
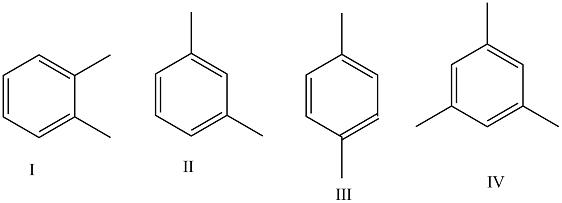
Which of the given structures corresponds to p-xylene?
A.I
B.II
C.III
D.IV

Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint:As we are aware that the p- stands for para-, P-xylene is a xylene with methyl groups occupying the diametrically opposite substituent positions, i.e. positions 1 and 4. The chemical formula of p-xylene is C6H4(CH3)2.
Complete answer:
p-xylene or para-xylene is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene which is known collectively as xylenes. The p- stands for para-, which indicates that the two methyl groups are present in p-xylene and occupy the diametrically opposite substituent positions i.e. 1 and 4. It is in the positions of the two methyl groups, their arene substitution pattern, that it differs from the other isomers, o-xylene and m-xylene. All have the same chemical formula \[{C_6}{H_4}{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}\]
The structure I use corresponds to o-xylene. O-xylene is 1,2-dimethylBenzene.
The structure II corresponds to m-xylene (1,3-dimethylBenzene).
The structure III corresponds to p-xylene (1,4-dimethylbenzene).
The structure IV corresponds to mesitylene (1,3,5-trimethylbenzene).
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note:
P-xylene is a colorless watery liquid with a sweet odor. It is less dense than water and it is also insoluble in water but very soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether. It is irritating vapor. Its freezing point is 55.8°F and its Boiling point is 281.03 °F and is highly flammable. The odor threshold of p-xylene is 0.62 parts per million (ppm). The commercial or mixed xylene usually contains about 40-65% m-xylene and up to 20% each of o-xylene and p-xylene and ethylbenzene. Xylenes are released into the atmosphere as fugitive emissions from industrial sources, from the auto exhaust, and through volatilization from their use as solvents. The short-term inhalation exposure to mixed xylenes in humans can cause irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, gastrointestinal effects, eye irritation, and neurological effects.
Complete answer:
p-xylene or para-xylene is an aromatic hydrocarbon. It is one of the three isomers of dimethylbenzene which is known collectively as xylenes. The p- stands for para-, which indicates that the two methyl groups are present in p-xylene and occupy the diametrically opposite substituent positions i.e. 1 and 4. It is in the positions of the two methyl groups, their arene substitution pattern, that it differs from the other isomers, o-xylene and m-xylene. All have the same chemical formula \[{C_6}{H_4}{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}\]
The structure I use corresponds to o-xylene. O-xylene is 1,2-dimethylBenzene.
The structure II corresponds to m-xylene (1,3-dimethylBenzene).
The structure III corresponds to p-xylene (1,4-dimethylbenzene).
The structure IV corresponds to mesitylene (1,3,5-trimethylbenzene).
Therefore, the correct answer is option (C).
Note:
P-xylene is a colorless watery liquid with a sweet odor. It is less dense than water and it is also insoluble in water but very soluble in ethanol and diethyl ether. It is irritating vapor. Its freezing point is 55.8°F and its Boiling point is 281.03 °F and is highly flammable. The odor threshold of p-xylene is 0.62 parts per million (ppm). The commercial or mixed xylene usually contains about 40-65% m-xylene and up to 20% each of o-xylene and p-xylene and ethylbenzene. Xylenes are released into the atmosphere as fugitive emissions from industrial sources, from the auto exhaust, and through volatilization from their use as solvents. The short-term inhalation exposure to mixed xylenes in humans can cause irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, gastrointestinal effects, eye irritation, and neurological effects.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




