
Which one is glucose?
(A) ${ C }_{ 3 }{ H }_{ 8 }{ O }_{ 3 }$
(B) ${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$
(C) ${ C }_{ 55 }{ H }_{ 70 }{ O }_{ 6 }$
(D) ${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 10 }{ O }_{ 6 }$
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: Glucose is a carbohydrate, which further in carbohydrates, comes under the class monosaccharide which means simple sugars and comes under the aldose group. Carbohydrate has the general formula as ${ C }_{ n }{ H }_{ 2n }{ O }_{ }$.
Complete step by step answer:
Monosaccharides are also known as simple sugars, and the most common of which is glucose whose formula is ${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$. In monosaccharides, the number of carbons usually ranges from 3 to 7. Most monosaccharide names end with the suffix –ose. If the sugar has an aldehyde group, it is known as an aldose, and if it has a ketone group, it is known as a ketose. The ratio of the number of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen in carbohydrate molecules. is 1:2:1. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate”: the components are carbon and also the water.
So, the correct answer is ‘${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$ ’.
Additional Information: Carbohydrates are classified into three categories, which are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
- Monosaccharides: Monosaccharides are simple sugars and cannot be broken down into a simpler form. Examples include glucose, fructose, etc.
- Disaccharides: Disaccharides form when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction. During this process, the hydroxyl of one monosaccharide combines with the hydrogen of another monosaccharide, releasing a molecule of water and forming a covalent bond. A bond formed between a carbohydrate molecule and another molecule is called a glycosidic bond. Common examples are lactose, maltose, and sucrose.
- Polysaccharides: A long chain of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds is called a polysaccharide. The chain may be branched or unbranched, and it either contains the same type of monosaccharides or may contain different types of monosaccharides. Common examples are Amylose, Starch, etc.
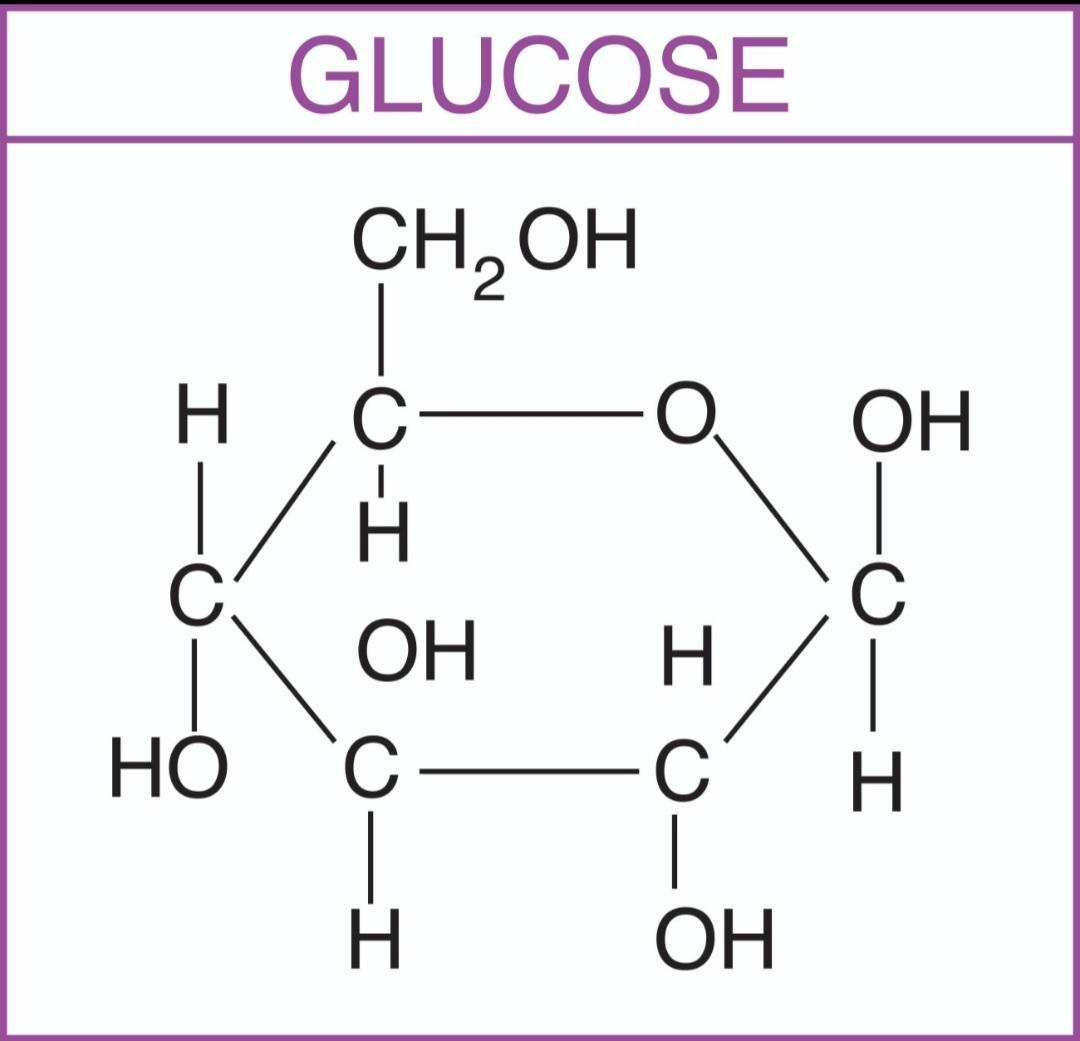
Note: Glucose in its ring form can have two different arrangements of the hydroxyl group (- OH) around the anomeric carbon. If the - OH is below carbon number one in the sugar, it's said to be in the alpha ($\alpha$) position, and if it's above the plane, it's said to be in the beta ($\beta$) position.
Complete step by step answer:
Monosaccharides are also known as simple sugars, and the most common of which is glucose whose formula is ${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$. In monosaccharides, the number of carbons usually ranges from 3 to 7. Most monosaccharide names end with the suffix –ose. If the sugar has an aldehyde group, it is known as an aldose, and if it has a ketone group, it is known as a ketose. The ratio of the number of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen in carbohydrate molecules. is 1:2:1. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate”: the components are carbon and also the water.
So, the correct answer is ‘${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$ ’.
Additional Information: Carbohydrates are classified into three categories, which are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
- Monosaccharides: Monosaccharides are simple sugars and cannot be broken down into a simpler form. Examples include glucose, fructose, etc.

- Disaccharides: Disaccharides form when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction. During this process, the hydroxyl of one monosaccharide combines with the hydrogen of another monosaccharide, releasing a molecule of water and forming a covalent bond. A bond formed between a carbohydrate molecule and another molecule is called a glycosidic bond. Common examples are lactose, maltose, and sucrose.
- Polysaccharides: A long chain of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds is called a polysaccharide. The chain may be branched or unbranched, and it either contains the same type of monosaccharides or may contain different types of monosaccharides. Common examples are Amylose, Starch, etc.
Note: Glucose in its ring form can have two different arrangements of the hydroxyl group (- OH) around the anomeric carbon. If the - OH is below carbon number one in the sugar, it's said to be in the alpha ($\alpha$) position, and if it's above the plane, it's said to be in the beta ($\beta$) position.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




