
Wood is a common name of
A. Phloem
B. Secondary xylem
C. Cambium
D. Vascular bundles
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: Wood is the fibrous and porous tissue found in the stems and roots of trees or woody plants. It consists of strong fibres and cellulose that provide support to plants. It is the result of the secondary growth of the water-conducting tissue in plants. Wood is a common feature of dicots and gymnosperms.
Complete answer: Wood has been used as fuel for several years and is used as a major construction material. It is used in making paper, furniture, weapons, etc. In plants, the conductive tissues like xylem and phloem form the vascular system. These tissues are specialized in conducting water and food respectively throughout the plant. These tissues lie in lateral bundles. Sometimes there is the presence of lateral meristem and cambium in between them. The cambium tissue undergoes anti clinical divisions that result in the formation of secondary xylem and phloem. The secondary growth in plants leads to the thickness in the stem. The monocot plants rarely show secondary growth but gymnosperms and dicots show prominent secondary growths.
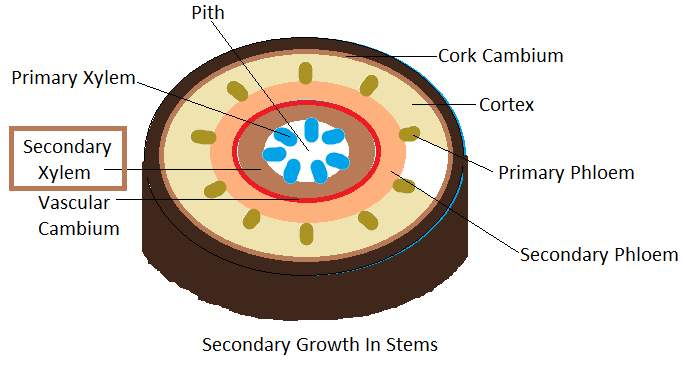
Wood is the result of secondary growth in the xylem tissue. Secondary tissue lies in front of the cambium tissue. On the other hand, the phloem at the back of the cambium due to secondary growth forms the bark of the trees. Another characteristic feature of secondary growth in the xylem is the formation of heartwood and sapwood. The inner layer of secondary xylem forms the heartwood and the outer layer forms the sapwood. The sapwood contains young layers of the tree and it performs water conduction in large woody trees. Thus, the common name of wood is called secondary xylem.
So, option B is the correct answer.
Note: The secondary growth in trees help in calculating the age and health of a tree. Wood formation occurs in the form of layers. Every growing season marks the formation of a new layer in the wood. This results in the formation of rings. These rings are called annual rings. Counting the annual rings gives an estimated measure of the tree’s age.
Complete answer: Wood has been used as fuel for several years and is used as a major construction material. It is used in making paper, furniture, weapons, etc. In plants, the conductive tissues like xylem and phloem form the vascular system. These tissues are specialized in conducting water and food respectively throughout the plant. These tissues lie in lateral bundles. Sometimes there is the presence of lateral meristem and cambium in between them. The cambium tissue undergoes anti clinical divisions that result in the formation of secondary xylem and phloem. The secondary growth in plants leads to the thickness in the stem. The monocot plants rarely show secondary growth but gymnosperms and dicots show prominent secondary growths.

Wood is the result of secondary growth in the xylem tissue. Secondary tissue lies in front of the cambium tissue. On the other hand, the phloem at the back of the cambium due to secondary growth forms the bark of the trees. Another characteristic feature of secondary growth in the xylem is the formation of heartwood and sapwood. The inner layer of secondary xylem forms the heartwood and the outer layer forms the sapwood. The sapwood contains young layers of the tree and it performs water conduction in large woody trees. Thus, the common name of wood is called secondary xylem.
So, option B is the correct answer.
Note: The secondary growth in trees help in calculating the age and health of a tree. Wood formation occurs in the form of layers. Every growing season marks the formation of a new layer in the wood. This results in the formation of rings. These rings are called annual rings. Counting the annual rings gives an estimated measure of the tree’s age.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




