
Write Archimedes principle and explain and when objects sink or float.
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint:Archimedes’ Principle is also called as ‘Physical Law of Buoyancy ‘. It was discovered by ancient Greek mathematician Archimedes.
Step-by-Step Explanation:
Step I:
According to this Principle, the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces.
${F_b} = {W_{fl}}$
${F_b}$ is the buoyant force
${W_{fl}}$ is the weight of the fluid
Step II:
If an object is completely or partially submerged in a fluid and the fluid is at rest, then a buoyant force or upward thrust is acted on by the liquid.
Step III:
The sinking or floating ability of an object can be known by comparing its density with that of water. If the density of the object immersed in fluid is less than the density of water, then the object will float. But if the density of the object in fluid is greater than the density of water, then the object will sink.
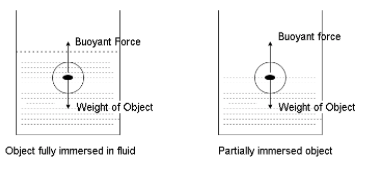
Step IV:
Another way to know the object will float or sink is by calculating the weight force acting on the object. If the weight force of the object is larger than the buoyant force of the water on the object, then it will sink. If the weight force of the object is smaller than the buoyant force of the water on the object, then it will rise.
Note:
Buoyant force is the force exerted by the fluid. The buoyant force opposes the weight of the object immersed in water whether it is fully dispersed or partially. This process is called buoyancy. Buoyancy is caused by the pressure exerted by the fluid in the object.
Step-by-Step Explanation:
Step I:
According to this Principle, the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces.
${F_b} = {W_{fl}}$
${F_b}$ is the buoyant force
${W_{fl}}$ is the weight of the fluid
Step II:
If an object is completely or partially submerged in a fluid and the fluid is at rest, then a buoyant force or upward thrust is acted on by the liquid.
Step III:
The sinking or floating ability of an object can be known by comparing its density with that of water. If the density of the object immersed in fluid is less than the density of water, then the object will float. But if the density of the object in fluid is greater than the density of water, then the object will sink.

Step IV:
Another way to know the object will float or sink is by calculating the weight force acting on the object. If the weight force of the object is larger than the buoyant force of the water on the object, then it will sink. If the weight force of the object is smaller than the buoyant force of the water on the object, then it will rise.
Note:
Buoyant force is the force exerted by the fluid. The buoyant force opposes the weight of the object immersed in water whether it is fully dispersed or partially. This process is called buoyancy. Buoyancy is caused by the pressure exerted by the fluid in the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




