
Which part of the human brain controls balance, posture, and coordination?
(A)Cerebrum
(B)Cerebellum
(C)Medulla oblongata
(D)Thalamus
(E)Hypothalamus
Answer
567.9k+ views
Hint The part of the human brain which controls balance, posture, and coordination of humans is a major structure of the hindbrain that is located near the brainstem. It is the largest structure of the hindbrain.
Complete answer: The cerebellum (which is Latin for “little brain”) is a major structure of the hindbrain that's located near the brainstem. This part of the brain is liable for coordinating voluntary movements. It's also liable for a variety of functions including motor skills like balance, coordination, and posture. The cerebellum is the largest structure of the hindbrain and can be found within the back portion of the skull below the temporal and occipital lobes and behind the brainstem.
Additional Information: When watching the brain, the cerebellum looks very similar to a smaller structure separate from the brain, found beneath the hemispheres of the cerebral cortex. The cerebellum consists of a cortex covering white matter, as well as a ventricle stuffed with fluid. It's also divided into two hemispheres just like the cerebral cortex.
There are two main parts of the cerebellum:
Cerebellar cortex- It is a layer that contains the folded tissue containing most of the cerebellum's neurons.
The cerebellar nuclei-The innermost part of the cerebellum contains nerve cells that communicate information from the cerebellum. While the cerebellum isn't thought to initiate movement, this is a part of the brain that helps in organizing all of the actions of the muscle groups involved during a particular movement to make sure that the body is in a position to produce a fluid, coordinated movement. This includes eye movements and movements related to speaking.
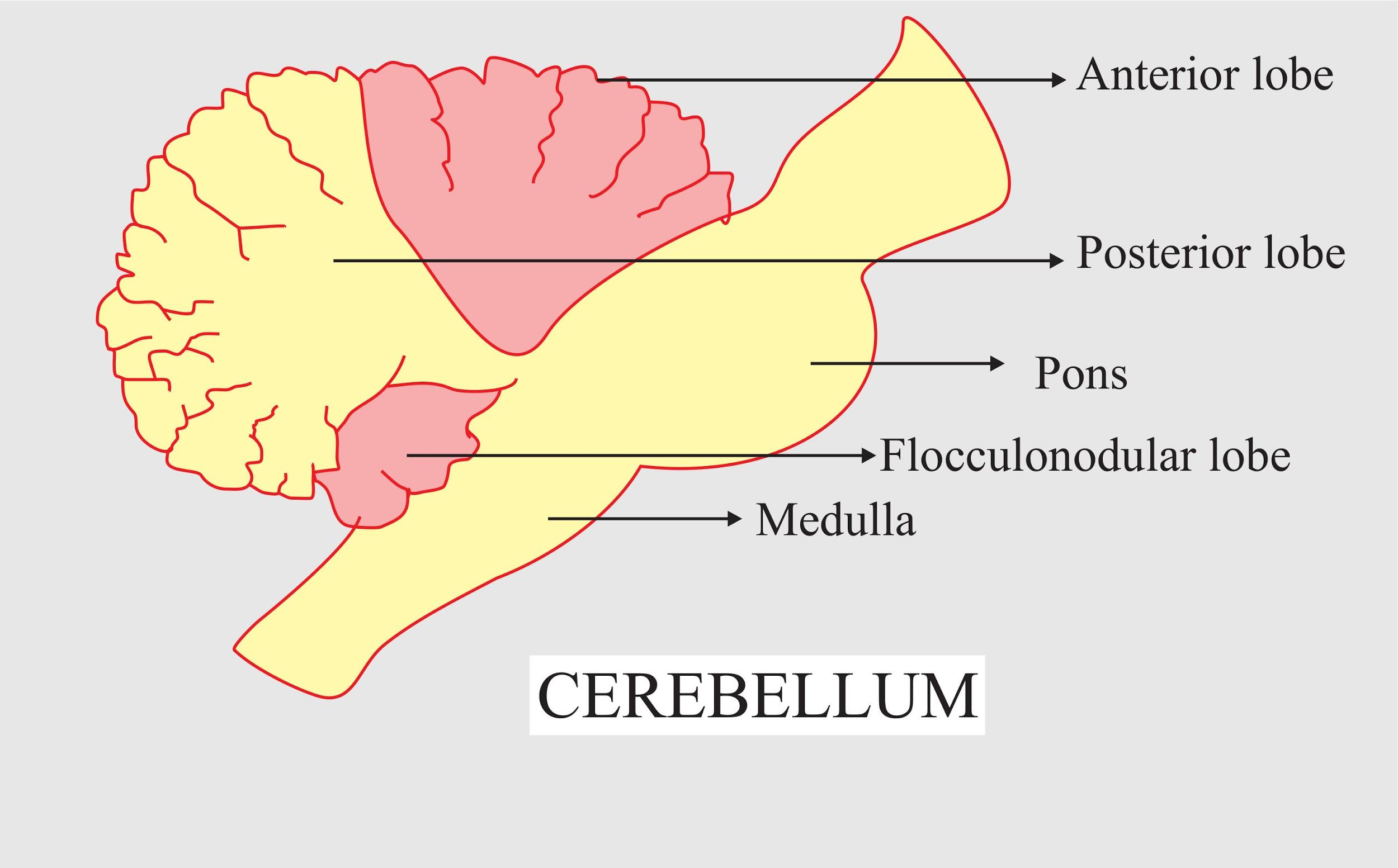
So, the correct answer is ‘Cerebellum’.
Note: The famous researchers believe the cerebellum plays a task in thinking, including processing language and mood, also as attention, fear response, and pleasure or reward response. The cerebellum plays a critical role during this motor learning process.
Complete answer: The cerebellum (which is Latin for “little brain”) is a major structure of the hindbrain that's located near the brainstem. This part of the brain is liable for coordinating voluntary movements. It's also liable for a variety of functions including motor skills like balance, coordination, and posture. The cerebellum is the largest structure of the hindbrain and can be found within the back portion of the skull below the temporal and occipital lobes and behind the brainstem.
Additional Information: When watching the brain, the cerebellum looks very similar to a smaller structure separate from the brain, found beneath the hemispheres of the cerebral cortex. The cerebellum consists of a cortex covering white matter, as well as a ventricle stuffed with fluid. It's also divided into two hemispheres just like the cerebral cortex.
There are two main parts of the cerebellum:
Cerebellar cortex- It is a layer that contains the folded tissue containing most of the cerebellum's neurons.
The cerebellar nuclei-The innermost part of the cerebellum contains nerve cells that communicate information from the cerebellum. While the cerebellum isn't thought to initiate movement, this is a part of the brain that helps in organizing all of the actions of the muscle groups involved during a particular movement to make sure that the body is in a position to produce a fluid, coordinated movement. This includes eye movements and movements related to speaking.

So, the correct answer is ‘Cerebellum’.
Note: The famous researchers believe the cerebellum plays a task in thinking, including processing language and mood, also as attention, fear response, and pleasure or reward response. The cerebellum plays a critical role during this motor learning process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




