
With the help of a block diagram, explain the operation of FM superheterodyne receivers.
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: FM Superheterodyne Receiver is a superheterodyne type like a typical AM receiver.
Selecting the incoming modulated signals and is simplified by the RF section. This simplified signal is then fed to the mixer and local oscillator. Here the frequency of the modulated signal is changed to an intermediate frequency. For FM receivers, the IF is 10.7MHz.
Complete step by step answer:
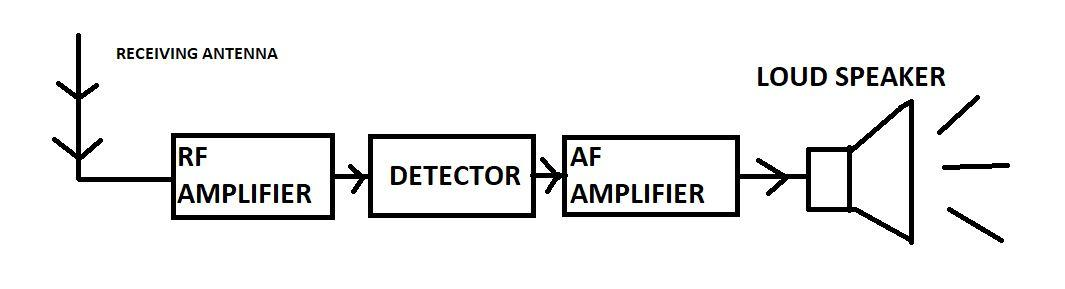
The above diagram shows the operation of FM superheterodyne receivers with the help of a block diagram.
The antenna receives the signals.
A tuned amplifier that amplifies high-frequency signals used in radio communications is known as a radio frequency amplifier, or RF amplifier. By changing the inductance or capacitance of the tuned circuit the frequency at which maximum gain occurs in an RF amplifier can be made variable
A device or circuit that extracts information from a modulated radio frequency current or voltage is known as a detector. In a superheterodyne receiver the term detector is also used many a time to refer to the mixer or the tube or the transistor which converts the radio frequency signal to the intermediate frequency.
To reject the image frequency the incoming signal through the antenna is filtered and then amplified by the RF amplifier. RF amplifiers can also be tuned to select and amplify a particular frequency which is a carrier within the AM broadcast range.
Note: The intermediate frequency wave is amplified using IF amplifier then its amplitude is maintained constant employing a limiter. The output of this section is then applied to the FM detector which works to demodulate the modulated wave. The AF signal from the FM detector is then passed on through a de-emphasis network, where the varied frequencies attain their original power distribution. Finally, it is fed into the loud speaker after performing AF amplification.
Selecting the incoming modulated signals and is simplified by the RF section. This simplified signal is then fed to the mixer and local oscillator. Here the frequency of the modulated signal is changed to an intermediate frequency. For FM receivers, the IF is 10.7MHz.
Complete step by step answer:

The above diagram shows the operation of FM superheterodyne receivers with the help of a block diagram.
The antenna receives the signals.
A tuned amplifier that amplifies high-frequency signals used in radio communications is known as a radio frequency amplifier, or RF amplifier. By changing the inductance or capacitance of the tuned circuit the frequency at which maximum gain occurs in an RF amplifier can be made variable
A device or circuit that extracts information from a modulated radio frequency current or voltage is known as a detector. In a superheterodyne receiver the term detector is also used many a time to refer to the mixer or the tube or the transistor which converts the radio frequency signal to the intermediate frequency.
To reject the image frequency the incoming signal through the antenna is filtered and then amplified by the RF amplifier. RF amplifiers can also be tuned to select and amplify a particular frequency which is a carrier within the AM broadcast range.
Note: The intermediate frequency wave is amplified using IF amplifier then its amplitude is maintained constant employing a limiter. The output of this section is then applied to the FM detector which works to demodulate the modulated wave. The AF signal from the FM detector is then passed on through a de-emphasis network, where the varied frequencies attain their original power distribution. Finally, it is fed into the loud speaker after performing AF amplification.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




