
Which organs perform the same function but structurally different?
(a) Homologous organs
(b) Analogous organs
(c) Vestigial organs
(d) Structurally homologous organs
Answer
585k+ views
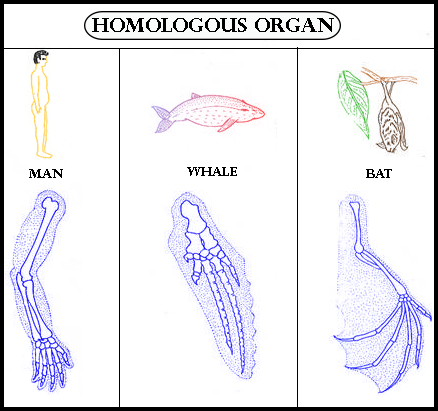
Hint: These organs are proof that organisms may have evolved from a common ancestor. The human arm, the wings of a bat, the leg of a panther, and the flipper of a whale are the example for these kinds of organs.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Homologous organs perform the same function but are structurally different. The structure of the vertebrae is a common homologous structure in all mammals. Human beings are related to dinosaurs by an auditory bone that exists inside the human ears is homologous to a dinosaurs’ jawbone.
So, the correct answer is ‘(a) Homologous organ’.
Additional information:
- Homologous organs are formed as a result of divergent evolution, where the same species develops two distinct abilities as they are separated by any geographical barriers.
Analogous organs: Organs that have similar or equivalent functions but not evolved from the same ancestor or evolutionary origin.
- This formed due to convergent evolution, for example, both bees and birds have wings which they use for flight; their wings came from different evolutionary origins or ancestors.
Vestigial organs: Organs which lost their ancestral function in the process of evolution are known as vestigial organs.
- The appendix of humans and wings of flightless birds are the example for vestigial organs where the structures are retained but the functions are lost.
Structurally homologous organs: A system of organs that are structurally different but function for the same plan or process is known as the structurally homologous organs.
Note:
- Organisms when exposed to a new environment try to adapt and evolve to survive better, forming the basic principle divergent evolution.
- Humans and giraffes have the same number of cervical vertebrae but due to the variation in the size of the bone, giraffes look taller than humans.
- Genetic similarity provides a better understanding of the connection between related species and about their common ancestor.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Homologous organs perform the same function but are structurally different. The structure of the vertebrae is a common homologous structure in all mammals. Human beings are related to dinosaurs by an auditory bone that exists inside the human ears is homologous to a dinosaurs’ jawbone.

So, the correct answer is ‘(a) Homologous organ’.
Additional information:
- Homologous organs are formed as a result of divergent evolution, where the same species develops two distinct abilities as they are separated by any geographical barriers.
Analogous organs: Organs that have similar or equivalent functions but not evolved from the same ancestor or evolutionary origin.
- This formed due to convergent evolution, for example, both bees and birds have wings which they use for flight; their wings came from different evolutionary origins or ancestors.
Vestigial organs: Organs which lost their ancestral function in the process of evolution are known as vestigial organs.
- The appendix of humans and wings of flightless birds are the example for vestigial organs where the structures are retained but the functions are lost.
Structurally homologous organs: A system of organs that are structurally different but function for the same plan or process is known as the structurally homologous organs.
Note:
- Organisms when exposed to a new environment try to adapt and evolve to survive better, forming the basic principle divergent evolution.
- Humans and giraffes have the same number of cervical vertebrae but due to the variation in the size of the bone, giraffes look taller than humans.
- Genetic similarity provides a better understanding of the connection between related species and about their common ancestor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




