
Which shows exothermic dissolution?
A.$KN{O_3}$
B.$KBr$
C.$NaCl$
D.$Ca{(OH)_2}$

Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: For dissolution to be exothermic, the solubility of a compound would decrease with increase in temperature.
Complete step by step answer:
Exothermic Reaction – A reaction in which there is evolution of heat is called an exothermic reaction.
Dissolution – The process of solubilisation of a solute into a solvent is called dissolution.
When a solute is dissolved in a liquid, there exists an equilibrium between the solid phase and the dissolved phase of the solute. A substance which shows exothermic dissolution shows more solubility at lower temperature and less solubility at high temperature. This occurs in accordance with the Le Chatelier's Principle. An increase in temperature of an exothermic reaction will decrease the rate of forward reaction.
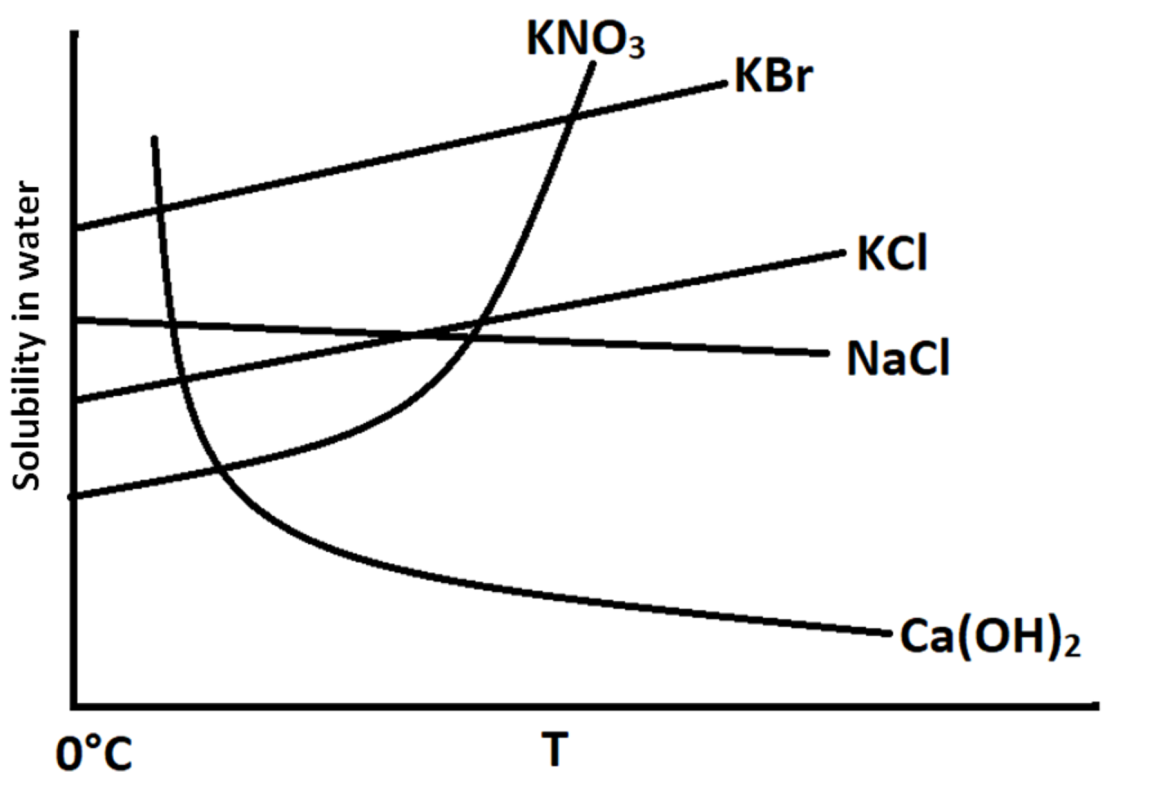
So, for a substance to exhibit exothermic dissolution, its solubility should decrease with increase in temperature. From the graph, we can see that the solubilities are shown on y – axis and the temperature is shown on the x – axis.
It is shown in the graph that the solubility of $KN{O_3}$ increases exponentially with increase in temperature. This means that this is a process of endothermic dissolution.
$KBr$ and $KCl$ show increase in solubility with increase in temperature. This means that this is a process of endothermic dissolution.
The solubility of $NaCl$ remains constant with increase in temperature. This means that this process is not affected by increase in temperature.
In case of $Ca{(OH)_2}$, there is an exponential drop in the solubility with increase in temperature. Therefore, this process is an exothermic process.
Hence, option D is correct.
Additional information:
Le Chatlier’s principle is also known as the Equilibrium Law. It states that when a system, which has been at equilibrium for a long period of time, is subjected to a change in temperature, concentration of reactants or products, volume or pressure, the equilibrium shifts in that direction in which the effect of change can be undone.
Note:
Any change in the equilibrium of a system is treated such that the impact of the change can be undone.
Complete step by step answer:
Exothermic Reaction – A reaction in which there is evolution of heat is called an exothermic reaction.
Dissolution – The process of solubilisation of a solute into a solvent is called dissolution.
When a solute is dissolved in a liquid, there exists an equilibrium between the solid phase and the dissolved phase of the solute. A substance which shows exothermic dissolution shows more solubility at lower temperature and less solubility at high temperature. This occurs in accordance with the Le Chatelier's Principle. An increase in temperature of an exothermic reaction will decrease the rate of forward reaction.
So, for a substance to exhibit exothermic dissolution, its solubility should decrease with increase in temperature. From the graph, we can see that the solubilities are shown on y – axis and the temperature is shown on the x – axis.
It is shown in the graph that the solubility of $KN{O_3}$ increases exponentially with increase in temperature. This means that this is a process of endothermic dissolution.
$KBr$ and $KCl$ show increase in solubility with increase in temperature. This means that this is a process of endothermic dissolution.
The solubility of $NaCl$ remains constant with increase in temperature. This means that this process is not affected by increase in temperature.
In case of $Ca{(OH)_2}$, there is an exponential drop in the solubility with increase in temperature. Therefore, this process is an exothermic process.
Hence, option D is correct.
Additional information:
Le Chatlier’s principle is also known as the Equilibrium Law. It states that when a system, which has been at equilibrium for a long period of time, is subjected to a change in temperature, concentration of reactants or products, volume or pressure, the equilibrium shifts in that direction in which the effect of change can be undone.
Note:
Any change in the equilibrium of a system is treated such that the impact of the change can be undone.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




