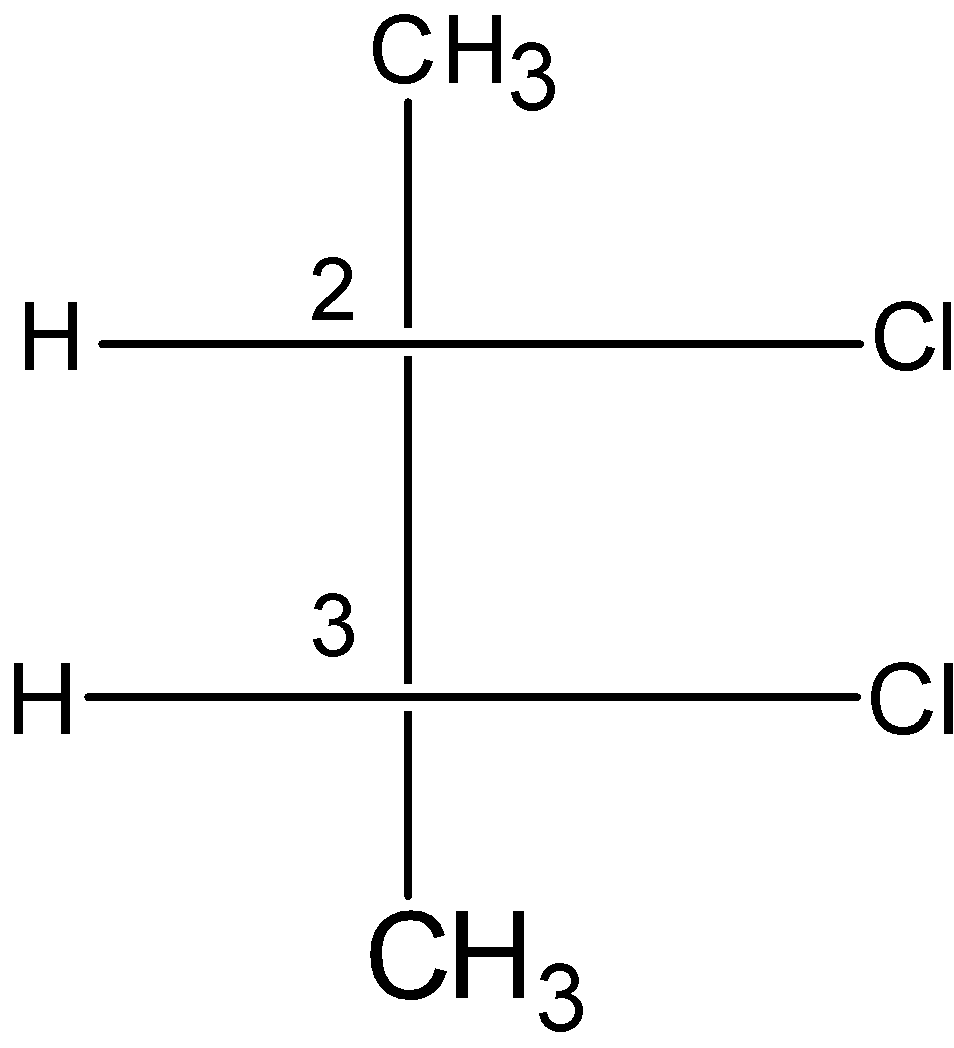
The dichlorobutane has two stereocenters at the \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] and \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\] carbon atom. Each stereocenter is attached to one chloro, one methyl, and a hydrogen atom. Let us have a look at the configuration at the stereocenters.

The \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] carbon has the stereochemistry of S and the \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\] carbon have the S configuration. The R and S configuration at the \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] and \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\] carbon cancel out the stereochemistry at the stereocenters.
The compound also contains the internal plane of symmetry passes through the \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] and \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\] bond, which divides the compound into two halves.

Therefore, the 2, 2-dichlorobutane is a meso compound or meso isomer.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The meso compound is the optically inactive compound. They have the stereocenters with opposite stereochemical configuration. When the meso compound is analysed through the polarimeter, the indicator does not show the $(+)\text{ or (}-)$ , it means that the compound cannot rotate the plane polarised light. Some of the examples of meso compounds are, 2, 3-dibromobutane.
Complete step by step answer:
In stereochemistry, the meso compounds are the isomers which have multiple chiral centres. The mirror image of the compound is superimposed on its mirror image. The meso compounds are optically inactive even the compound have the stereocenters.
In general, the meso compound contains the two or more identically substituted stereocenters. The mesocompound has the internal plane of symmetry. It divides the compound in equal halve such that the one half is a mirror image of the other.
Here, the stereochemistry cancels out at the stereocenters. The meso compounds are optically inactive compounds.
The meso compound is identified as follows,
1) Let A be the meso compound. It must have two or more stereocenters, an internal plane. First look at the internal plane within the compound.
2) Find out the stereochemistry (R and S configuration) of the compound concerning the stereocenters.
3) If the compound has R and S configuration at the neighbouring stereocenters, which cancels out are the meso compounds.
Let us have a look at the given compound in the question.
A) 2-Chlorobutane:
The compound is as follows:
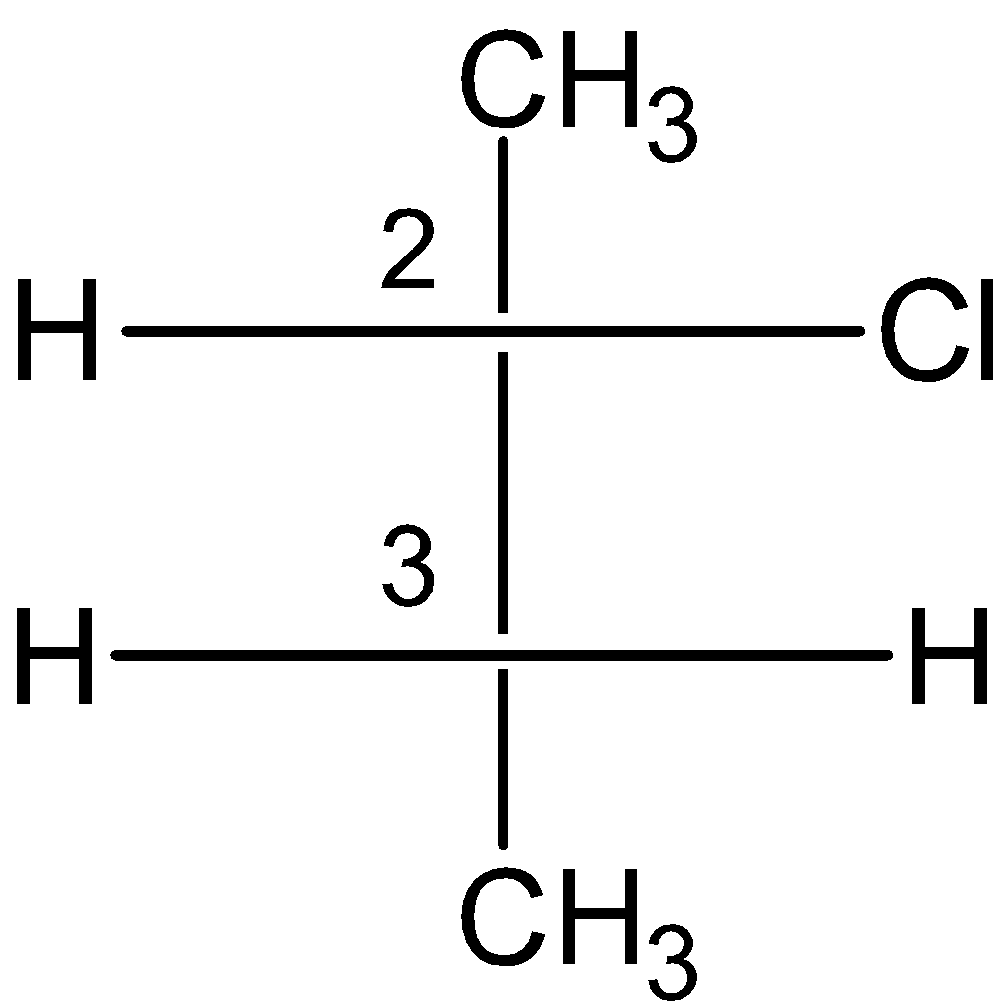
The compound does not possess the internal plane of symmetry. Since the chlorine at the 2 number carbon restricts the formation of the meso compound.
B) 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid:
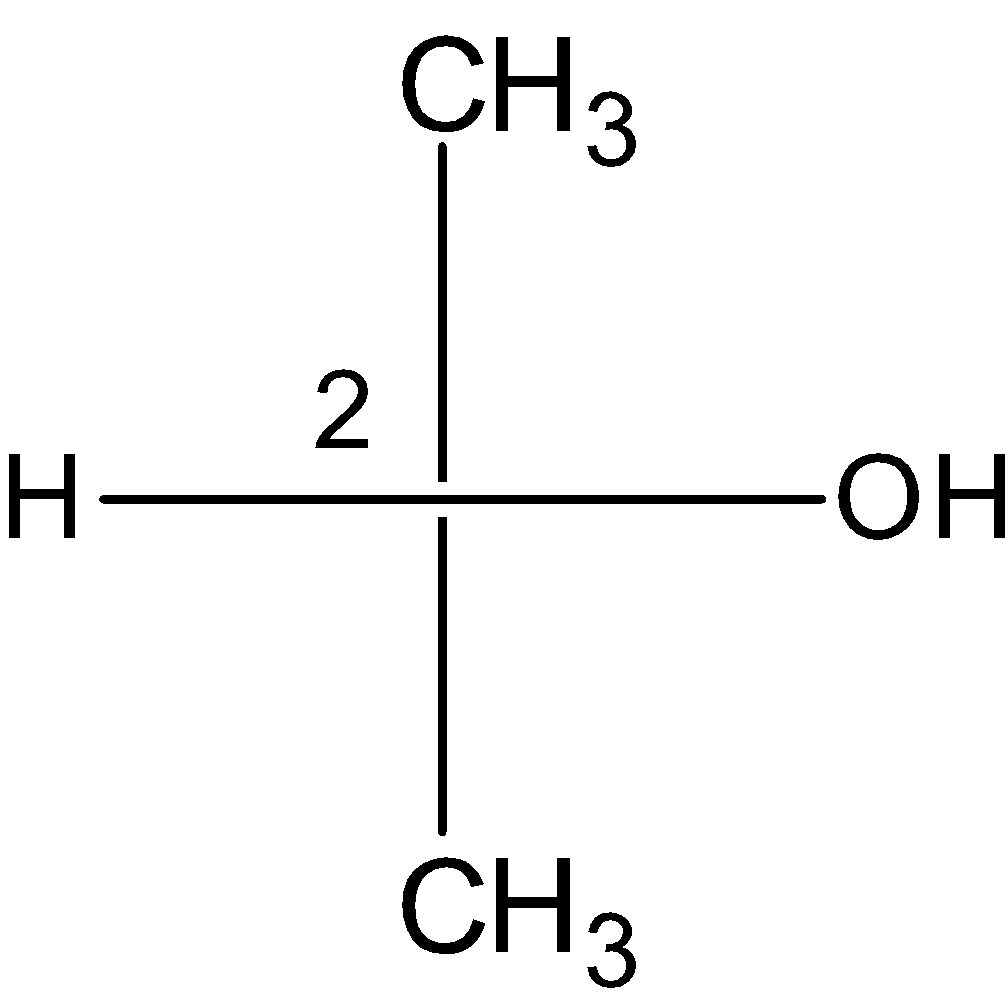
The compound contains an achiral centre at the ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}$ carbon. The compound does not contain the two or more stereocenters and therefore, the 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid is not a meso compound.
C) 2,3-dichloropentane :
2, 3-dichlorobenzene contains the two stereocenters at \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] and \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\]a carbon atom. The compound has an S configuration at the \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] carbon and R configuration at the \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\] carbon atom. But, the compound does not possess the internal plane of symmetry. As the compound have the methyl and ethyl group at the \[{{\text{C}}_{1}}\] and \[{{\text{C}}_{4}}\] carbon atoms. Therefore, 2, 3-dichloropentane is not a meso compound.

D) 2, 2-dichlorobutane:
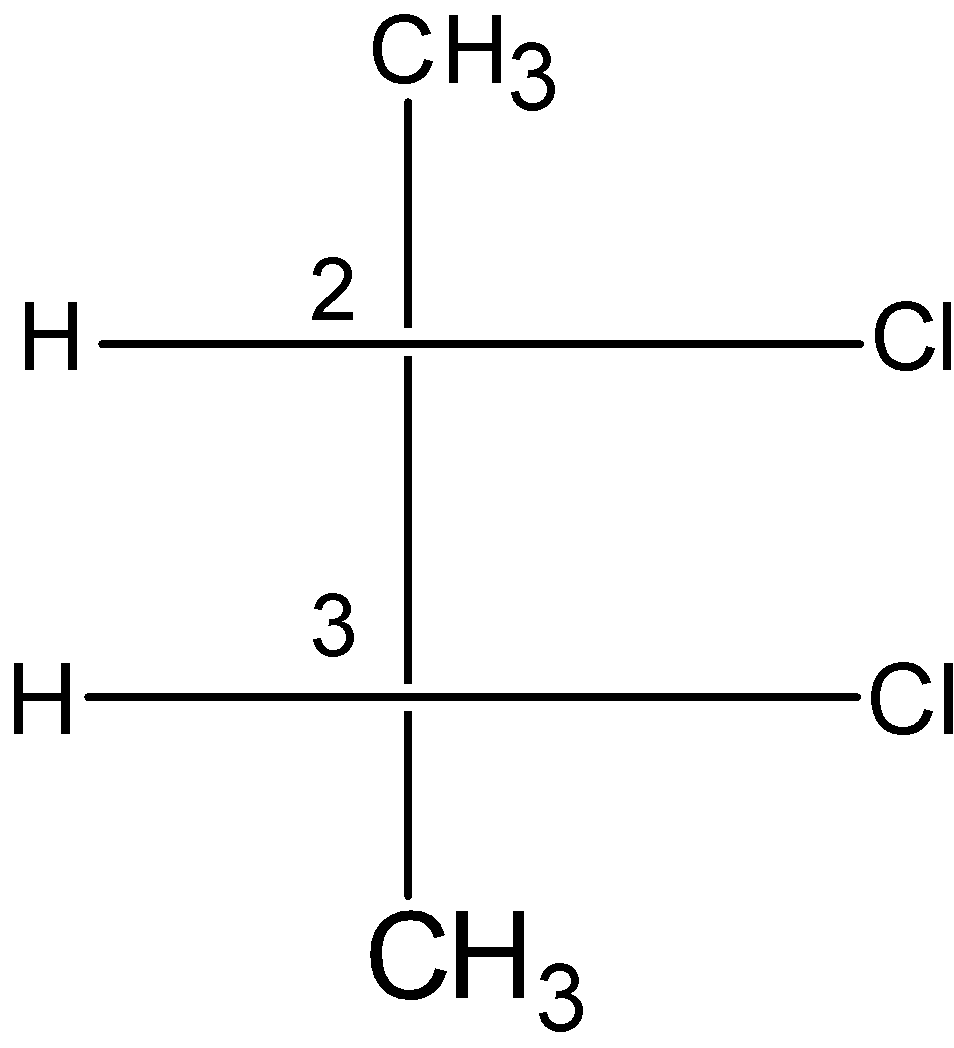
The dichlorobutane has two stereocenters at the \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] and \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\] carbon atom. Each stereocenter is attached to one chloro, one methyl, and a hydrogen atom. Let us have a look at the configuration at the stereocenters.

The \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] carbon has the stereochemistry of S and the \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\] carbon have the S configuration. The R and S configuration at the \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] and \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\] carbon cancel out the stereochemistry at the stereocenters.
The compound also contains the internal plane of symmetry passes through the \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}\] and \[{{\text{C}}_{3}}\] bond, which divides the compound into two halves.

Therefore, the 2, 2-dichlorobutane is a meso compound or meso isomer.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The meso compound is the optically inactive compound. They have the stereocenters with opposite stereochemical configuration. When the meso compound is analysed through the polarimeter, the indicator does not show the $(+)\text{ or (}-)$ , it means that the compound cannot rotate the plane polarised light. Some of the examples of meso compounds are, 2, 3-dibromobutane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




