
Write a note on Brownian movement
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Brownian movement refers to the zig-zag motion of a particle that is usually observed under a high power ultra-microscope. Basically, it is the uncontrolled motion of particles in a fluid due to collision.
Complete step by step answer:
-Brownian movement also known as Brownian motion is defined as the uncontrolled or erratic movement of particles in a fluid due to their constant collision with other fast-moving molecules. Some of the examples of Brownian movement are:
Pollen grains in oil drop
Plasma particles in the cell
-This movement is named after the Scottish botanist Robert brown, who first observed random movement of pollen grains in water. An illustration is as shown:
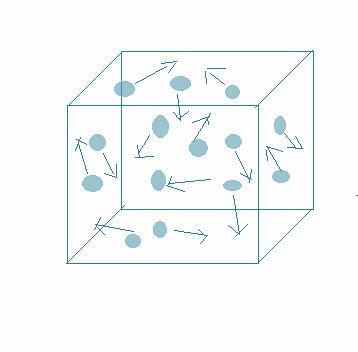
-Moreover, it is one of the simplest models of randomness. Some of the effects of this motion are listed below:
-It causes the particles in a fluid to be in a constant motion.
-This prevents the particles from settling down and thus leading to the stability of the colloidal solution.
-A true solution can be distinguished from a colloidal solution with the help of this motion.
Note:
The kinetic theory of gases which explains the pressure, temperature and volume of gases is based on the Brownian motion model of particles. Moreover, during this motion, there is a transfer or exchange of momentum/energy between the particles and the speed of the Brownian motion is inversely proportional to the viscosity of the fluid. Hence, the lower the viscosity of the fluid, the faster will be the movement.
Complete step by step answer:
-Brownian movement also known as Brownian motion is defined as the uncontrolled or erratic movement of particles in a fluid due to their constant collision with other fast-moving molecules. Some of the examples of Brownian movement are:
Pollen grains in oil drop
Plasma particles in the cell
-This movement is named after the Scottish botanist Robert brown, who first observed random movement of pollen grains in water. An illustration is as shown:

-Moreover, it is one of the simplest models of randomness. Some of the effects of this motion are listed below:
-It causes the particles in a fluid to be in a constant motion.
-This prevents the particles from settling down and thus leading to the stability of the colloidal solution.
-A true solution can be distinguished from a colloidal solution with the help of this motion.
Note:
The kinetic theory of gases which explains the pressure, temperature and volume of gases is based on the Brownian motion model of particles. Moreover, during this motion, there is a transfer or exchange of momentum/energy between the particles and the speed of the Brownian motion is inversely proportional to the viscosity of the fluid. Hence, the lower the viscosity of the fluid, the faster will be the movement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




