
Which type of reaction is when aniline reacts with benzaldehyde.
A. Polymerisation
B. Condensation
C. Addition
D. Substitution
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint:Reaction of aniline and benzaldehyde forms products with the removal of water molecules leads to the formation of the product benzylidene aniline.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, let’s discuss all the given processes or reactions given. Let’s understand the meaning of polymerisation. It is a process of relatively small molecules known as monomers combined together chemically to produce a long chain-like network molecule called polymer. Polymerisation occurs in three steps i.e.
$1.$ Chain initiation step
$2.$ Chain propagation step
$3.$ Chain termination step
Polymerisation is of two types i.e. homogeneous and heterogeneous polymerisation. The example of polymerisation is formation of polythene, nylon $6,6$ etc. Addition refers to the reaction involving addition of two or more molecules to form a large compound with no other by-products. The example of addition reaction is the addition of \[{\text{H - Br}}\] in ethene molecule to give ${\text{1 - Bromoethane}}$
Substitution reaction is one in which one functional group in a chemical compound is replaced by another functional group. And, the last type of reaction is condensation reaction which refers to the process of removal of water molecules that takes place during the reaction.
Moving on to the given statement, when aniline reacts with benzaldehyde, benzylideneaniline is formed by the removal of water molecules. The structure of benzylideneaniline is
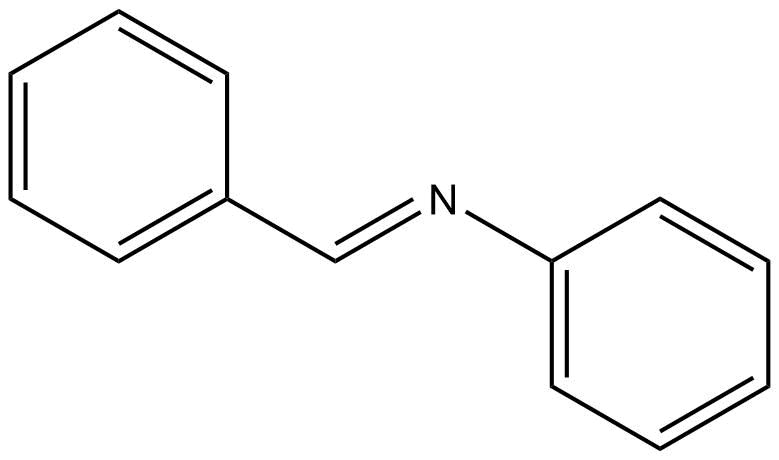
Since the reaction proceeds with the removal of water molecules, it is a condensation reaction.
So, the correct option is (B).
Note:
${C_6}{H_5}$ in above equations represents a benzene ring. Moreover, polymerization reactions occur in both addition and condensation reactions. Remember condensation is a reaction in which water molecules are removed.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, let’s discuss all the given processes or reactions given. Let’s understand the meaning of polymerisation. It is a process of relatively small molecules known as monomers combined together chemically to produce a long chain-like network molecule called polymer. Polymerisation occurs in three steps i.e.
$1.$ Chain initiation step
$2.$ Chain propagation step
$3.$ Chain termination step
Polymerisation is of two types i.e. homogeneous and heterogeneous polymerisation. The example of polymerisation is formation of polythene, nylon $6,6$ etc. Addition refers to the reaction involving addition of two or more molecules to form a large compound with no other by-products. The example of addition reaction is the addition of \[{\text{H - Br}}\] in ethene molecule to give ${\text{1 - Bromoethane}}$
Substitution reaction is one in which one functional group in a chemical compound is replaced by another functional group. And, the last type of reaction is condensation reaction which refers to the process of removal of water molecules that takes place during the reaction.
Moving on to the given statement, when aniline reacts with benzaldehyde, benzylideneaniline is formed by the removal of water molecules. The structure of benzylideneaniline is

Since the reaction proceeds with the removal of water molecules, it is a condensation reaction.
So, the correct option is (B).
Note:
${C_6}{H_5}$ in above equations represents a benzene ring. Moreover, polymerization reactions occur in both addition and condensation reactions. Remember condensation is a reaction in which water molecules are removed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




