
With the help of diagram, explain secondary growth in dicot roots.
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Width of the secondary tissue increases with the age of plant. Pith initially is narrow but with time it vanished. And growth of the secondary xylem is also affected by the environmental conditions like seasons, temperature, etc.
Complete answer:
To answer this question let us understand the term secondary growth.
Secondary growth: It is defined as the increase in stem diameter due to the activity of the lateral meristem tissues.
Let us now try to understand secondary growth in dicot plants:
Secondary tissues in dicots are formed by lateral meristems which are of two types vascular cambium and cork cambium or phellogen.
Given diagram represents the tissue arrangement of the root starting form the primary root to the secondary root.
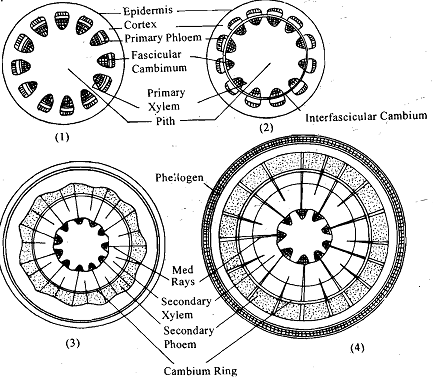
1.Vascular rays: In secondary growth first of all, these rays start emerging from the radially arranged cells and they are involved in giving height to the roots. These rays are present in the xylem tissues. They may be made up of one type of cells or may have different types of the cells.
2.Secondary phloem: This is the covering layer outside the vascular cambium. It is made up of the same cells which are found in primary phloem tissue. It is a regular arrangement of the tissues and has no fibre in it.
3.Secondary xylem: This is the woody part of the roots and made up of the vessels, fibres, parenchyma tissues and tracheids.
Note: Origin of secondary vascular tissues: Vascular cambium is involved in formation of secondary vascular tissues. It is formed by two types of meristem tissues intra fascicular cambium and inter fascicular cambium.
Intra fascicular cambium: It is present in between phloem and xylem vascular bundles.
Inter fascicular cambium: It is present in between two consecutive vascular bundles.
Complete answer:
To answer this question let us understand the term secondary growth.
Secondary growth: It is defined as the increase in stem diameter due to the activity of the lateral meristem tissues.
Let us now try to understand secondary growth in dicot plants:
Secondary tissues in dicots are formed by lateral meristems which are of two types vascular cambium and cork cambium or phellogen.
Given diagram represents the tissue arrangement of the root starting form the primary root to the secondary root.

1.Vascular rays: In secondary growth first of all, these rays start emerging from the radially arranged cells and they are involved in giving height to the roots. These rays are present in the xylem tissues. They may be made up of one type of cells or may have different types of the cells.
2.Secondary phloem: This is the covering layer outside the vascular cambium. It is made up of the same cells which are found in primary phloem tissue. It is a regular arrangement of the tissues and has no fibre in it.
3.Secondary xylem: This is the woody part of the roots and made up of the vessels, fibres, parenchyma tissues and tracheids.
Note: Origin of secondary vascular tissues: Vascular cambium is involved in formation of secondary vascular tissues. It is formed by two types of meristem tissues intra fascicular cambium and inter fascicular cambium.
Intra fascicular cambium: It is present in between phloem and xylem vascular bundles.
Inter fascicular cambium: It is present in between two consecutive vascular bundles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




