
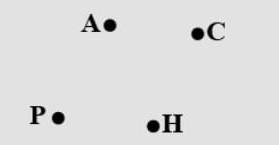
With a sharp tip of the pencil, mark four points on a paper and name them by the letters A, C, P, H. Try to name these points in different ways. One such way could be this.

Answer
619.2k+ views
Hint: Approach by fixing each point to all locations such that one letter is considered at each true. We have to find all the possible naming methods applicable without repetition.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, consider the letter A. For A, we have four different positions available amongst which we can select one.
So, number of ways of arranging A, $\therefore A=4$
Since, we have placed A so we are left with three other letters, that is C, P, H.
Now, consider the letter C. Since, one place is occupied by A, so we have three different positions available amongst which we can select one.
So, number of ways of arranging C, $\therefore C=3$
Since we have placed A & C. So, we are left with two other letters, that is P, H.
Again, consider the letter H. It has only two places for solution amongst four places.
So, number of ways of arranging H, $\therefore H=2$
We have fixed three letters up till now and left with only P.
At last consider P but we have only one left space for placing P.
So, no of ways of arranging P, $\therefore P=1$
As we know that for two events ${{a}_{1}}\text{ and }{{a}_{2}}$ the total outcomes are${{a}_{1}}\times {{a}_{2}}$ by multiplication principle.
By using the rule of multiplication principle:
$\begin{align}
& A\times C\times H\times P=4\times 3\times 2\times 1 \\
& =24 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the total outcomes are 24.
Note: Common confusion about application of rule of addition and rule of multiplication. Here, we cannot use the rule of addition because events are not disjoint.
One simpler method of solving this question is by using permutation.
Total number of outcomes $={}^{n}{{P}_{r}}$
Here, n=4 and r=4.
$\begin{align}
& \therefore {}^{4}{{P}_{4}}=\dfrac{4!}{\left( 4-4 \right)!} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{4!}{0!}=24 \\
\end{align}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, consider the letter A. For A, we have four different positions available amongst which we can select one.
So, number of ways of arranging A, $\therefore A=4$
Since, we have placed A so we are left with three other letters, that is C, P, H.
Now, consider the letter C. Since, one place is occupied by A, so we have three different positions available amongst which we can select one.
So, number of ways of arranging C, $\therefore C=3$
Since we have placed A & C. So, we are left with two other letters, that is P, H.
Again, consider the letter H. It has only two places for solution amongst four places.
So, number of ways of arranging H, $\therefore H=2$
We have fixed three letters up till now and left with only P.
At last consider P but we have only one left space for placing P.
So, no of ways of arranging P, $\therefore P=1$
As we know that for two events ${{a}_{1}}\text{ and }{{a}_{2}}$ the total outcomes are${{a}_{1}}\times {{a}_{2}}$ by multiplication principle.
By using the rule of multiplication principle:
$\begin{align}
& A\times C\times H\times P=4\times 3\times 2\times 1 \\
& =24 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the total outcomes are 24.
Note: Common confusion about application of rule of addition and rule of multiplication. Here, we cannot use the rule of addition because events are not disjoint.
One simpler method of solving this question is by using permutation.
Total number of outcomes $={}^{n}{{P}_{r}}$
Here, n=4 and r=4.
$\begin{align}
& \therefore {}^{4}{{P}_{4}}=\dfrac{4!}{\left( 4-4 \right)!} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{4!}{0!}=24 \\
\end{align}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 6 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 6 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 6 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 6 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 6 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Give 10 examples for herbs , shrubs , climbers , creepers

How many millions make a billion class 6 maths CBSE

What is the capital city of Australia? A) Sydney B) Melbourne C) Brisbane D) Canberra

What is the shape of Earth A Circle B Square C Sphere class 6 social science CBSE

The planet nearest to earth is A Mercury B Venus C class 6 social science CBSE

What are the main physical divisions of India class 6 social science CBSE





