
Which one of the following is an example of the taproot system?
(a) Wheat
(b) Mustard
(c) Millet
(d) Maize
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: The plant which is an example of the taproot system also shows alternate phyllotaxy in its leave’s arrangement. The flower of this plant is actinomorphic i.e. it can be divided into two equal radial halves in any radial plane passing through the center.
Complete answer:
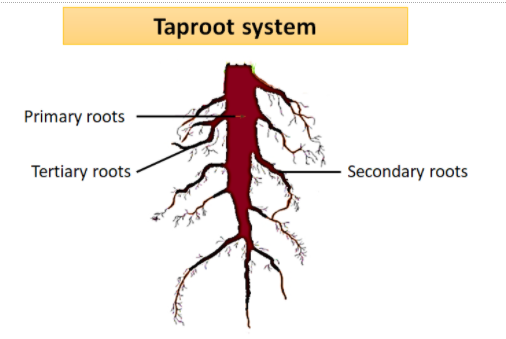
An example of the taproot system is a mustard plant. In most of the dicotyledonous plants, the radicle directly elongates to form the ‘primary root’ which grows inside the soil. The primary root along with its branches constitutes the ‘tap root system.’
Additional Information:
-The root system in monocotyledonous plants is different. Here the primary root is short-lived. It is then replaced by a large number of roots. The origin of these new roots is from the base of the stem, this constitutes the ‘fibrous root system’. A classic example of the fibrous root system is seen in wheat plants. Millets being a monocotyledon also shows the same type of roots.
- Another type of root system is seen in plants like grass, Monstera, and the banyan tree. Here there is an arrival of roots from parts of the plants other than the radicle. Such roots are called ‘adventitious roots’.
-Taproots in carrot, turnip and adventitious roots in sweet potato, get swollen, and store food.
So, the correct answer is ‘Mustard.’
Note:
- Gymnosperms like Sequoia also have taproots.
- ‘Radicle’ is the first part to emerge out of a seedling.
- ‘Alternate phyllotaxy’ is the arrangement of leaves in which a single leaf occupies each node in an alternate manner. Some examples of such an arrangement are china rose, sunflower, along with mustard.
Complete answer:
An example of the taproot system is a mustard plant. In most of the dicotyledonous plants, the radicle directly elongates to form the ‘primary root’ which grows inside the soil. The primary root along with its branches constitutes the ‘tap root system.’
Additional Information:
-The root system in monocotyledonous plants is different. Here the primary root is short-lived. It is then replaced by a large number of roots. The origin of these new roots is from the base of the stem, this constitutes the ‘fibrous root system’. A classic example of the fibrous root system is seen in wheat plants. Millets being a monocotyledon also shows the same type of roots.
- Another type of root system is seen in plants like grass, Monstera, and the banyan tree. Here there is an arrival of roots from parts of the plants other than the radicle. Such roots are called ‘adventitious roots’.
-Taproots in carrot, turnip and adventitious roots in sweet potato, get swollen, and store food.

So, the correct answer is ‘Mustard.’
Note:
- Gymnosperms like Sequoia also have taproots.
- ‘Radicle’ is the first part to emerge out of a seedling.
- ‘Alternate phyllotaxy’ is the arrangement of leaves in which a single leaf occupies each node in an alternate manner. Some examples of such an arrangement are china rose, sunflower, along with mustard.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




