
Write any two differences below bonding molecular orbital and antibonding molecular orbital.
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: Basically, molecular orbital theory is a theory based on chemical bonding. It is used to describe the structure and properties of different molecules. To solve this question, we need to know the different types of molecular orbitals and their properties.
Complete step by step answer:
Basically, in molecular theory, the total number of molecular orbitals formed are always equal to the total number of atomic orbitals offered by the bonding species. The electrons are filled into molecular orbitals in the increasing order of orbital energy i.e. from the orbital with the lowest energy to the orbital with the highest energy. Now, there are different types of molecular orbitals such as bonding molecular orbitals, antibonding orbitals and non-bonding molecular orbitals.
Now, let’s discuss different types of orbitals. The molecular orbital refers to the space in a molecule in which the probability of finding an electron is maximum. These are basically mathematical functions that describe the wave nature of electrons in a given molecule. The first one is anti-bonding molecular orbitals. The probability of finding the electron in the inter nuclear region decreases in the antibonding molecular orbitals. Moreover, they have high energy because of repulsive forces and lower stability. The electrons present in these orbitals result in the repulsion between the two atoms.
The other one is bonding molecular orbitals. In this, the probability of finding the electron in the internuclear region is greater than that of combining atomic orbitals. Moreover, the electrons present in the bonding molecular orbital result in the attraction between the two atoms. Both the orbitals are as shown:
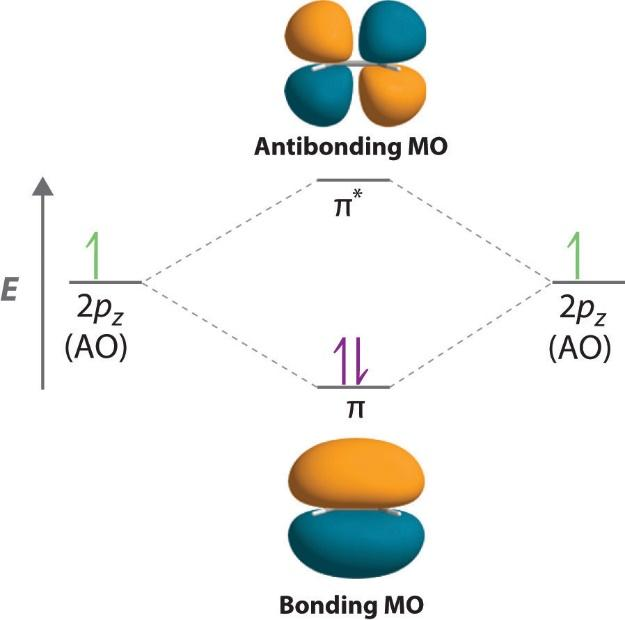
Note: In case of non-bonding molecular orbitals, due to complete lack of symmetry in the compatibility of two bonding atomic orbitals, the molecular orbitals formed have no positive or negative interactions with each other. Moreover, these types of orbitals do not affect the bond between the two atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
Basically, in molecular theory, the total number of molecular orbitals formed are always equal to the total number of atomic orbitals offered by the bonding species. The electrons are filled into molecular orbitals in the increasing order of orbital energy i.e. from the orbital with the lowest energy to the orbital with the highest energy. Now, there are different types of molecular orbitals such as bonding molecular orbitals, antibonding orbitals and non-bonding molecular orbitals.
Now, let’s discuss different types of orbitals. The molecular orbital refers to the space in a molecule in which the probability of finding an electron is maximum. These are basically mathematical functions that describe the wave nature of electrons in a given molecule. The first one is anti-bonding molecular orbitals. The probability of finding the electron in the inter nuclear region decreases in the antibonding molecular orbitals. Moreover, they have high energy because of repulsive forces and lower stability. The electrons present in these orbitals result in the repulsion between the two atoms.
The other one is bonding molecular orbitals. In this, the probability of finding the electron in the internuclear region is greater than that of combining atomic orbitals. Moreover, the electrons present in the bonding molecular orbital result in the attraction between the two atoms. Both the orbitals are as shown:

Note: In case of non-bonding molecular orbitals, due to complete lack of symmetry in the compatibility of two bonding atomic orbitals, the molecular orbitals formed have no positive or negative interactions with each other. Moreover, these types of orbitals do not affect the bond between the two atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




