
Which overlapping is involved in HCl molecules?
A s – s overlap
B p – p overlap
C s – d overlap
D s – p overlap
Answer
489.9k+ views
Hint: An atomic orbital is a mathematical function in atomic theory and quantum physics that describes the position and wave-like behaviour of an electron in an atom. This function may be used to determine the likelihood of locating any atom's electron in any given area surrounding the nucleus. The phrase atomic orbital can also refer to the actual region or space in which the electron can be calculated to be present, based on the orbital's mathematical structure.
Complete answer:
Depending on the phase and sign of the two interacting orbitals, the overlap between two atoms can be positive, negative, or even zero when they come into contact to form a bond. The amount of overlap is determined by the size and valence electrons of the two involved atoms. In general, the stronger the connection established between the two atoms is the bigger the overlap. As a result of the orbital overlap idea, atoms join by overlapping their orbitals, producing a lower energy state in which their valence electrons with opposing spin link up to create a covalent bond.
As we know, p-orbitals have dumbbell-shaped orbitals with one lobe positively spinning and the other lobe spinning negatively, and we also know that when two orbitals with the same spin overlap, they result in a positive overlap, and when two orbitals with two different spins overlap, they result in a negative overlap.
Let's take a look at each of the options one by one. In the first choice, we can see that there are two distinct orbitals with positive and negative spins, one p-orbital and one s-orbital. As a result, there will be no bonding between these two, resulting in a zero overlap.
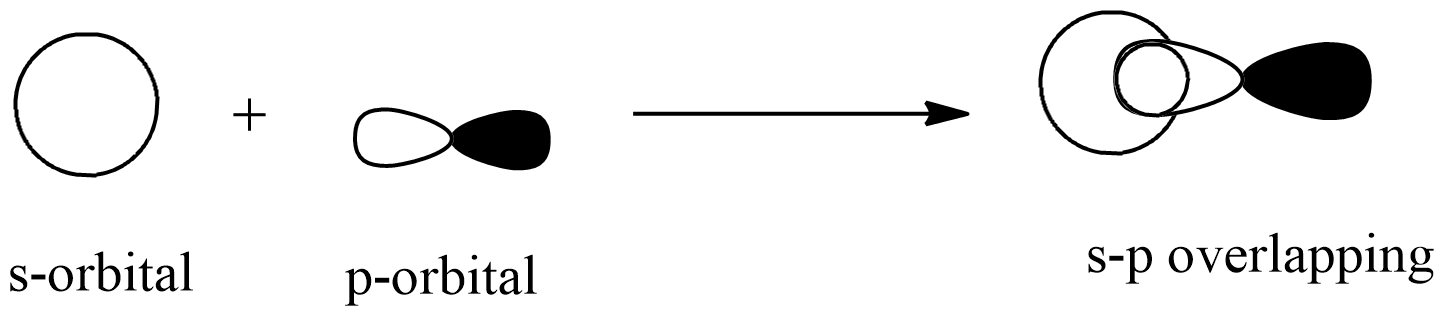
The overlap of the hydrogen 1s orbital with the half-filled \[3{{p}_{z}}\] orbital of chlorine causes bonding in the HCl molecule. As a result, the solution is s-p overlap.
Note:
Hydrochloric acid, commonly known as muriatic acid, is a hydrogen chloride aqueous solution. It's a colourless liquid with a strong, unpleasant odour. It's considered a strong acid. In the digestive tracts of most animal species, including humans, it is a component of stomach acid. Hydrochloric acid is a common laboratory reagent and chemical used in industry.
Complete answer:
Depending on the phase and sign of the two interacting orbitals, the overlap between two atoms can be positive, negative, or even zero when they come into contact to form a bond. The amount of overlap is determined by the size and valence electrons of the two involved atoms. In general, the stronger the connection established between the two atoms is the bigger the overlap. As a result of the orbital overlap idea, atoms join by overlapping their orbitals, producing a lower energy state in which their valence electrons with opposing spin link up to create a covalent bond.
As we know, p-orbitals have dumbbell-shaped orbitals with one lobe positively spinning and the other lobe spinning negatively, and we also know that when two orbitals with the same spin overlap, they result in a positive overlap, and when two orbitals with two different spins overlap, they result in a negative overlap.
Let's take a look at each of the options one by one. In the first choice, we can see that there are two distinct orbitals with positive and negative spins, one p-orbital and one s-orbital. As a result, there will be no bonding between these two, resulting in a zero overlap.
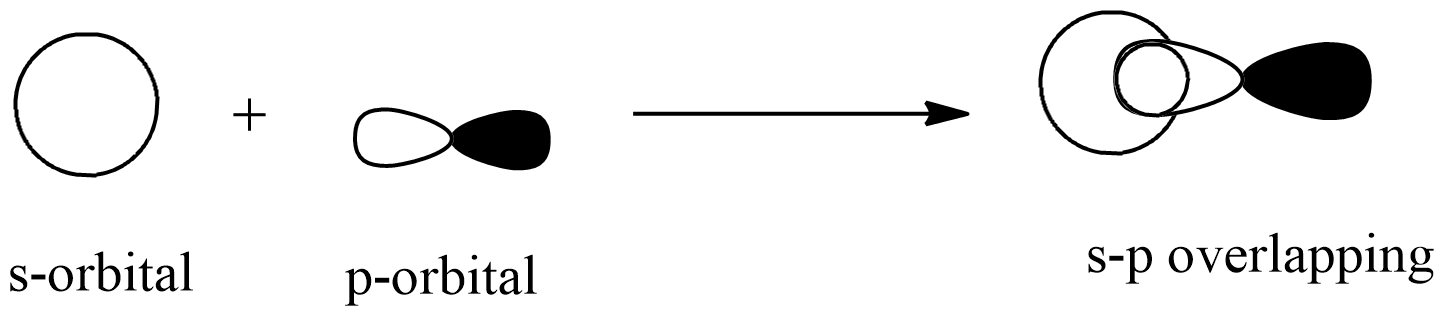
The overlap of the hydrogen 1s orbital with the half-filled \[3{{p}_{z}}\] orbital of chlorine causes bonding in the HCl molecule. As a result, the solution is s-p overlap.
Note:
Hydrochloric acid, commonly known as muriatic acid, is a hydrogen chloride aqueous solution. It's a colourless liquid with a strong, unpleasant odour. It's considered a strong acid. In the digestive tracts of most animal species, including humans, it is a component of stomach acid. Hydrochloric acid is a common laboratory reagent and chemical used in industry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




