
Which one of the following organelles is the garbage disposal system of the cell?
(A)Leukocyte
(B)Leucoplast
(C)Lysosome
(D)Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: They preserve starch grains and oil drops. Such a colorless plastid is within the underground roots, stems. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) presents a network of the membrane which encloses a fluid-filled lumen that almost fills the intercellular cavity. This organelle is also called a suicidal bag of cells.
Complete answer:
The other name of Leukocytes is called white blood cells. They are helpful in the management of the immune system of the body.
Leucoplasts are a type of plastid found in plants. The lysosome is the smallest cell and performs several functions such as:
(i) Extracellular digestion: lysosomal enzymes are removed outside the cell to move out the extracellular material. Therefore they are called digestive bags.
(ii) Digestion of foreign matter: Lysosomes also damage much foreign body within the cell, some of them are bacteria.
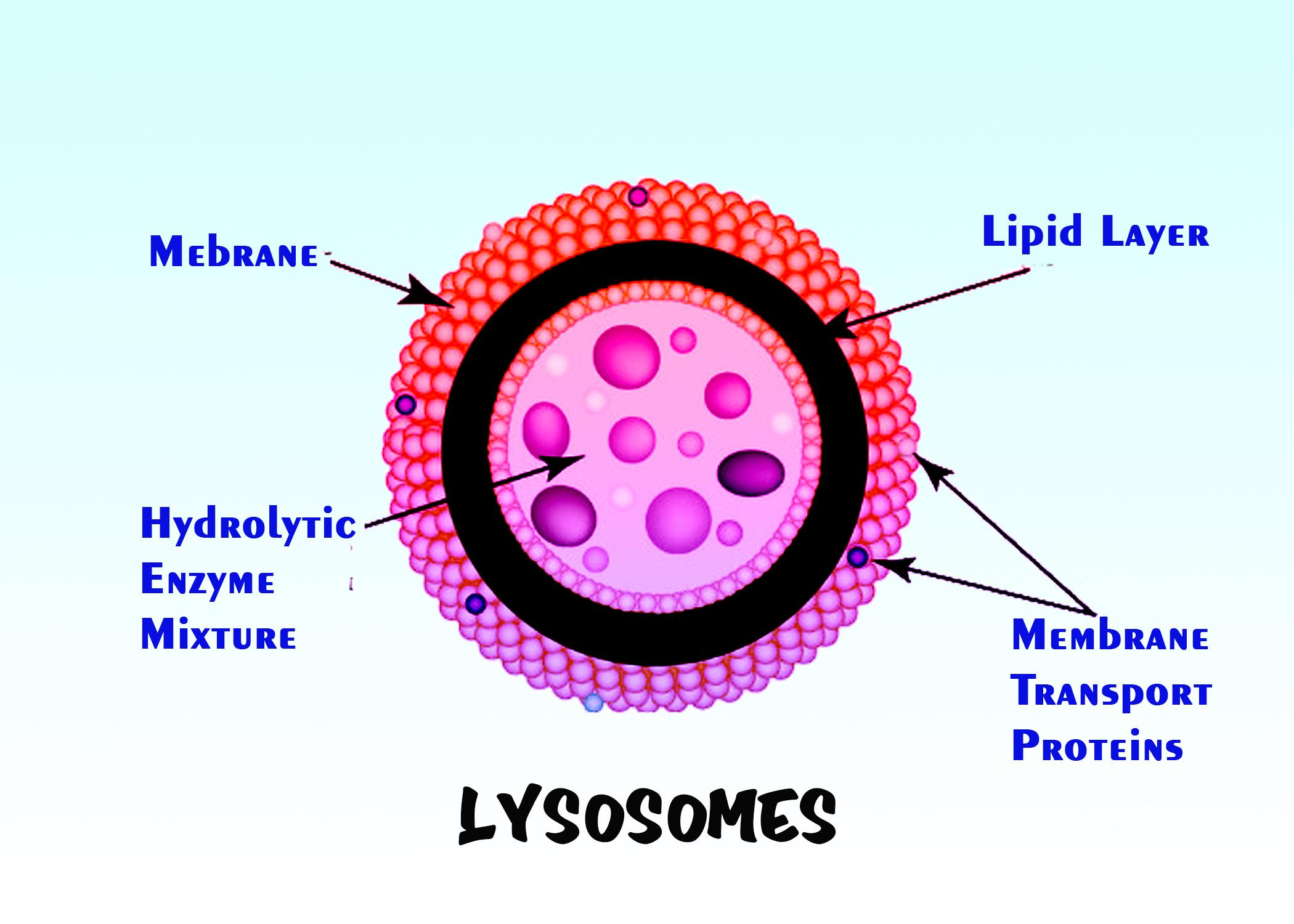
(iii) Cellular Digestion: Lysosomes break down and enzymes are released freely in damaged cells, old cells, dead cells, or cell organelles that do not work to digest them. In these processes, they remove cellular debris. Therefore, they are also called Cellular Waste Disposal Systems.
Additional information:
Lysosomes can also use their hydrolytic enzymes to damage the pathogenic organisms that might enter the cell. The perfect example of this happens in a group of white blood cells called macrophages, that are part of your body's immune system. In a process known as phagocytosis, a section of the macrophage's plasma membrane protrudes (folds) and envelops a pathogen. The invaginated section detaches from the plasma membrane, with the pathogen inside, and becomes a vesicle. The gallbladder fuses with a lysosome. The hydrolytic enzymes of the lysosome eventually destroy the diseased organism.
So, the correct answer is ‘Lysosome’.
Note: In animal cells, lysosomes are the "trash" of the cell. Digestive enzymes in lysosomes help break down proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, and even spent organelles. In unicellular eukaryotes, lysosomes are important for the digestion of the food they consume and the recycling of organelles. These enzymes are active at a much lower (more acidic) pH than those found in the cytoplasm. Many reactions cannot occur at low pH that takes place in the cytoplasm, so the benefit of compartmentalizing the eukaryotic cell into organelles is evident.
Complete answer:
The other name of Leukocytes is called white blood cells. They are helpful in the management of the immune system of the body.
Leucoplasts are a type of plastid found in plants. The lysosome is the smallest cell and performs several functions such as:
(i) Extracellular digestion: lysosomal enzymes are removed outside the cell to move out the extracellular material. Therefore they are called digestive bags.
(ii) Digestion of foreign matter: Lysosomes also damage much foreign body within the cell, some of them are bacteria.
(iii) Cellular Digestion: Lysosomes break down and enzymes are released freely in damaged cells, old cells, dead cells, or cell organelles that do not work to digest them. In these processes, they remove cellular debris. Therefore, they are also called Cellular Waste Disposal Systems.
Additional information:
Lysosomes can also use their hydrolytic enzymes to damage the pathogenic organisms that might enter the cell. The perfect example of this happens in a group of white blood cells called macrophages, that are part of your body's immune system. In a process known as phagocytosis, a section of the macrophage's plasma membrane protrudes (folds) and envelops a pathogen. The invaginated section detaches from the plasma membrane, with the pathogen inside, and becomes a vesicle. The gallbladder fuses with a lysosome. The hydrolytic enzymes of the lysosome eventually destroy the diseased organism.

So, the correct answer is ‘Lysosome’.
Note: In animal cells, lysosomes are the "trash" of the cell. Digestive enzymes in lysosomes help break down proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, and even spent organelles. In unicellular eukaryotes, lysosomes are important for the digestion of the food they consume and the recycling of organelles. These enzymes are active at a much lower (more acidic) pH than those found in the cytoplasm. Many reactions cannot occur at low pH that takes place in the cytoplasm, so the benefit of compartmentalizing the eukaryotic cell into organelles is evident.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




