
Which one of the following is a free radical substitution reaction?
A.
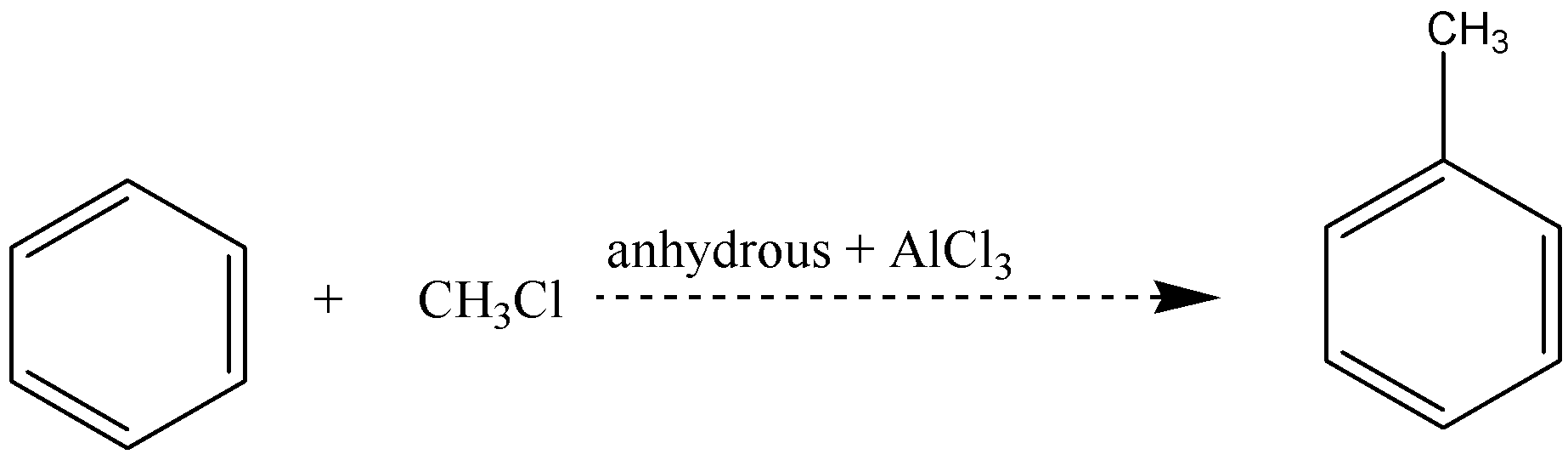
B.
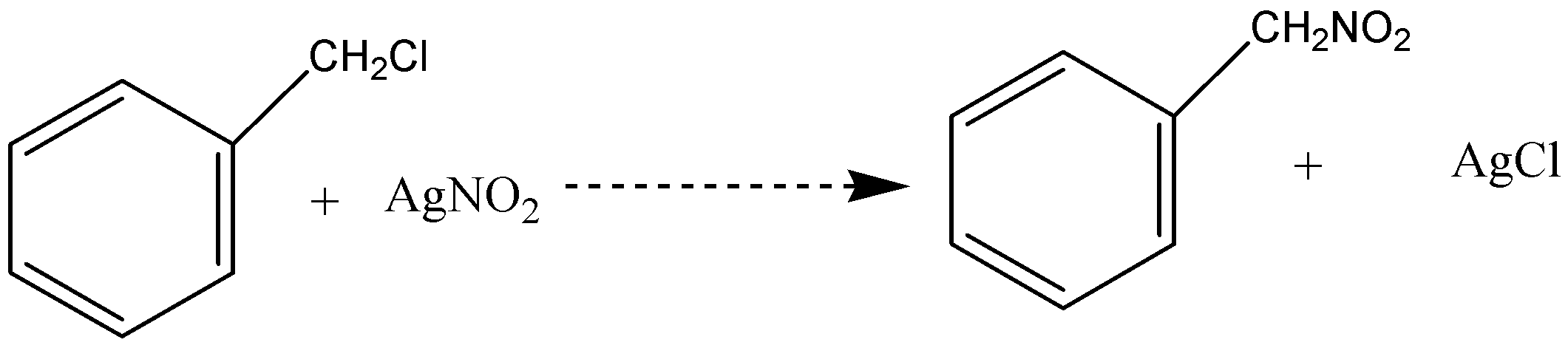
C.
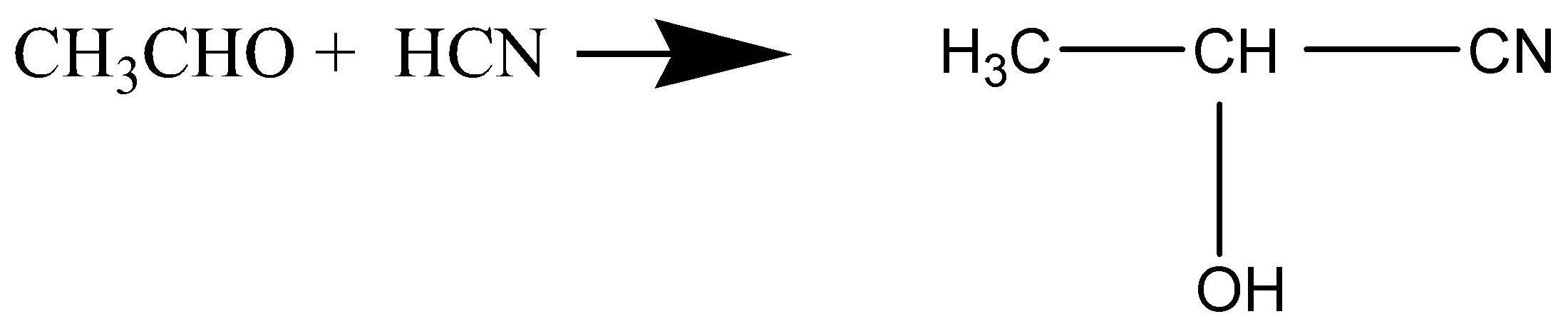
D.
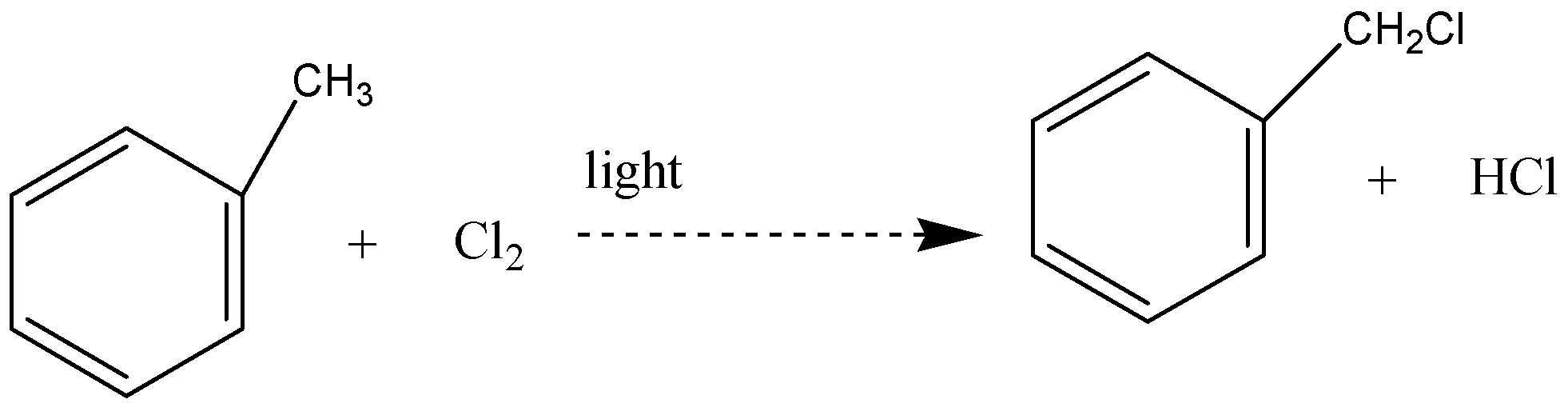




Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Free radical substitution reaction is the one that involves the radicals. Reaction of toluene with chlorine in presence of light is one of the examples of free radical substitution reaction. Hydrogen atoms from side chain get replaced by chlorine
Complete step by step answer:
Free radicals are atoms or groups of atoms that have a single unpaired electron and a free radical substitution reaction is the one involving these radicals. Free radicals are formed if a bond splits evenly - each atom getting one of the two electrons. The name given to this is homolytic fission.
To show that a species (either an atom or a group of atoms) is a free radical, the symbol is written with a dot attached to show the unpaired electron.
The reaction between methylbenzene and chlorine in the presence of light – typically sunlight is a free radical substitution reaction. The organic product is (chloromethyl) benzene. One of the atoms in the methyl group is replaced by a chlorine atom, so this is a substitution reaction. And all the three hydrogens in the methyl group can in turn be replaced by chlorine atoms.
Initiation Phase: This phase is initiation phase in which free radical specie is created
The chain is initiated by UV light breaking a Chlorine $(C{l_2})$ molecule into free radicals.
\[C{l_2}\xrightarrow[{sunlight}]{{energy}}2\mathop C\limits^. l\]
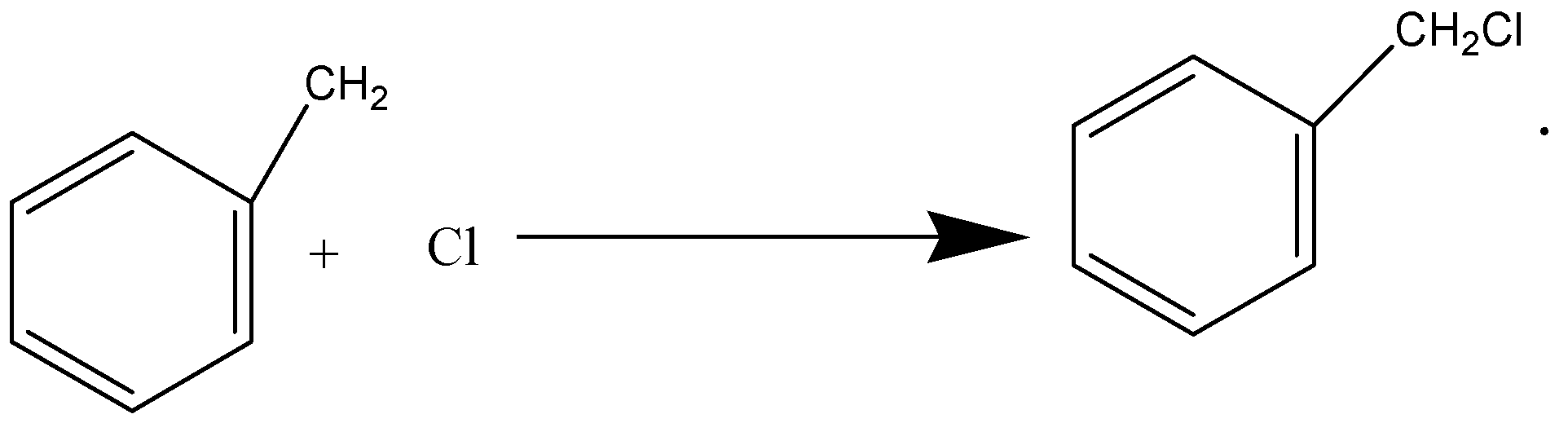
Propagation Phase:
In this, the reaction keeps the chain going
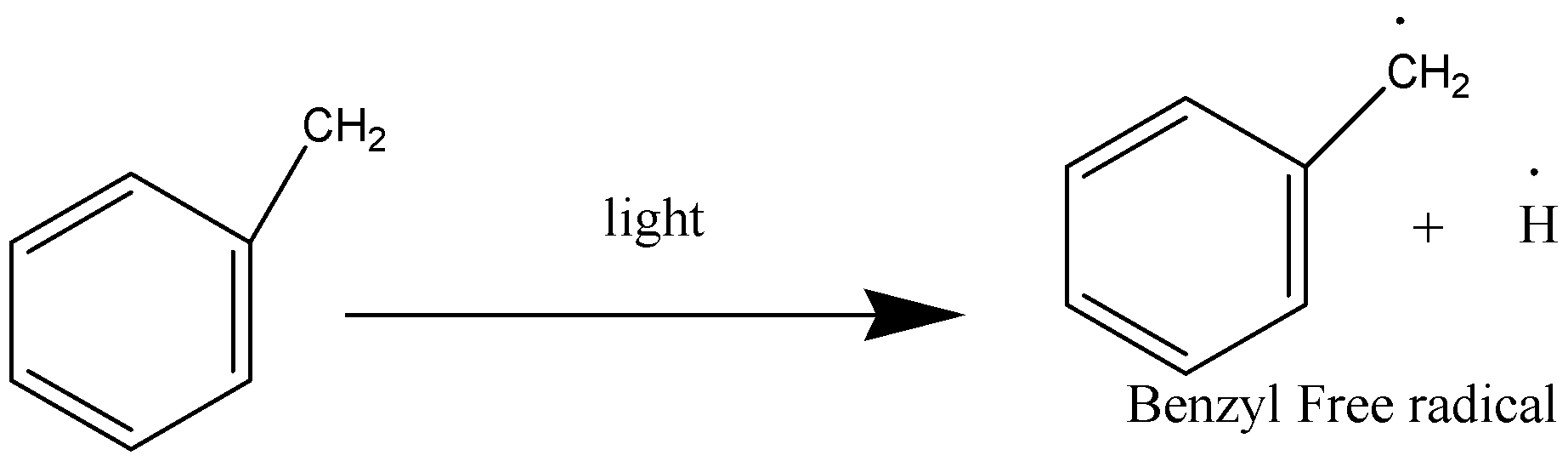
Termination Phase:
These are reactions which remove free radicals from the system without replacing them with new ones. If any two free radicals collide, they will join together without producing any new radicals.
In this reaction, hydrogen atoms from the side chain get replaced by chlorine. On monochlorination, benzyl chloride is formed on dichlorination benzal chloride
Whereas in option (A), when benzene reacts with $C{H_3}Cl$ in presence of anhydrous $AlC{l_3}$ to give Toluene, it is fried crafts alkylation and electrophilic substitution. In option (C), when acetaldehyde reacts with hydrogen cyanide, nucleophilic attack takes place by cyanide ion to give 2-hydroxypropanenitrile as a product.
So, the correct answer is option (D).
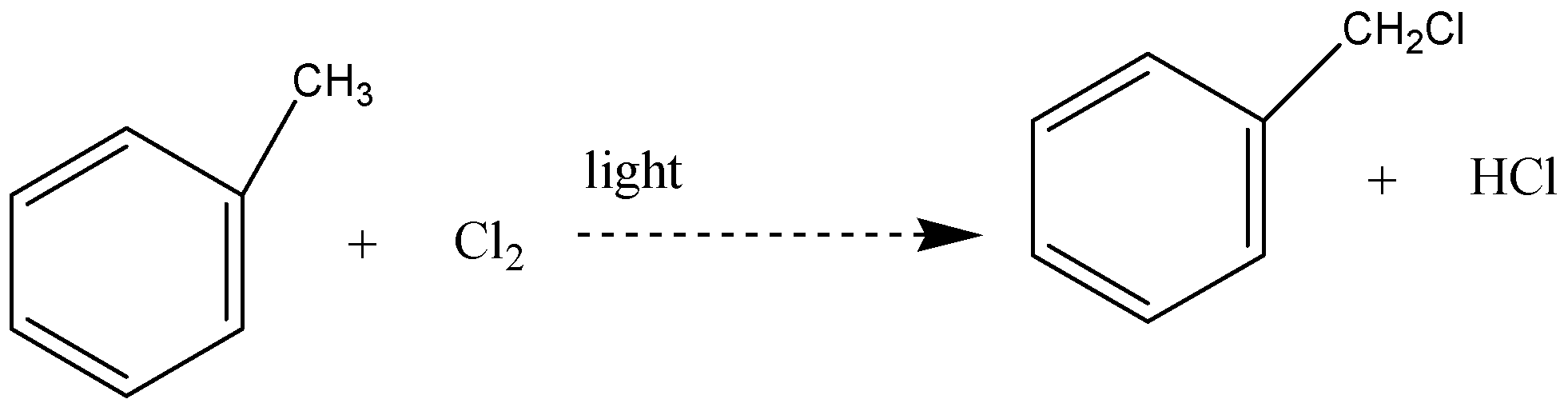
Note: Free radicals have the potential to be both extremely powerful chemical tools and extremely harmful contaminants due to their high reactivity. Most of the power of free radical species stems from the natural tendency of radical processes to occur in a chain reaction fashion Radical chain reaction has three different phases that are initiation, propagation and termination.
Complete step by step answer:
Free radicals are atoms or groups of atoms that have a single unpaired electron and a free radical substitution reaction is the one involving these radicals. Free radicals are formed if a bond splits evenly - each atom getting one of the two electrons. The name given to this is homolytic fission.
To show that a species (either an atom or a group of atoms) is a free radical, the symbol is written with a dot attached to show the unpaired electron.
The reaction between methylbenzene and chlorine in the presence of light – typically sunlight is a free radical substitution reaction. The organic product is (chloromethyl) benzene. One of the atoms in the methyl group is replaced by a chlorine atom, so this is a substitution reaction. And all the three hydrogens in the methyl group can in turn be replaced by chlorine atoms.
Initiation Phase: This phase is initiation phase in which free radical specie is created
The chain is initiated by UV light breaking a Chlorine $(C{l_2})$ molecule into free radicals.
\[C{l_2}\xrightarrow[{sunlight}]{{energy}}2\mathop C\limits^. l\]
Propagation Phase:
In this, the reaction keeps the chain going

Termination Phase:
These are reactions which remove free radicals from the system without replacing them with new ones. If any two free radicals collide, they will join together without producing any new radicals.
In this reaction, hydrogen atoms from the side chain get replaced by chlorine. On monochlorination, benzyl chloride is formed on dichlorination benzal chloride

Whereas in option (A), when benzene reacts with $C{H_3}Cl$ in presence of anhydrous $AlC{l_3}$ to give Toluene, it is fried crafts alkylation and electrophilic substitution. In option (C), when acetaldehyde reacts with hydrogen cyanide, nucleophilic attack takes place by cyanide ion to give 2-hydroxypropanenitrile as a product.
So, the correct answer is option (D).

Note: Free radicals have the potential to be both extremely powerful chemical tools and extremely harmful contaminants due to their high reactivity. Most of the power of free radical species stems from the natural tendency of radical processes to occur in a chain reaction fashion Radical chain reaction has three different phases that are initiation, propagation and termination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




