
With the help of a neat diagram describe the life history of a mushroom.
Answer
540.6k+ views
Hint: Mushroom is a club-shaped, fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body present in the Basidiomycetes fungi. It is also known as ‘gilled fungi'.
Complete answer:
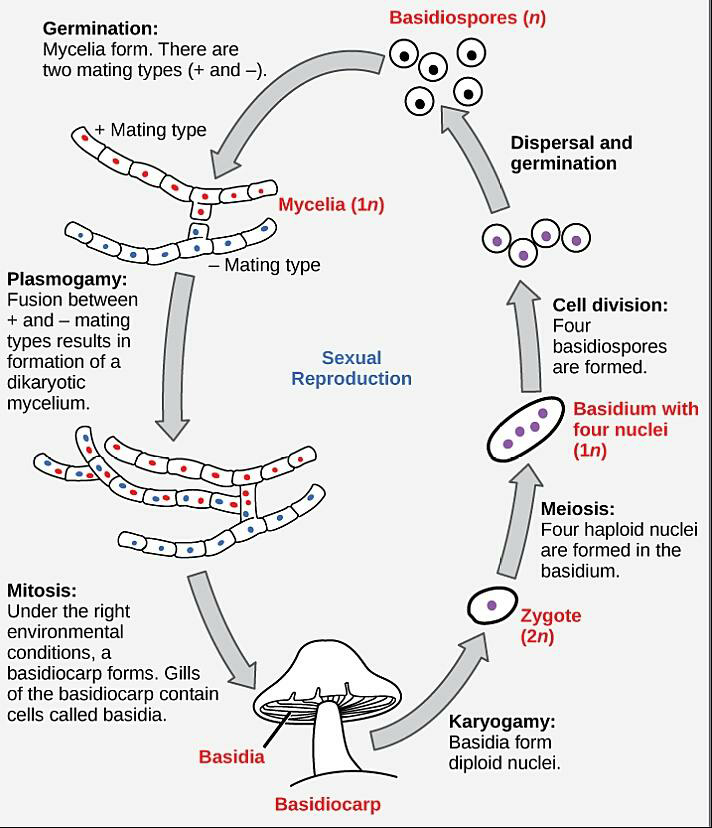
-The mushroom is a typical example of Basidiomycetes. Some of the varieties of mushrooms are Puffballs, Morels, Truffles, Stinkhorn, etc.
-The fruiting bodies of basidiomycetes are known as basidiocarps which bear the spore-producing cells called basidia (singular- basidium). These basidia are present inside the gills.
-The reproductive cycle in mushrooms starts with the formation of a diploid zygote by the fusion of two compatible nuclei (karyogamy) in the basidia present inside the basidiocarp.
-The zygote undergoes meiosis to form four haploid basidiospores.
-The basidiospores germinate to give rise to monokaryotic hyphae. These hyphae together form the Primary mycelia.
-The mycelium of different strains cluster to form the Secondary mycelium. Each secondary mycelium contains two compatible mating nuclei. This represents the dikaryotic stage of the mushroom.
-The secondary mycelia gradually grow and differentiate under the suitable condition to form a new basidiocarp and the cycle continues.
-The newly formed basidiocarp (mushroom) bears the basidia under its cap.
-The formation of the fruiting bodies takes place only at the end of the life cycle and that too for a few days only.
Note:
This mode of life cycle involving both the haploid and diploid phase of life is known as ‘Alternation of the generation’. In basidiomycetes like mushrooms, the dominant phase is dikaryotic or diploid. It is represented by the zygote formed from the secondary mycelia whereas the basidiospores represent the haploid or the monokaryotic phase.
Complete answer:
-The mushroom is a typical example of Basidiomycetes. Some of the varieties of mushrooms are Puffballs, Morels, Truffles, Stinkhorn, etc.
-The fruiting bodies of basidiomycetes are known as basidiocarps which bear the spore-producing cells called basidia (singular- basidium). These basidia are present inside the gills.
-The reproductive cycle in mushrooms starts with the formation of a diploid zygote by the fusion of two compatible nuclei (karyogamy) in the basidia present inside the basidiocarp.
-The zygote undergoes meiosis to form four haploid basidiospores.
-The basidiospores germinate to give rise to monokaryotic hyphae. These hyphae together form the Primary mycelia.
-The mycelium of different strains cluster to form the Secondary mycelium. Each secondary mycelium contains two compatible mating nuclei. This represents the dikaryotic stage of the mushroom.
-The secondary mycelia gradually grow and differentiate under the suitable condition to form a new basidiocarp and the cycle continues.
-The newly formed basidiocarp (mushroom) bears the basidia under its cap.
-The formation of the fruiting bodies takes place only at the end of the life cycle and that too for a few days only.

Note:
This mode of life cycle involving both the haploid and diploid phase of life is known as ‘Alternation of the generation’. In basidiomycetes like mushrooms, the dominant phase is dikaryotic or diploid. It is represented by the zygote formed from the secondary mycelia whereas the basidiospores represent the haploid or the monokaryotic phase.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




