
Which one of the following is a ${{2}^{\circ }}$- allylic carbocation?
(A)- $\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{C{{H}_{2}}}}\,-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$
(B)- $C{{H}_{3}}-CH=CH-\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{C}}\,{{H}_{2}}$
(C)- ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-CH=\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{CH}}\,$
(D)- $C{{H}_{3}}-\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{C}}\,H-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: The degree of the carbocation is determined by the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the positively charged carbon. Also, the allylic carbon adjacent to the double-bonded carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly, the allylic carbon is the carbon atom adjacent to the double- bonded carbon atom. And the allylic carbocation is formed by the removal of a hydrogen atom from the allylic carbon.
Depending on the number of alkyl or aryl group attached to the allylic carbon of the carbocation, except for the C-C bond with the adjacent double bonded carbon, it can be divided into:
- Primary or ${{1}^{\circ }}$ allylic carbocation having a positive charge over the carbon having only two hydrogens attached to it. So, compound (A) and (B) are primary allylic carbocation.
- Secondary or ${{2}^{\circ }}$ allylic carbocation has positive charge over the carbon having one alkyl or aryl group and one hydrogen attached to it. So, the compound (D) having a positive charge over the secondary carbon is a ${{2}^{\circ }}$ allylic carbocation.
- Tertiary or ${{3}^{\circ }}$ allylic carbocation has positive charge over the carbon with two alkyl or aryl groups attached to it.
Therefore, the a ${{2}^{\circ }}$- allylic carbocation is option (D)- $C{{H}_{3}}-\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{C}}\,H-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$.
Additional information: There is a presence of the empty p-orbital on the $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised carbon atom, adjacent to the double-bonded carbon in allylic carbocation. Due to which resonance takes place and causes the stabilisation, as there is an increase in the dispersion of the positive charge over the structure.
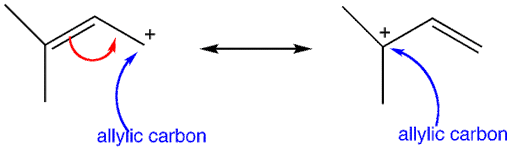
Note: The compound (C) having a positive charge directly over the double-bonded carbon atom, it is a vinylic carbocation. Also, the secondary allylic carbocation has only one alkyl and one hydrogen atom attached to it.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly, the allylic carbon is the carbon atom adjacent to the double- bonded carbon atom. And the allylic carbocation is formed by the removal of a hydrogen atom from the allylic carbon.
Depending on the number of alkyl or aryl group attached to the allylic carbon of the carbocation, except for the C-C bond with the adjacent double bonded carbon, it can be divided into:
- Primary or ${{1}^{\circ }}$ allylic carbocation having a positive charge over the carbon having only two hydrogens attached to it. So, compound (A) and (B) are primary allylic carbocation.
- Secondary or ${{2}^{\circ }}$ allylic carbocation has positive charge over the carbon having one alkyl or aryl group and one hydrogen attached to it. So, the compound (D) having a positive charge over the secondary carbon is a ${{2}^{\circ }}$ allylic carbocation.
- Tertiary or ${{3}^{\circ }}$ allylic carbocation has positive charge over the carbon with two alkyl or aryl groups attached to it.
Therefore, the a ${{2}^{\circ }}$- allylic carbocation is option (D)- $C{{H}_{3}}-\overset{\oplus }{\mathop{C}}\,H-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$.
Additional information: There is a presence of the empty p-orbital on the $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised carbon atom, adjacent to the double-bonded carbon in allylic carbocation. Due to which resonance takes place and causes the stabilisation, as there is an increase in the dispersion of the positive charge over the structure.

Note: The compound (C) having a positive charge directly over the double-bonded carbon atom, it is a vinylic carbocation. Also, the secondary allylic carbocation has only one alkyl and one hydrogen atom attached to it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




